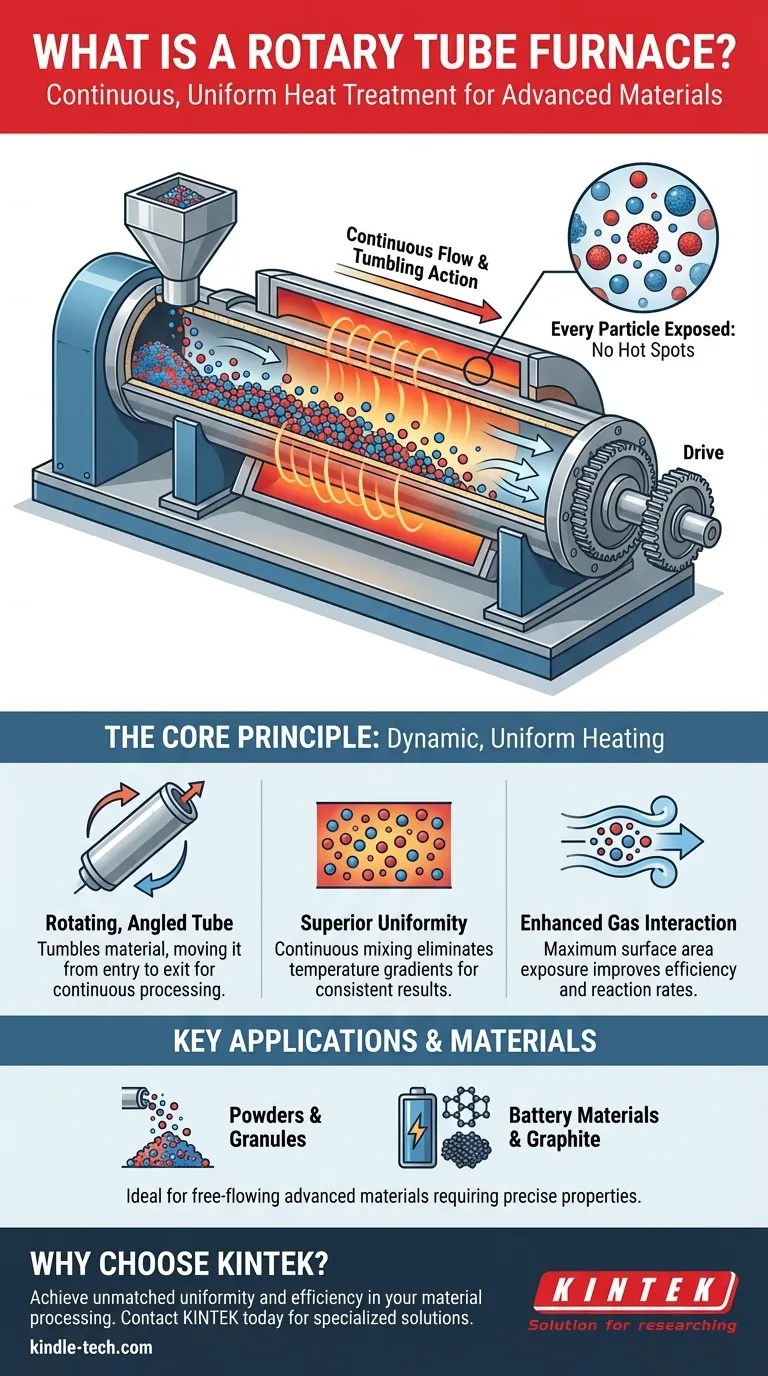
In essence, a rotary tube furnace is a specialized piece of high-temperature equipment designed for the continuous heat treatment of materials. It features a slowly rotating, cylindrical tube, typically mounted at a slight angle, which tumbles the material as it passes through a heated zone, ensuring every particle is processed with exceptional uniformity.
The central advantage of a rotary tube furnace lies in its dynamic motion. Unlike static furnaces where materials sit still, the constant rotation exposes the entire surface area of the sample to the heat and atmosphere, leading to more efficient, consistent, and higher-quality results, especially for powders and granules.
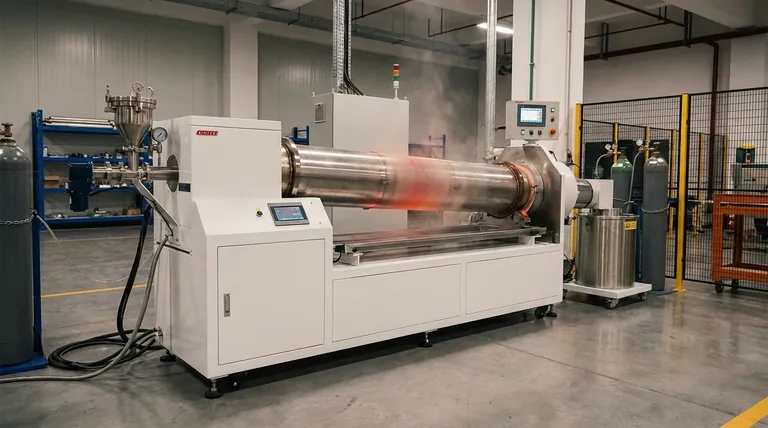

The Core Principle: Dynamic, Uniform Heating
A rotary tube furnace overcomes the limitations of traditional batch-style heating. Its design is engineered to ensure that every part of the material receives the same treatment, eliminating hot spots and inconsistencies.
The Rotating, Angled Tube
The heart of the system is the process tube, which is rotated by a drive mechanism. This tube is often made of metal and lined with a refractory material to withstand extreme temperatures.
It is installed at a slight incline. This angle, combined with the rotation, causes the material to gradually tumble and move from the higher entry point to the lower exit point, enabling continuous processing.
How It Achieves Superior Uniformity
As the tube rotates, the material inside is continuously mixed. This tumbling action prevents any single part of the sample from being over-exposed or under-exposed to the heat source.
This complete mixing drastically reduces temperature gradients within the material batch, which is a common problem in static furnaces. The result is a far more uniform and predictable final product.
Enhanced Gas Interaction and Efficiency
The constant movement ensures the entire surface area of every particle is exposed to the furnace's controlled atmosphere.
This improves the efficiency of processes that rely on gas diffusion or reactions. It can also reduce the total amount of process gas needed compared to static methods where the gas can only interact with the top layer of the material.
Key Applications and Suitable Materials
The unique design of a rotary tube furnace makes it exceptionally well-suited for specific types of materials and processes where uniformity is paramount.
Ideal for Powders and Granules
The furnace excels at processing free-flowing materials like powders, granules, and other small, solid particles. The rotating motion would not be suitable for large, single objects.
Common Industrial Uses
These furnaces are frequently used for processing advanced materials where precise properties are critical.
Examples include the manufacturing of battery components like positive and negative electrode materials, creating graphitized carbon materials, and processing silicon-based anode materials.
Control and Precision
Modern rotary tube furnaces are equipped with precise computer control systems. These systems manage the rotation speed, temperature profile, and gas atmosphere, ensuring high-quality heating and repeatable product outcomes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, a rotary tube furnace is a specialized tool. Its benefits are most pronounced when applied to the correct problem, and it is not a universal solution for all heat treatment needs.
Mechanical Complexity
The drive system—whether a friction wheel, rack and pinion, or chain drive—adds mechanical complexity compared to a simple static box furnace. The choice of drive depends on the scale and production requirements of the application.
Material Limitations
The furnace is fundamentally designed for materials that can tumble freely. It is not suitable for heat-treating large, singular components, delicate structures that could be damaged by tumbling, or materials that might clump or stick together when heated.
Process Design
Achieving optimal results requires careful tuning of the rotation speed and tube angle. These parameters control the "residence time"—how long the material spends in the hot zone—which is critical for process success.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
To determine if this technology fits your needs, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible uniformity for powders or granules: A rotary tube furnace is the ideal choice due to its continuous mixing action.
- If your primary focus is efficient gas-phase reactions or surface treatments: The enhanced surface area exposure provided by the tumbling motion makes this an exceptionally efficient option.
- If your primary focus is establishing a high-throughput, continuous production line: The design allows for material to be constantly fed and discharged, integrating perfectly into automated manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating a single, large, or static part: A traditional box or static tube furnace would be the more appropriate and straightforward solution.
Ultimately, choosing a rotary tube furnace is a decision to prioritize process consistency and efficiency for the right kind of material.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Rotating Tube | Cylindrical tube rotates at an angle, tumbling material. | Ensures every particle is uniformly exposed to heat and atmosphere. |
| Dynamic Heating | Continuous mixing action as material moves through the hot zone. | Eliminates hot spots and temperature gradients for consistent product quality. |
| Enhanced Gas Interaction | Tumbling exposes maximum particle surface area to process gases. | Improves reaction efficiency and can reduce gas consumption. |
| Ideal Materials | Best suited for free-flowing powders, granules, and small particles. | Perfect for battery materials, graphite, and other advanced material synthesis. |
Ready to Enhance Your Material Processing?
If your goal is to achieve unmatched uniformity and efficiency in heat-treating powders or granules, a KINTEK rotary tube furnace is the solution. Our furnaces are engineered for precision and reliability, helping you produce higher-quality materials for applications like battery manufacturing and advanced ceramics.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Let our experts help you integrate the right rotary tube furnace into your workflow.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can power your innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- At what temperature is conventional pyrolysis done? Unlock the Right Temperature for Your Desired Product
- What are the factors affecting the yield of bio-oil from the pyrolysis of coconut shell? Control 4 Key Parameters
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results



















