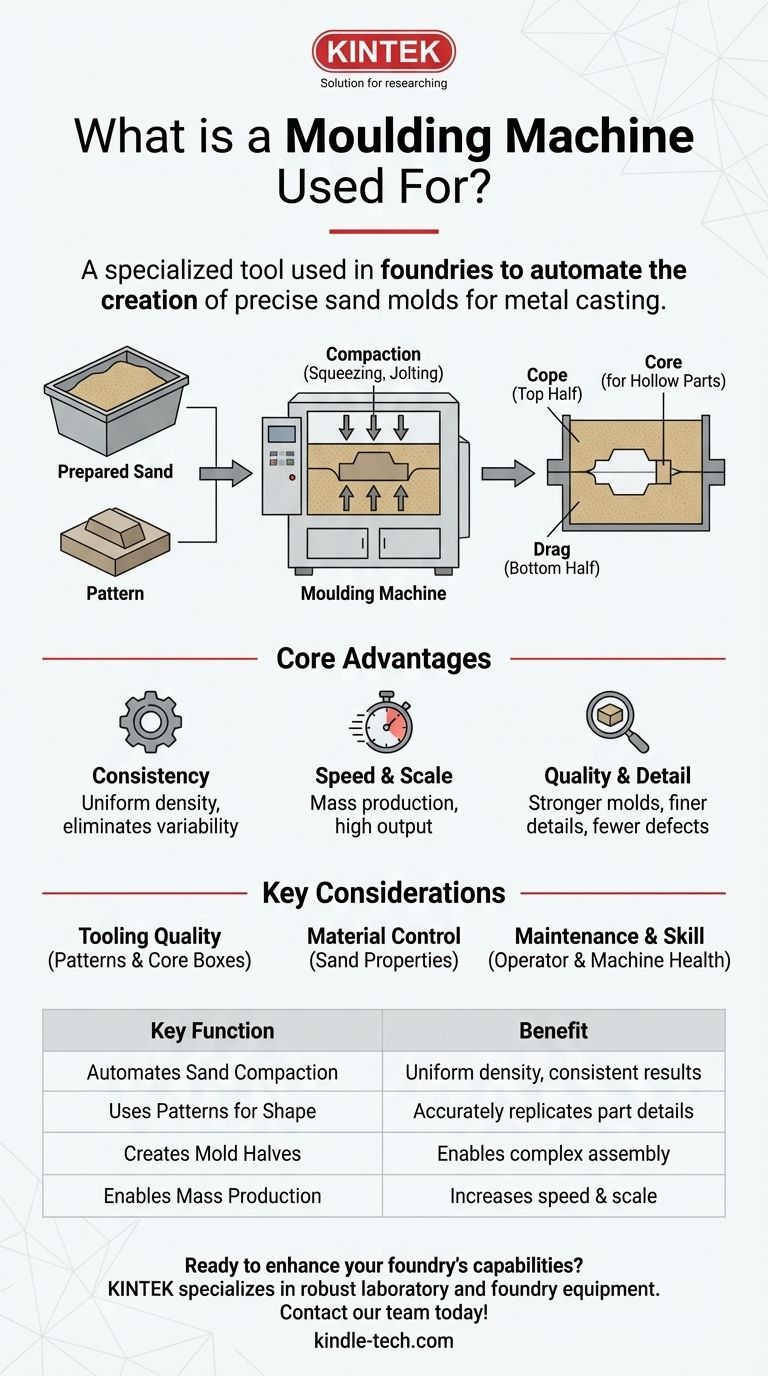
At its core, a moulding machine is a specialized tool used in foundries to create sand molds for metal casting. It automates the process of compacting specially prepared sand around a pattern, forming a precise cavity. This cavity, once the pattern is removed, is what gets filled with molten metal to create a finished part.
The fundamental purpose of a moulding machine is to industrialize the process of sand casting. It replaces manual labor to achieve vastly superior speed, consistency, and precision, turning loose sand into a stable, detailed mold capable of producing high-quality metal components at scale.

The Core Function: From Sand to a Precise Cavity
A moulding machine’s job is to execute the most critical step of the sand casting process with mechanical precision. It systematically transforms moulding material into a finished mold half, ready for assembly and pouring.
Compacting the Moulding Sand
The primary action of the machine is to compact sand. Loose sand would immediately collapse when filled with heavy, molten metal. The machine applies immense force—through squeezing, jolting, or other methods—to create a dense, rigid, and stable mold.
Using a Pattern to Create the Shape
The sand isn't just compacted into a block; it's packed around a pattern. This pattern is a master model of the final part. The machine ensures the sand conforms perfectly to every detail of the pattern, accurately capturing the desired shape.
Creating Mold Halves (Cope and Drag)
Most castings are made using a two-part mold. The moulding machine typically creates one half at a time in a container called a flask. The top half is known as the cope, and the bottom half is the drag. The machine produces these halves so they can be perfectly aligned and assembled later.
Accommodating Cores for Hollow Parts
For parts that require internal features or hollow sections, sand shapes called cores are used. These are created separately (often using a tool called a core box) and are placed into the main mold cavity before it is closed. The moulding machine creates the main mold with the precision needed to securely hold these cores in place.
Why Use a Machine Instead of Manual Methods?
While sand molds can be made by hand, a moulding machine provides definitive advantages that are essential for any modern manufacturing operation.
Unmatched Consistency
A machine applies the exact same forces and follows the exact same sequence for every single mold. This eliminates the human variability of manual ramming, ensuring that every mold has a uniform density and hardness. This directly translates to more consistent final castings.
Superior Speed and Production Scale
The speed of a moulding machine is orders of magnitude faster than a manual process. This automation is what enables the mass production of cast metal parts, making it a cornerstone of industries from automotive to aerospace.
Higher Mold Quality and Detail
The high, uniform compaction achieved by a machine results in a stronger mold. This strength allows for finer details, sharper corners, and a smoother surface finish on the final metal part. It also significantly reduces defects caused by mold wall movement or erosion during pouring.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While powerful, a moulding machine is part of a larger, complex system. Its effectiveness is not guaranteed without understanding its limitations.
The Critical Role of Tooling
The machine is only as good as its tooling—the pattern plates and core boxes. Poorly designed or worn-out tooling will produce poor-quality molds, regardless of how advanced the machine is. The investment in high-quality tooling is non-negotiable.
Material Control is Essential
The machine assumes it is being fed high-quality, consistent moulding sand. Variations in sand properties like moisture content, clay levels, or grain size will lead to inconsistent mold quality and casting defects, even if the machine's parameters are unchanged.
Maintenance and Operator Skill
These are robust industrial machines, but they require skilled operation and a strict preventative maintenance schedule. A poorly maintained machine can lose its precision, leading to a gradual or sudden decline in the quality of the molds it produces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the role of a moulding machine helps clarify when it is the appropriate technology for a given manufacturing need.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: A moulding machine is the only viable path to achieve the necessary speed, low per-unit cost, and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is high-precision casting: The machine's ability to create dense, uniform, and stable molds is critical for achieving tight dimensional tolerances and excellent surface finishes.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or one-off parts: The significant cost of creating the required pattern tooling often makes manual methods or alternative technologies, like 3D-printed sand molds, a more practical choice.
Ultimately, a moulding machine is the engine that powers the modern foundry, providing the essential bridge between raw sand and the complex metal components that shape our world.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automates Sand Compaction | Ensures uniform mold density and strength for consistent results. |
| Uses Patterns for Shape | Accurately replicates part details for high-precision castings. |
| Creates Mold Halves (Cope & Drag) | Enables assembly of complex, two-part molds. |
| Enables Mass Production | Drastically increases speed and scale compared to manual methods. |
Ready to enhance your foundry's capabilities? KINTEK specializes in providing robust laboratory and foundry equipment to streamline your production process. Whether you're scaling up or seeking greater precision, our expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help you achieve superior mold quality and efficiency. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your metal casting needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between blown and extruded film? Choose the Right Film for Your Packaging Needs
- What is twin screw extrusion? Achieve Superior Mixing and Uniform Product Quality
- What is the use of a blown film machine? To Produce Strong, Versatile Plastic Films for Packaging
- What is the difference between single screw and twin screw? Choose the Right Extruder for Your Process
- What is the process of calendering? A Guide to High-Volume Plastic Film Production
- What are the advantages of twin screw extruder? Superior Mixing, Flexibility & Efficiency
- What is pyrolysis of rubber? Transform Waste Tires into Oil, Carbon & Gas
- What are the disadvantages of twin screw? Higher Cost and Complexity vs. Single Screw



















