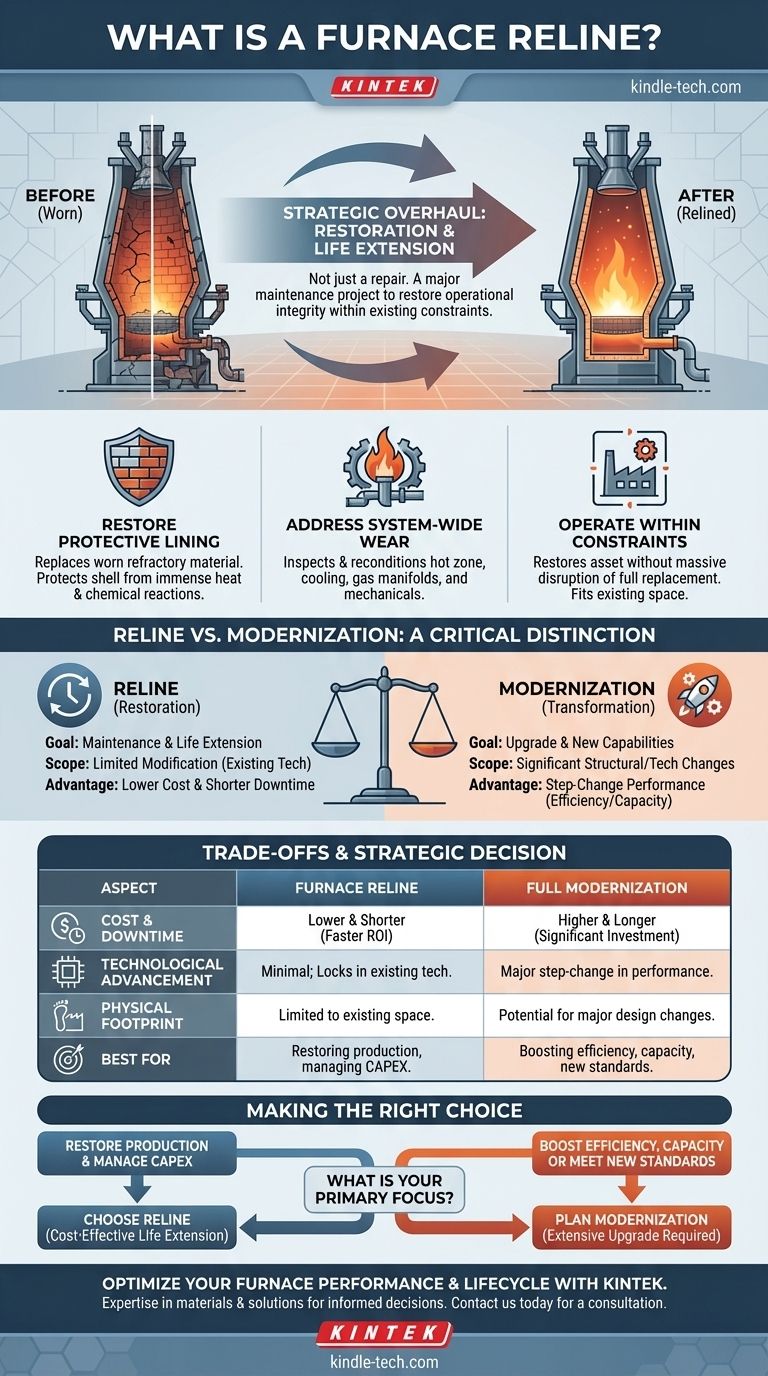
At its core, a furnace reline is a major maintenance project focused on reconditioning an industrial furnace, particularly a blast furnace. It involves replacing the worn-out internal refractory lining and repairing or replacing associated systems, but with a deliberately limited scope for significant modifications or technological upgrades.
A furnace reline should be understood not as a simple repair, but as a strategic overhaul. Its primary goal is to restore the furnace's operational integrity and extend its service life within the constraints of its existing design and physical footprint.

The Core Purpose of a Reline
A furnace reline is a planned, mission-critical event in the lifecycle of heavy industrial equipment. The decision to perform a reline is driven by the inevitable degradation of the furnace's internal components under extreme operating conditions.
Restoring the Protective Lining
The term "reline" directly refers to the most crucial part of the process: replacing the furnace's inner lining. This refractory material protects the steel shell from immense heat and chemical reactions. Over time, this lining erodes and must be completely replaced to ensure safety and efficiency.
Addressing System-Wide Wear
While replacing the lining is central, a reline project is more comprehensive. It includes the inspection and reconditioning of the entire furnace system, which can involve the hot zone, cooling systems, gas manifolds, and mechanical components.
Operating Within Existing Constraints
A reline is often chosen over a full replacement because of significant physical and logistical constraints. Industrial plants are densely packed, and a reline allows the asset to be restored without the massive disruption of removing and replacing the entire structure.
Reline vs. Modernization: A Critical Distinction
Understanding the difference between a reline and a full modernization is essential for making sound strategic decisions about industrial assets. The primary difference lies in the project's scope and objective.
The Goal of a Reline
The objective of a reline is restoration. The project aims to bring the furnace back to its original design specifications or make minor, incremental improvements. It is fundamentally a maintenance and life-extension activity.
The Goal of Modernization
A modernization project's objective is transformation. This involves adapting or replacing the furnace to meet new requirements, such as incorporating new technology, increasing production capacity, or improving energy efficiency.
Scope Defines the Project
A reline operates under the principle of "limited modification." A modernization project, by contrast, is defined by its intent to significantly alter the furnace's structure or technological capabilities.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a reline and a more extensive upgrade involves a careful evaluation of competing priorities. Each approach has distinct advantages and limitations.
The Advantage of Cost and Downtime
A furnace reline is almost always faster and less expensive than a complete modernization or replacement. This allows a facility to restore production capacity with a lower capital investment and a shorter period of lost revenue.
The Limitation of Technology
The key trade-off is technological advancement. A reline essentially locks in the existing technology of the furnace. It does not provide the step-change in performance or efficiency that a full modernization can deliver.
The Constraint of Physical Space
By its nature, a reline is performed within the furnace's existing footprint. This inherently limits the potential for major design changes that could, for example, increase the furnace's internal volume or alter its core operational mechanics.
Making the Right Strategic Decision
Your choice depends entirely on your operational and financial goals for the asset.
- If your primary focus is restoring production and managing capital expenditure: A furnace reline is the most direct and cost-effective strategy to extend the asset's life.
- If your primary focus is boosting efficiency, increasing capacity, or meeting new environmental standards: You must plan for a more extensive modernization project, as a reline will not achieve these goals.
Ultimately, recognizing a furnace reline as a strategic restoration project is the first step toward effective long-term asset management.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Furnace Reline | Full Modernization |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Restoration & Life Extension | Transformation & Upgrade |
| Scope | Limited modifications within existing footprint | Significant structural/tech changes |
| Cost & Downtime | Lower & Shorter | Higher & Longer |
| Technological Advancement | Minimal; locks in existing tech | Major step-change in performance |
| Best For | Restoring production, managing capex | Boosting efficiency, capacity, or meeting new standards |
Need to optimize your furnace performance and lifecycle?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for industrial furnace maintenance and efficiency. Whether you're planning a reline or exploring modernization options, our expertise can help you make informed decisions to maximize your asset's value and operational uptime.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and industrial furnace needs. Reach out via our contact form for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is high-temperature vacuum heat treatment critical for Cr-Ni steel? Optimize Strength & Surface Integrity
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials
- What are the methods of brazing heating? Choose the Right Method for Your Production Needs
- Why is environmental control within a vacuum furnace important for diffusion bonding? Master Titanium Alloy Laminates



















