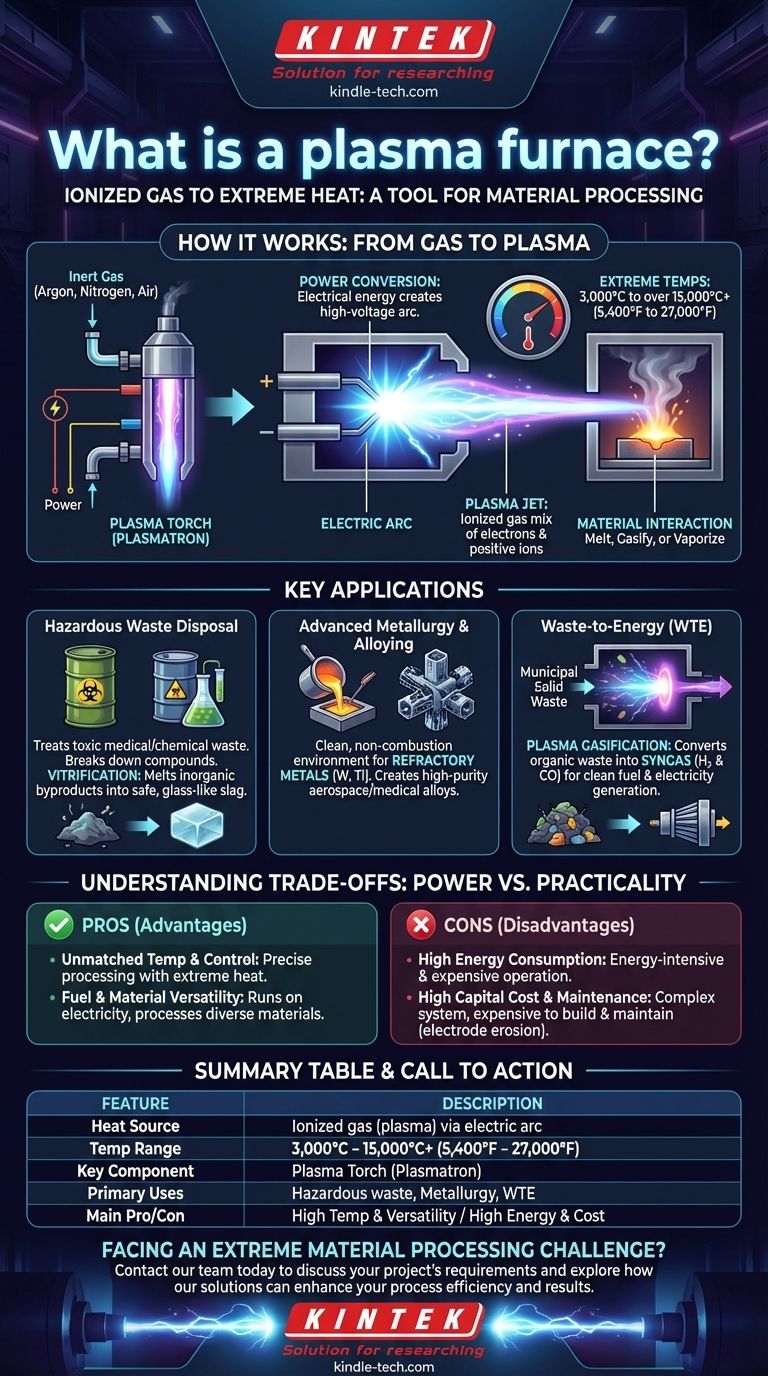
At its core, a plasma furnace is an industrial device that uses a stream of ionized gas—known as plasma—to achieve extremely high temperatures. Unlike conventional furnaces that burn fuel, a plasma furnace uses electricity to superheat a gas, creating a controlled, high-energy plasma jet or arc capable of melting, gasifying, or vaporizing virtually any material.
A plasma furnace should be understood not just as a hotter furnace, but as a fundamentally different tool for material processing. Its value lies in its ability to deliver precisely controlled, ultra-high temperatures without combustion byproducts, making it ideal for tasks impossible for conventional methods.

How a Plasma Furnace Works: From Gas to Plasma
A plasma furnace’s operation centers on its ability to generate and sustain a stable plasma arc, which acts as the primary heat source. This process is clean, powerful, and highly controllable.
The Plasma Torch: The Heart of the System
The key component of the furnace is the plasma torch, sometimes called a plasmatron. This device is responsible for converting electrical energy into thermal energy by creating plasma.
Creating the Plasma Arc
Inside the torch, an inert gas like argon, nitrogen, or even air is forced through a narrow channel containing two electrodes. A high-voltage electric current is passed between these electrodes, creating a powerful electric arc.
This intense arc strips electrons from the gas atoms, a process called ionization. The resulting mixture of free electrons and positive ions is plasma—a distinct state of matter.
Reaching Extreme Temperatures
As the plasma forms, its electrical resistance generates immense heat, with temperatures inside the arc reaching anywhere from 3,000°C to over 15,000°C (5,400°F to 27,000°F). This is significantly hotter than the flame in a fossil fuel furnace.
Material Interaction
The superheated plasma is directed out of the torch as a jet or arc and aimed at the target material. The intense thermal energy transfer rapidly melts, gasifies, or chemically alters the substance within the furnace chamber.
Key Applications: Where Plasma Furnaces Excel
The unique capabilities of plasma furnaces make them essential for specialized, high-value industrial processes that demand extreme conditions.
Hazardous Waste Disposal
Plasma technology is exceptionally effective for treating hazardous waste, such as medical waste, asbestos, or chemical sludge. The extreme heat breaks down complex toxic compounds into their basic elements.
The process often results in vitrification, where inorganic byproducts are melted into a stable, non-leachable, glass-like slag, safely immobilizing heavy metals and other hazardous materials.
Advanced Metallurgy and Alloying
Plasma furnaces provide a clean, non-combustion environment ideal for melting refractory metals with very high melting points, like tungsten and titanium. This purity is critical for creating high-performance alloys for the aerospace and medical industries.
Waste-to-Energy (WTE) Production
When used to process municipal solid waste or other organic materials, a process known as plasma gasification occurs. The intense heat breaks down the waste into a synthetic gas, or syngas, which is rich in hydrogen and carbon monoxide and can be used as a clean fuel to generate electricity.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Power vs. Practicality
While powerful, plasma technology is not a universal solution. Its adoption is governed by a clear set of advantages and significant operational challenges.
Advantage: Unmatched Temperature and Control
The primary benefit is the ability to achieve temperatures far beyond the limits of chemical combustion. This heat can be precisely controlled by adjusting the electrical input, allowing for fine-tuned material processing.
Advantage: Fuel and Material Versatility
Plasma furnaces are fuel-agnostic, running on electricity rather than specific fossil fuels. They are also material-agnostic, capable of processing nearly any type of feed material, from solid metals to liquid sludge.
Disadvantage: High Energy Consumption
Generating and sustaining plasma is an energy-intensive process. The high electricity consumption makes plasma furnaces significantly more expensive to operate than conventional furnaces for bulk heating applications.
Disadvantage: High Capital Cost and Maintenance
Plasma furnaces are complex systems that are expensive to build. The electrodes within the plasma torch are subject to extreme conditions and erode over time, requiring regular and costly maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing technology depends entirely on balancing the need for performance against operational costs.
- If your primary focus is hazardous waste neutralization: Plasma offers unparalleled effectiveness in destroying toxic compounds and achieving permanent, safe encapsulation through vitrification.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity or refractory alloys: The clean, ultra-hot, and controllable environment of a plasma furnace is a distinct technological advantage.
- If your primary focus is bulk material melting with low operational costs: A conventional combustion or electric arc furnace remains the more economical and practical choice for most standard applications.
Ultimately, a plasma furnace is a specialized instrument for solving extreme material challenges where its unique capabilities justify its significant energy and capital investment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Heat Source | Ionized gas (plasma) created by an electric arc |
| Typical Temperature Range | 3,000°C to over 15,000°C (5,400°F to 27,000°F) |
| Key Component | Plasma Torch (Plasmatron) |
| Primary Applications | Hazardous waste disposal, advanced metallurgy, waste-to-energy (gasification) |
| Main Advantage | Unmatched temperature & control; fuel/material versatility |
| Main Disadvantage | High energy consumption and capital cost |
Facing an extreme material processing challenge?
If your work involves hazardous waste neutralization, creating high-purity alloys, or advanced gasification, the unique capabilities of a plasma furnace could be your solution. KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for demanding industrial and research applications.
Our experts can help you determine if a plasma furnace is the right tool for your specific goals. Contact our team today to discuss your project's requirements and explore how our solutions can enhance your process efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How is a crucible used in the crucible? Unpacking Arthur Miller's Powerful Metaphor
- What are the benefits of setting an ultra-low temperature freezer to -70C instead of -80C? Save 30-40% on Energy Costs
- What is a rotary flash evaporator used for? Gentle Solvent Removal for Heat-Sensitive Compounds
- What is the temperature of activated carbon regeneration? Unlock the 1000°F Process for Reuse
- What is the theory and practice of RF sputtering? Master Thin-Film Deposition for Insulating Materials
- Why is the thermal conductivity of graphite so high? Unlock Superior Heat Transfer with Its Unique Structure
- What is gold sputtered? A Guide to High-Purity Vacuum Coating for Electronics & SEM
- What are the limitations of fluidized bed reactor? Key Challenges in Design and Operation



















