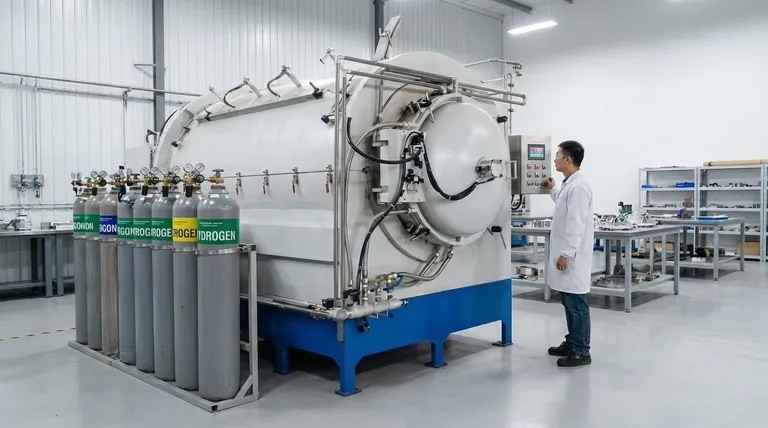
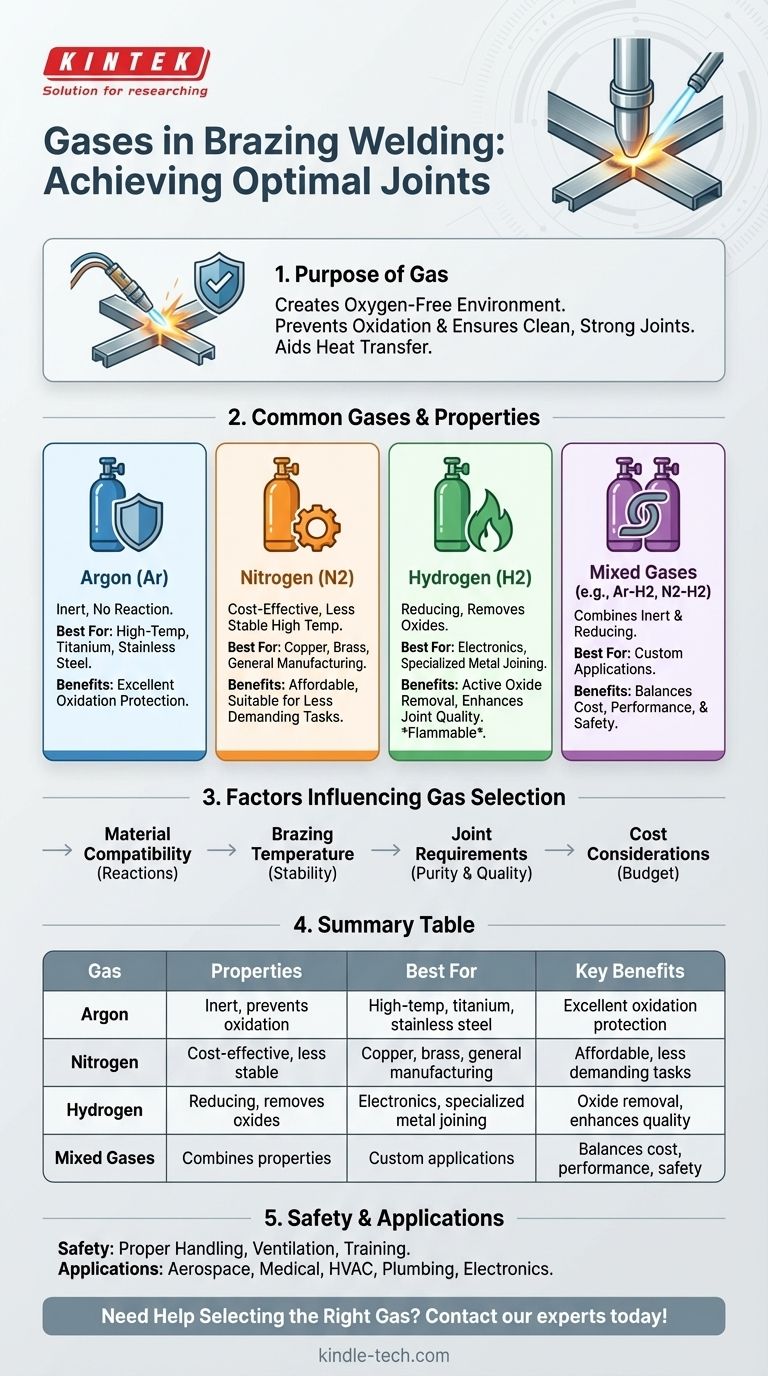
Brazing welding typically uses inert or reducing gases to create an oxygen-free environment, ensuring a clean and strong joint. The most common gases used are argon, nitrogen, hydrogen, and sometimes a mixture of these gases. Argon is widely used due to its inert nature, preventing oxidation. Nitrogen is cost-effective and suitable for certain materials. Hydrogen is used for its reducing properties, which help remove oxides. The choice of gas depends on the materials being joined, the brazing method, and the desired joint quality. Understanding these gases and their properties is crucial for achieving optimal results in brazing welding.

Key Points Explained:
-
Purpose of Using Gas in Brazing Welding
- The primary role of gases in brazing welding is to create an oxygen-free environment.
- Oxygen can cause oxidation, leading to weak joints and poor adhesion of the filler metal.
- Gases also help in heat transfer and maintaining consistent temperatures during the process.
-
Common Gases Used in Brazing Welding
-
Argon:
- An inert gas that does not react with the base or filler metals.
- Ideal for high-temperature brazing and sensitive materials like titanium and stainless steel.
- Provides excellent protection against oxidation.
-
Nitrogen:
- A cost-effective alternative to argon.
- Suitable for materials like copper and brass.
- Less effective at high temperatures compared to argon.
-
Hydrogen:
- A reducing gas that actively removes oxides from the metal surface.
- Often used in combination with other gases (e.g., forming gas, which is a mix of hydrogen and nitrogen).
- Requires careful handling due to its flammability.
-
Mixed Gases:
- Combinations like argon-hydrogen or nitrogen-hydrogen are used to balance cost, performance, and safety.
- These mixtures provide both inert and reducing properties, enhancing joint quality.
-
Argon:
-
Factors Influencing Gas Selection
-
Material Compatibility:
- Different metals react differently to gases. For example, hydrogen is excellent for copper but risky with titanium.
-
Brazing Temperature:
- Higher temperatures may require more stable gases like argon.
-
Joint Requirements:
- Critical applications may demand higher-purity gases or specific mixtures.
-
Cost Considerations:
- Nitrogen is cheaper than argon, making it a preferred choice for less demanding applications.
-
Material Compatibility:
-
Advantages of Using Gases in Brazing Welding
- Prevents oxidation and contamination of the joint.
- Enhances the flow of the filler metal, ensuring a strong and uniform bond.
- Improves the overall quality and appearance of the brazed joint.
-
Safety Considerations
- Some gases, like hydrogen, are flammable and require proper handling and storage.
- Adequate ventilation and gas monitoring systems are essential to prevent accidents.
- Proper training for operators is crucial to ensure safe usage.
-
Applications of Different Gases
- Argon: Used in aerospace, medical devices, and high-precision industries.
- Nitrogen: Common in HVAC systems, plumbing, and general manufacturing.
- Hydrogen: Preferred in electronics and specialized metal joining processes.
By understanding the properties and applications of these gases, equipment and consumable purchasers can make informed decisions to optimize brazing welding processes for their specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Properties | Best For | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Argon | Inert, prevents oxidation | High-temp brazing, titanium, stainless steel | Excellent oxidation protection |
| Nitrogen | Cost-effective, less stable at high temps | Copper, brass, general manufacturing | Affordable, good for less demanding tasks |
| Hydrogen | Reducing, removes oxides | Electronics, specialized metal joining | Oxide removal, enhances joint quality |
| Mixed Gases | Combines inert and reducing properties | Custom applications | Balances cost, performance, and safety |
Need help selecting the right gas for your brazing welding process? Contact our experts today for personalized advice!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum brazing? Achieve High-Purity, Strong Metal Joining
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is oxidation in brazing? How to prevent it for strong, durable joints
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy



















