In simple terms, to "sinter" something is to form a solid mass of material from a powder using heat and pressure. Crucially, this process works without melting the material into a liquid state. Instead, the individual particles of the powder are heated just enough for their atoms to diffuse and fuse together, bonding the powder into a strong, solid object.
The core reason sintering is important is that it allows engineers to create strong, complex parts from materials—like ceramics and high-performance metals—that are extremely difficult or impossible to shape using traditional melting and casting methods.
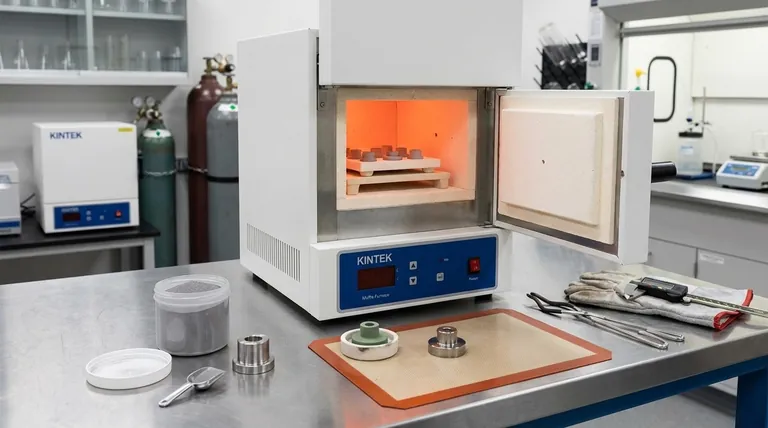

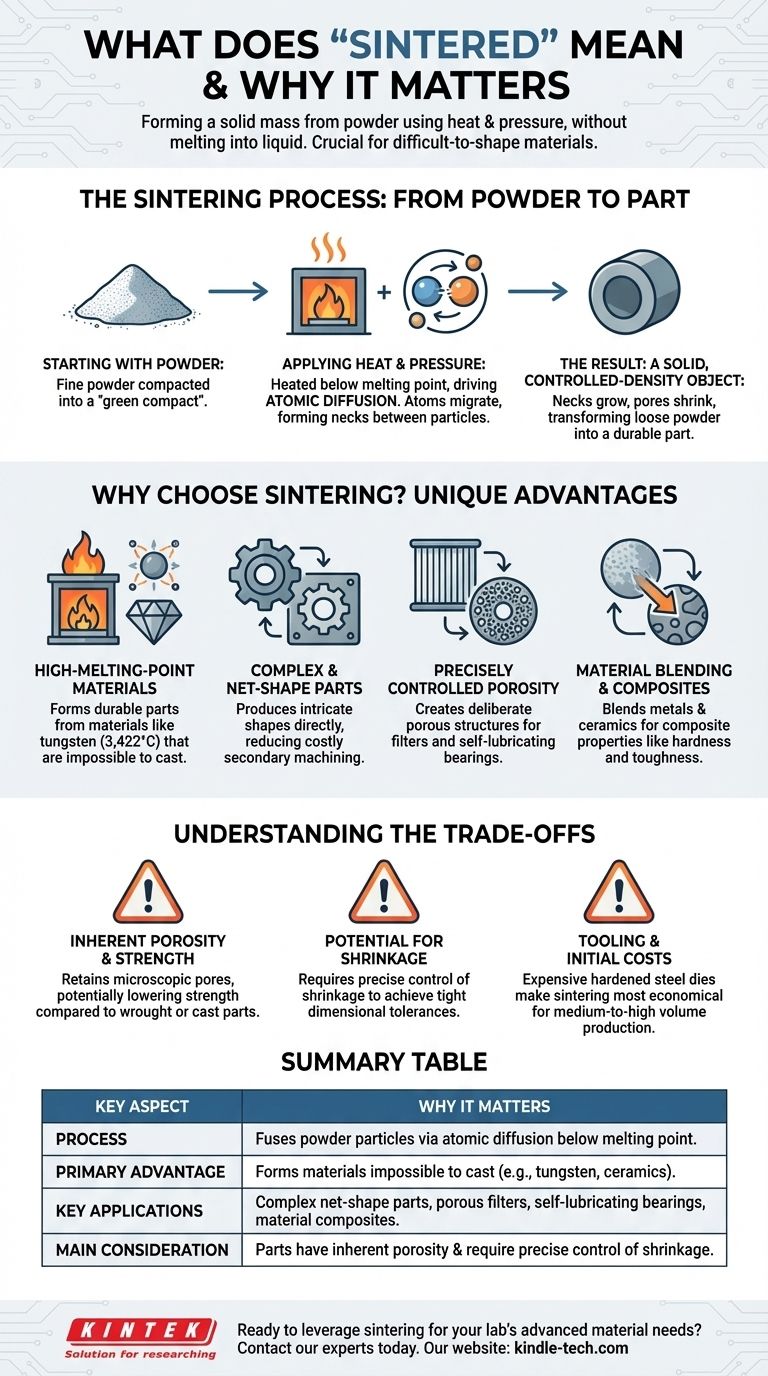
The Sintering Process: From Powder to Part
Understanding sintering begins with visualizing how loose particles can become a unified whole. The process is a careful balance of material science and thermal engineering.
Starting with Powder
The journey begins with a fine powder, which can be a metal, a ceramic, or even a blend of different materials. This powder is placed into a mold or die and often compacted under high pressure to create a fragile, preliminary shape known as a "green compact."
Applying Heat and Pressure
This green compact is then placed into a furnace. The temperature is raised significantly, but always kept below the material's melting point. This thermal energy is the key driver of the process.
Atomic Diffusion: The Core Mechanism
The heat energizes the atoms on the surface of each powder particle. These energized atoms begin to move and migrate across the boundaries between adjacent particles. This atomic movement forms "necks" or bridges, which gradually grow and pull the particles closer together, eliminating the empty spaces between them.
The Result: A Solid, Controlled-Density Object
As the necks grow and pores shrink, the loose powder transforms into a dense, solid part. A major advantage of sintering is that this densification can be precisely controlled, allowing for the creation of either fully dense components or objects with intentionally engineered porosity.
Why Choose Sintering Over Other Methods?
Sintering is not just an alternative; for many applications, it is the only viable manufacturing method. Its unique advantages solve several critical engineering challenges.
Working with High-Melting-Point Materials
Many advanced materials, like tungsten (melting point 3,422°C) or technical ceramics like alumina, have melting points that are too high for practical and economical casting. Sintering bypasses the need for complete melting, making it possible to form these materials into durable parts.
Creating Complex and Net-Shape Parts
Sintering can produce intricate shapes with a high degree of precision directly from the mold. This "net-shape" or "near-net-shape" capability drastically reduces or eliminates the need for expensive and wasteful secondary machining, making it highly efficient for producing small, complex components like gears, cams, and bushings.
Controlling Porosity with Precision
Unlike melting, sintering allows for the deliberate creation of porous structures. This is essential for products like metal filters, porous vents, and self-lubricating bearings, where a network of interconnected pores is the primary design feature.
Material Blending and Composites
Because it doesn't rely on melting, sintering is an excellent method for creating composite materials. Powders of different materials, such as a metal and a ceramic, can be blended to create a final part that exhibits the desired properties of both, such as the hardness of a ceramic and the toughness of a metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Inherent Porosity and Strength
Unless specific secondary steps like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) are used, sintered parts almost always retain some level of microscopic porosity. This can make them less strong or tough than parts made from a solid block of the same material (wrought stock) or through casting.
Potential for Shrinkage
As the powder densifies, the part shrinks. Predicting and controlling this shrinkage is a complex science and is critical for achieving tight dimensional tolerances. Inconsistent powder or heating can lead to warped or out-of-spec parts.
Tooling and Initial Costs
The hardened steel dies used to form the initial green compact are expensive to design and manufacture. This high initial tooling cost means sintering is most economical for medium-to-high volume production runs that can amortize the investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge, consider how the advantages of sintering align with your project's specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance or wear resistance: Sintering is the premier choice for creating parts from ceramics, cermets, or refractory metals that cannot be easily melted.
- If your primary focus is complex, small parts in high volume: Sintering offers excellent net-shape manufacturing, reducing material waste and post-processing costs for components like automotive gears or electronic sensor housings.
- If your primary focus is controlled porosity: Sintering is the definitive method for manufacturing components like filters, vents, or self-lubricating bearings where pores are a functional design feature.
Understanding sintering empowers you to design and manufacture parts that would otherwise be out of reach, unlocking a new class of materials and solutions.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Process | Fuses powder particles using heat below melting point via atomic diffusion. |
| Primary Advantage | Forms materials impossible to cast, like tungsten and technical ceramics. |
| Key Applications | Complex net-shape parts, porous filters, self-lubricating bearings, material composites. |
| Main Consideration | Parts have inherent porosity and require precise control of shrinkage during production. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's advanced material needs? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables essential for sintering processes. Whether you are developing new materials, creating complex components, or need reliable furnace technology, our expertise ensures you achieve consistent, high-quality results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your sintering projects and enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the function of the sintering process in ceramic manufacturing? Achieve High Density and Structural Integrity
- What is the body structure of a furnace? Unlocking the Dual-Layer Design for Superior Thermal Control
- How to cool a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Maximize Equipment Lifespan
- Why is ceramic used in making furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Resistance and Efficiency
- What is the inside material of a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lining for Your Application



















