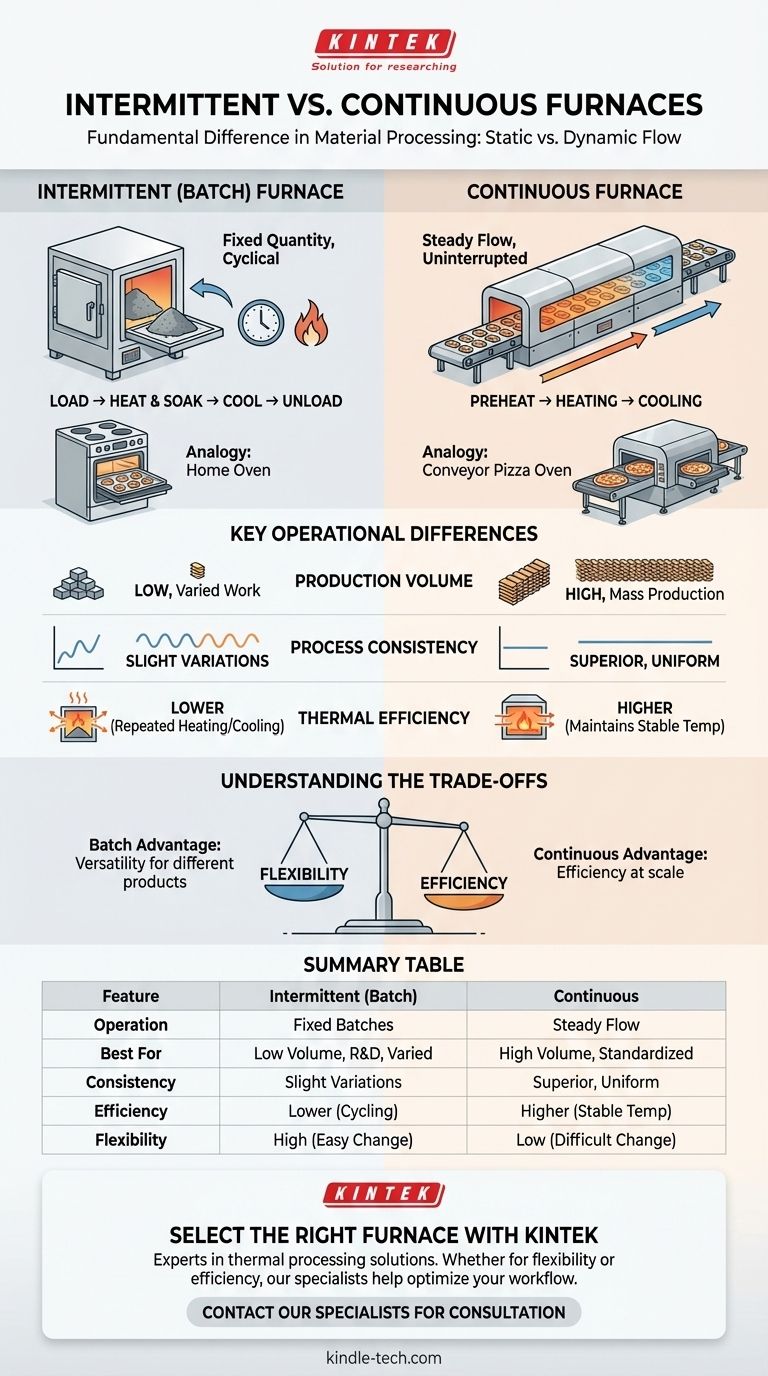
In industrial heating, the fundamental difference between an intermittent and a continuous furnace lies in how material is processed. An intermittent furnace, also known as a batch or periodical furnace, processes a fixed quantity of material in a single, complete cycle. In contrast, a continuous furnace processes a steady, uninterrupted flow of material that moves through the unit at a constant speed.
The choice between intermittent and continuous designs is a core strategic decision based on production volume versus process flexibility. Intermittent furnaces offer versatility for varied tasks, while continuous furnaces deliver efficiency and consistency for mass production.

The Defining Principle: Static vs. Dynamic Processing
The most critical distinction is whether the material being heated remains stationary or is in constant motion during the thermal cycle. This single factor influences every other aspect of the furnace's design and application.
How Intermittent (Batch) Furnaces Work
An intermittent furnace operates in a distinct, cyclical manner. A specific amount, or batch, of material is loaded into the furnace at once.
The entire chamber is then heated to the required temperature, held for a set duration (soaking), and finally cooled before the processed material is removed. The cycle then repeats with a new batch.
This process is analogous to a conventional home oven—you place a tray of items inside, bake them for a set time, and remove them before starting again.
How Continuous Furnaces Work
A continuous furnace is designed for an uninterrupted production flow. Material enters one end, travels through various temperature-controlled zones on a conveyor system, and exits the other end fully processed.
The furnace maintains a stable thermal gradient along its length, ensuring that every part of the material receives the exact same heat treatment as it passes through.
Think of it like a conveyor-belt pizza oven at a large commercial pizzeria, where pizzas are constantly being loaded on one side and emerge perfectly cooked from the other.
Key Operational Differences
The choice between these two furnace types has significant implications for production scale, consistency, and energy usage.
Production Volume and Scale
Intermittent furnaces are best suited for lower production volumes, prototype work, or processes where the product type or size changes frequently.
Continuous furnaces are built for high-volume, standardized mass production. Their efficiency is only realized when they are run for long, uninterrupted periods.
Process Consistency
Continuous furnaces offer superior process consistency. Since every unit of material follows the identical path through the same thermal zones, the final product quality is extremely uniform.
In a batch furnace, slight variations in loading, sensor placement, or atmospheric conditions can lead to minor inconsistencies between different batches.
Thermal Efficiency
For large-scale operations, continuous furnaces are far more energy-efficient. Once at operating temperature, they maintain it, with the primary energy input being used to heat the new material entering the system.
Intermittent furnaces are inherently less efficient because a significant amount of energy is lost each time the furnace is cooled for unloading and then reheated for the next batch. The furnace structure itself (the refractory walls) must be repeatedly heated, consuming substantial energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither design is universally superior; they are engineered for different operational priorities.
The Flexibility of Batch Furnaces
The primary advantage of a batch furnace is its versatility. It can easily accommodate different product sizes, shapes, and complex heating cycles. This makes it the ideal choice for job shops or research and development.
The main drawback is lower throughput and the inherent energy inefficiency caused by its start-stop thermal cycling.
The Efficiency of Continuous Furnaces
The strength of a continuous furnace lies in its efficiency at scale. For a single, repeatable process, it delivers unmatched throughput and lower per-unit energy costs.
Its primary disadvantage is a near-total lack of flexibility. Changing the product or thermal profile is a complex and time-consuming undertaking, and the initial capital investment is significantly higher.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Process
The correct choice depends entirely on your specific manufacturing goals and constraints.
- If your primary focus is flexibility and varied production: An intermittent (batch) furnace is the superior choice, allowing you to adapt to different jobs and product specifications.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized manufacturing: A continuous furnace provides unparalleled efficiency and process consistency, significantly lowering per-unit costs at scale.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy conservation in a high-throughput environment: A continuous furnace is inherently more efficient as it avoids the repeated heating and cooling cycles of a batch process.
Ultimately, a clear understanding of your production flow, volume, and consistency requirements is the key to choosing the correct furnace technology.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Intermittent (Batch) Furnace | Continuous Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Processes material in fixed batches | Processes material in a steady flow |
| Best For | Low volume, varied products, R&D | High-volume, standardized production |
| Consistency | Slight variations between batches | Superior, uniform product quality |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower (repeated heating/cooling) | Higher (maintains stable temperature) |
| Flexibility | High (easy to change cycles/products) | Low (difficult to change process) |
Still unsure which furnace type is right for your lab or production line?
KINTEK specializes in providing the ideal lab equipment and consumables for your specific thermal processing needs. Whether you require the flexibility of a batch furnace for R&D or the high-throughput efficiency of a continuous system, our experts can help you select the right solution to enhance your process consistency and reduce energy costs.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and let us help you optimize your industrial heating workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Can a muffle furnace be used for calcination? Achieve Pure, Controlled Thermal Decomposition
- Why do we need to use properly some of the laboratory apparatus in the laboratory? The Foundation of Safe and Accurate Science
- How long is the calcination process? Optimize Your Process Time for Maximum Efficiency
- What affects the rate of melting? Master the Key Factors for Precise Control
- What is the temperature range of a laboratory muffle furnace? Find the Right Model for Your Application



















