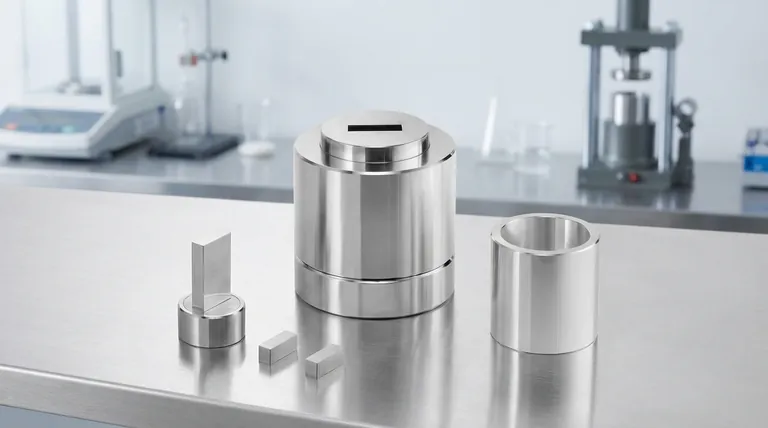
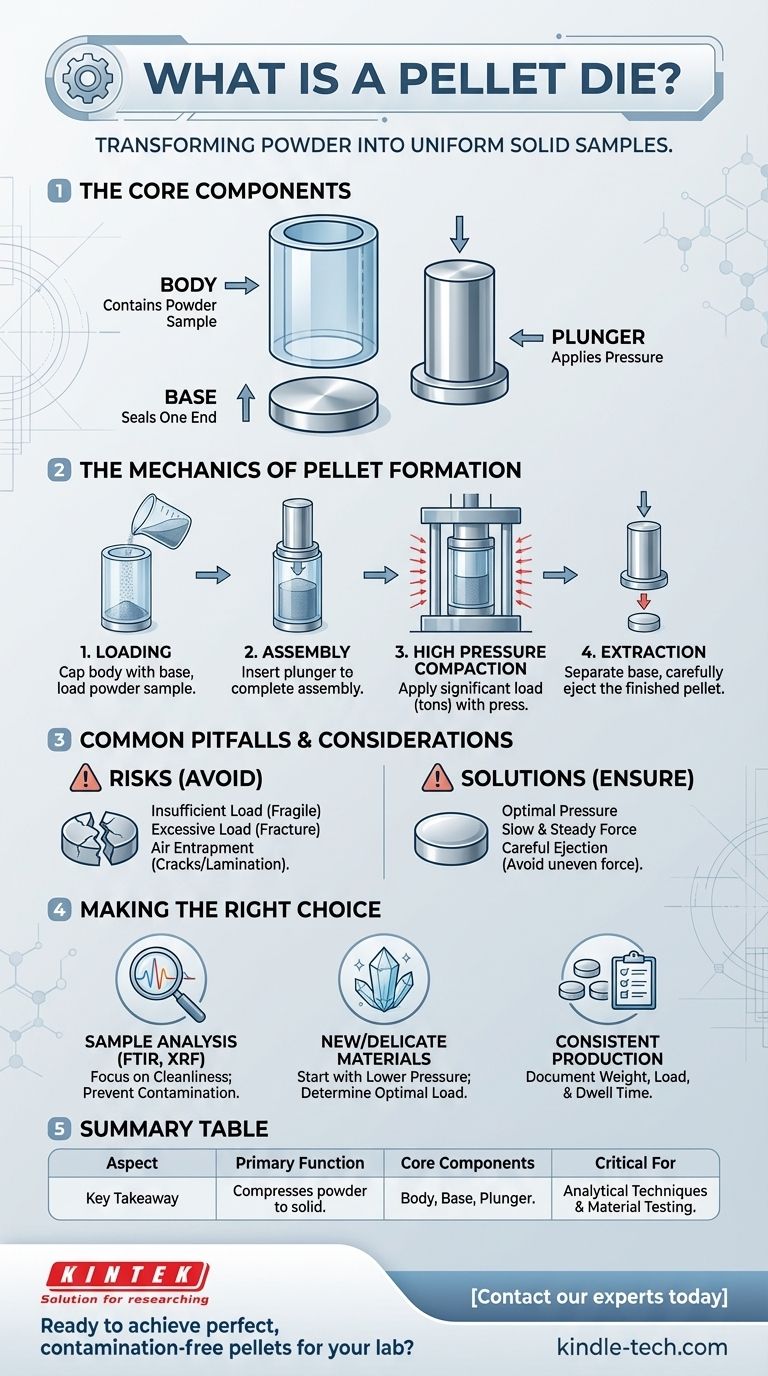
In material science and sample preparation, a pellet die is a precision tool designed to compress a powdered substance into a solid, cylindrical disc known as a pellet. At its most fundamental level, it consists of three primary parts: a hollow cylindrical body, a solid base that seals one end, and a plunger that fits snugly into the body to apply pressure. The entire assembly is used within a hydraulic or mechanical press to achieve the high forces necessary for compaction.
A pellet die is the essential component in a high-pressure process that transforms loose, inconsistent powder into a dense, uniform solid. This conversion is critical for preparing samples for a wide range of analytical techniques and material testing.

The Mechanics of Pellet Formation
Understanding how a pellet die functions requires looking at its simple components and the powerful process they enable. The goal is to apply immense, uniform pressure to force individual powder grains to bind together.
The Core Components
The die's design is straightforward. The hollow body contains the powder sample. The base provides a solid, flat surface for the powder to be compressed against. The plunger transmits the force from the press directly onto the powder.
The Loading and Assembly
The process begins by capping the cylindrical body with the base to form a self-contained tube. The powdered sample is then carefully poured into this cavity. Finally, the plunger is inserted into the top of the body, completing the assembly.
The Role of High Pressure
With the powder sealed inside, the die is placed into a press. The press applies a significant load, often several tons, to the plunger. This immense pressure compacts the powder, eliminating voids and forcing the individual grains into intimate contact until they mechanically lock and bind into a solid mass.
Extracting the Finished Pellet
Once the desired pressure has been applied and released, the pellet is formed. To remove it, the base is separated from the die body. A small amount of force is then applied to the plunger to carefully push the newly formed pellet out of the body without fracturing it.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While the concept is simple, achieving a perfect, durable pellet requires attention to detail. Several factors can influence the quality of the final product.
Insufficient or Excessive Load
The amount of pressure applied is critical. Too little force will result in a fragile, crumbly pellet that falls apart easily. Conversely, applying too much force can sometimes cause the pellet to fracture upon extraction due to stored stress.
The Risk of Air Entrapment
If pressure is applied too quickly, air can become trapped within the powder. This trapped air can cause the pellet to crack or even laminate (split into layers) when the pressure is released. A slow, steady application of force is key.
The Challenge of Ejection
Removing the finished pellet is a delicate step. The pellet is held tightly within the die body by friction. Improper or uneven force during ejection is a common cause of breakage, especially with brittle materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The successful use of a pellet die depends on your specific objective. The ideal process parameters are dictated by the material properties and the intended application of the pellet.
- If your primary focus is preparing samples for analysis (e.g., FTIR or XRF): Your top priority is preventing contamination. Ensure the die is immaculately cleaned between samples to maintain the integrity of your results.
- If you are working with a new or delicate material: Begin with a lower pressure and create a series of pellets at increasing loads to determine the optimal compaction force that yields a stable pellet without causing fractures.
- If you need to produce many pellets consistently: Focus on a repeatable process. Document the exact weight of the powder, the applied load, and the dwell time (how long the pressure is held) for every sample.
Ultimately, mastering the use of a pellet die is about transforming an unrefined powder into a standardized, reliable solid sample ready for precise measurement.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Compresses powdered substances into solid, cylindrical pellets. |
| Core Components | Hollow body, solid base, and plunger. |
| Key Process | Uses high pressure (often tons of force) in a hydraulic or mechanical press. |
| Critical for | Sample preparation for analytical techniques (FTIR, XRF) and material testing. |
| Common Pitfalls | Insufficient/excessive load, air entrapment, and improper pellet ejection. |
Ready to achieve perfect, contamination-free pellets for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including durable pellet dies designed for precise and repeatable sample preparation. Whether your focus is FTIR, XRF, or material testing, our tools help you create uniform solid samples with ease.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect pellet die for your specific application and ensure the integrity of your analytical results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Assemble Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Cylindrical Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity
- What is the physical role of graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Cu-Al2O3 Composite Densification
- What is the lifespan of a mold? It's Immortal Unless You Control Moisture
- How do graphite molds and hydraulic presses work together? Perfect Your FeCrAl Pre-Forming Today!
- What is the role of a laboratory hydraulic press in molecular sieve catalyst preparation? Achieve Optimal Pelleting



















