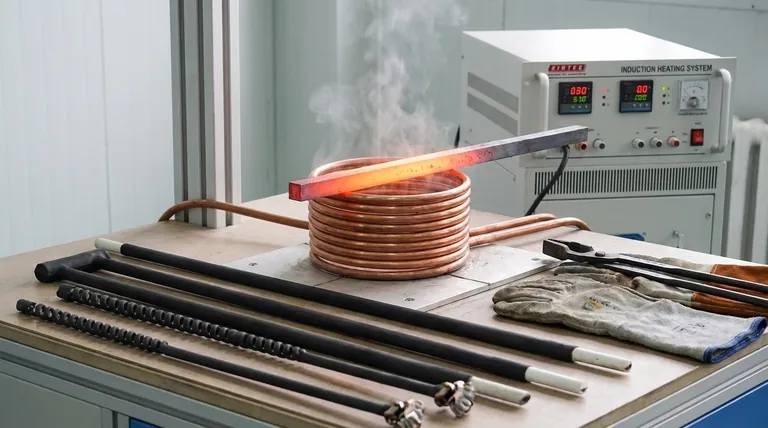
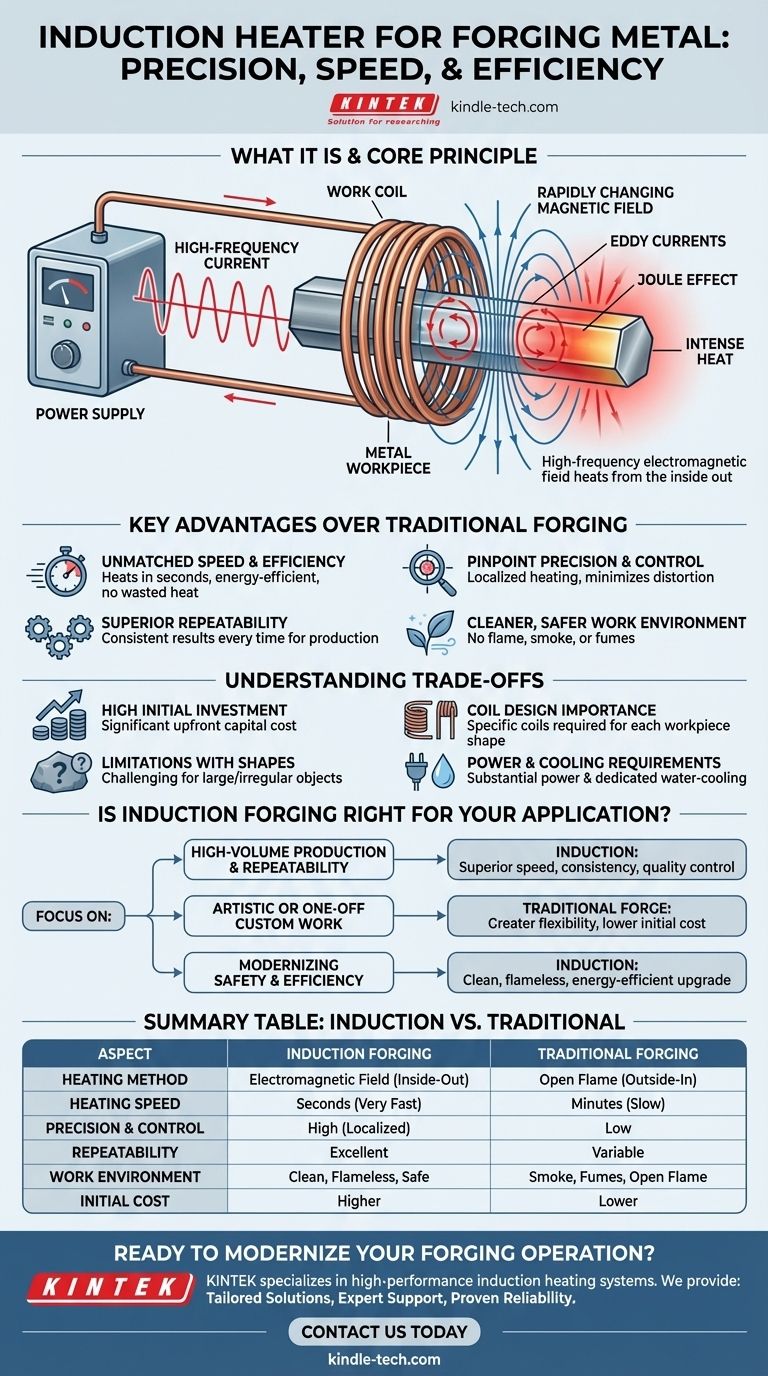
In essence, an induction heater for forging is a high-speed, flameless method for heating metal. Instead of using a traditional flame from gas or coal, it uses a powerful, high-frequency electromagnetic field to rapidly heat the metal workpiece from the inside out.
The central advantage of induction forging lies in its precision, speed, and repeatability. By making the metal its own source of heat, it offers a level of control and efficiency that traditional forges cannot match, particularly in production environments.

The Core Principle: How Induction Actually Works
To understand the value of an induction heater, it's crucial to grasp the underlying physics, which are fundamentally different from conventional heating methods.
The Alternating Magnetic Field
The process begins with a power supply that sends a high-frequency alternating current through a copper work coil. This coil, often shaped to fit around the workpiece, generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within and around it.
The Creation of Eddy Currents
When a conductive material like a steel bar is placed inside this magnetic field, the field induces circulating electrical currents within the metal itself. These are known as eddy currents.
Resistance and Heat Generation
The metal has a natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents. This resistance creates intense heat through a principle known as the Joule effect—the same basic principle that makes an electric stovetop get hot. The metal becomes its own heating element, resulting in extremely rapid and uniform heating from the core outwards.
Key Advantages Over Traditional Forging
Choosing induction heating is a strategic decision that brings significant operational benefits compared to a gas or coal forge.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
Induction heating is incredibly fast, often bringing a steel bar to forging temperature in seconds rather than minutes. Because it only heats the workpiece and not the surrounding air, very little energy is wasted, making it far more energy-efficient.
Pinpoint Precision and Control
The magnetic field can be precisely controlled and localized. This allows you to heat only a specific section of a metal bar, leaving the rest of the piece cool and unaffected. This level of precision is invaluable for complex operations and minimizing heat distortion.
Superior Repeatability
Once the power settings and heating time are dialed in, an induction heater will produce the exact same result every single time. This repeatability is critical for manufacturing and production runs, ensuring consistent quality and eliminating the guesswork inherent in manually judging temperature by color.
A Cleaner, Safer Work Environment
The absence of an open flame, smoke, fuel, and noxious gases creates a dramatically cleaner and safer workplace. It reduces fire hazards and improves air quality, contributing to a better operational environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Despite its advantages, induction technology is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging its specific challenges.
The High Initial Investment
The primary barrier to entry is cost. A professional-grade induction heating system represents a significantly higher upfront capital investment compared to a traditional gas or coal forge.
The Importance of Coil Design
The efficiency of the heater is entirely dependent on the work coil. Different sizes and shapes of workpieces require specifically designed coils to ensure proper coupling and efficient heating. A single, universal coil does not exist, adding a layer of complexity and potential cost.
Limitations with Large or Irregular Shapes
While excellent for uniform parts like bars and billets, heating very large or oddly shaped objects can be challenging. It may require complex, custom-built coils or multiple heating stages, where a large box forge might be more straightforward.
Power and Cooling Requirements
These units draw a substantial amount of electrical power and nearly always require a dedicated water-cooling system. The cooling circuit is essential to protect the expensive work coil and power electronics from overheating during operation, adding to the system's infrastructure requirements.
Is Induction Forging Right for Your Application?
The decision to invest in induction technology should be driven by your specific goals and the nature of your work.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and repeatability: Induction is the superior choice for its unmatched speed, precision, and consistency, which directly translate to higher output and quality control.
- If your primary focus is artistic or one-off custom work: A traditional forge often provides greater flexibility for large, irregular shapes at a much lower initial cost, making it a more practical choice for bespoke projects.
- If your primary focus is modernizing operations for safety and efficiency: The clean, flameless, and energy-efficient nature of induction heating presents a clear and compelling operational upgrade.
Ultimately, understanding these core principles and trade-offs empowers you to select the heating technology that best aligns with your specific forging goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Induction Forging | Traditional Forging |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Electromagnetic field (inside-out) | Open flame (outside-in) |
| Heating Speed | Seconds (Very Fast) | Minutes (Slow) |
| Precision & Control | High (localized heating) | Low |
| Repeatability | Excellent | Variable |
| Work Environment | Clean, flameless, safe | Smoke, fumes, open flame |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
Ready to modernize your forging operation with precision and speed?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab and industrial equipment, including advanced induction heating systems for forging. Our solutions are designed to boost your productivity, ensure consistent quality, and create a safer work environment.
We provide:
- Tailored Solutions: Get an induction system configured for your specific workpiece and production goals.
- Expert Support: Our specialists will guide you from selection to installation and beyond.
- Proven Reliability: Trust KINTEK for durable equipment that maximizes uptime and ROI.
Contact us today to discuss how an induction heater can transform your metal forging process. Let's achieve superior results together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere














