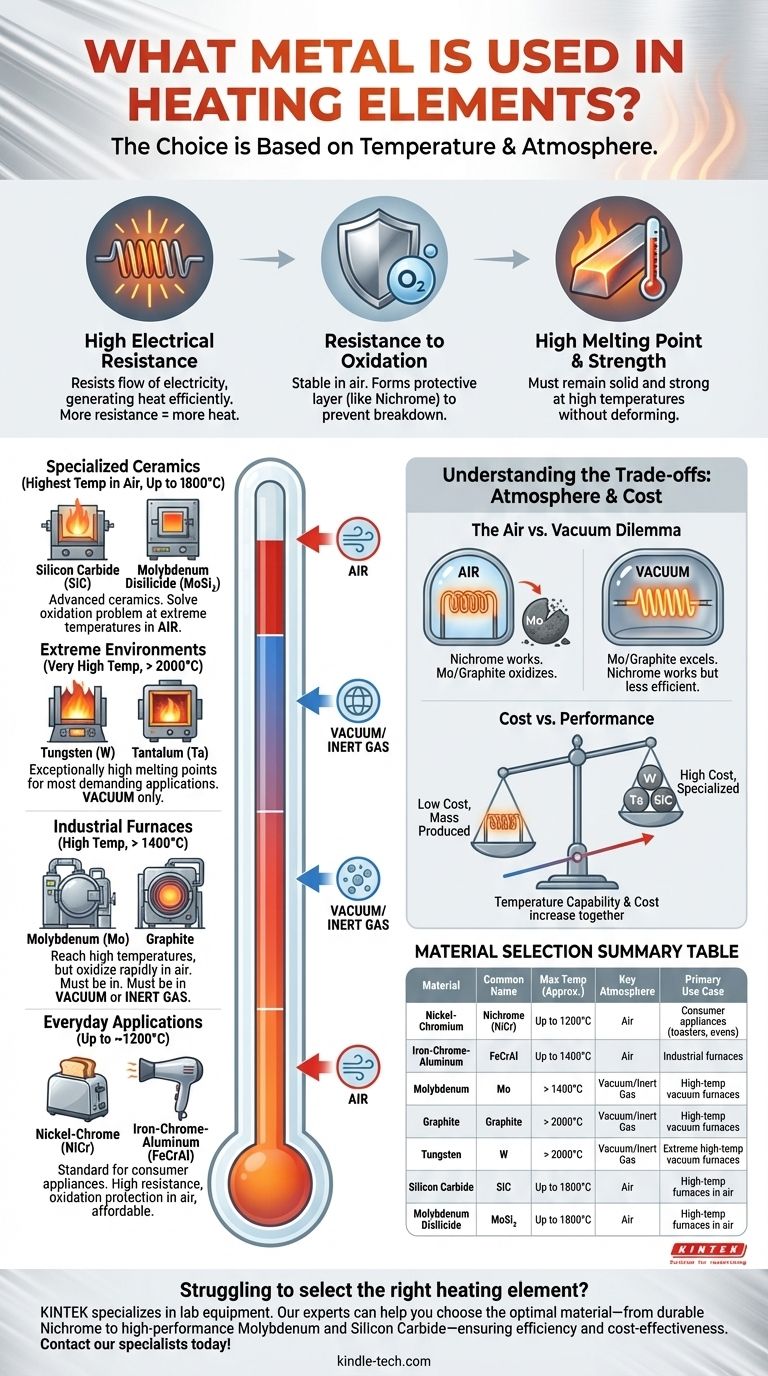
The most common metal used for heating elements is an alloy of Nickel and Chromium, often called Nichrome (NiCr). This material is the workhorse in countless everyday appliances because it has a high resistance to electricity and, crucially, it doesn't easily break down or oxidize when heated in open air.
The choice of material for a heating element is not arbitrary; it is a direct function of the required operating temperature and the surrounding atmosphere. While Nichrome is perfect for a toaster, a high-temperature industrial furnace requires entirely different, more exotic materials.

Why These Materials? The Core Properties of a Heating Element
To understand why certain materials are chosen, you have to understand the core challenges of turning electricity into heat efficiently and reliably. The ideal material must master three key properties.
High Electrical Resistance
A heating element works by resisting the flow of electricity. This friction on an atomic level generates heat.
A material with high resistance is more efficient at this conversion, generating significant heat without needing to be impractically long or thin.
Resistance to Oxidation
At high temperatures, most metals react with oxygen in the air in a process called oxidation. This is the same process that causes iron to rust.
For a heating element, oxidation causes it to degrade and eventually fail. Materials like Nichrome are exceptional because they form a stable, protective outer layer of chromium oxide that prevents further degradation, allowing them to have a long life in open air.
High Melting Point and Strength
This is the most intuitive requirement. The material must remain solid and structurally stable at temperatures well above its intended operating range.
Materials must also be strong enough to be formed into coils, ribbons, or rods without breaking.
A Spectrum of Materials for Different Temperatures
The specific material used is almost always determined by the peak temperature the element needs to reach.
Everyday Applications (Up to ~1200°C): Nickel-Chrome (NiCr)
For consumer appliances like toasters, hair dryers, and electric ovens, Nickel-Chrome (NiCr) is the undisputed standard.
Its combination of high resistance, excellent oxidation protection in air, and relatively low cost makes it the perfect choice for these common applications. Iron-Chrome-Aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys serve a similar purpose in some industrial furnaces.
Industrial Furnaces (High Temp): Molybdenum & Graphite
When temperatures need to go higher, we enter the realm of industrial processing and vacuum furnaces.
Materials like Molybdenum (Mo) and Graphite can reach much higher temperatures than Nichrome, but they have a critical weakness: they oxidize and burn away almost instantly in air at those temperatures. Therefore, they can only be used in a vacuum or an inert gas environment.
Extreme Environments (Very High Temp): Tungsten & Tantalum
For the most demanding applications, engineers turn to refractory metals like Tungsten (W) and Tantalum (Ta).
These metals have exceptionally high melting points, making them suitable for very high-temperature vacuum furnaces. Like Molybdenum, they lack natural oxidation resistance and must be protected from air.
Specialized Ceramics (Highest Temp in Air): Silicon Carbide & MoSi₂
To solve the oxidation problem at extreme temperatures, we must move beyond pure metals.
Advanced ceramics like Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) can operate at incredibly high temperatures (up to 1800°C) while in the open air, a feat that is impossible for Molybdenum or Tungsten.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Atmosphere is Everything
The single most important factor beyond temperature is the operating atmosphere. Failing to account for this is the most common point of confusion.
The Air vs. Vacuum Dilemma
A Nichrome element is designed to operate in air. If you put a Molybdenum or Graphite element in the same air-filled furnace, it would rapidly disintegrate.
Conversely, Molybdenum, Tungsten, and Graphite are the superior choice for high-heat applications precisely because they will be used inside a sealed vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace where oxygen is not a concern.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between temperature capability and cost. Nichrome is inexpensive and mass-produced.
Materials for extreme temperatures, such as platinum or tantalum, are far more expensive, restricting their use to specialized scientific or industrial processes where no other material can perform the job.
Matching the Material to the Application
Ultimately, the material selection is a precise engineering decision. Here is how to think about it based on the primary goal.
- If your primary focus is a consumer appliance or low-temp kiln: Nickel-Chrome (NiCr) is the standard choice for its perfect balance of cost, durability, and performance in air.
- If your primary focus is a high-temperature process in a vacuum furnace: Molybdenum and Graphite are the workhorses, providing excellent heat capability when oxygen is not present.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible temperatures in open air: Specialized ceramics like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) or Silicon Carbide (SiC) are required to withstand both extreme heat and oxidation.
Choosing the right heating element material is about balancing the demands of temperature against the realities of the environment and budget.
Summary Table:
| Material | Common Name | Max Temp (Approx.) | Key Atmosphere | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel-Chromium | Nichrome (NiCr) | Up to 1200°C | Air | Consumer appliances (toasters, ovens) |
| Iron-Chrome-Aluminum | FeCrAl | Up to 1400°C | Air | Industrial furnaces |
| Molybdenum | Mo | > 1400°C | Vacuum/Inert Gas | High-temp vacuum furnaces |
| Graphite | Graphite | > 2000°C | Vacuum/Inert Gas | High-temp vacuum furnaces |
| Tungsten | W | > 2000°C | Vacuum/Inert Gas | Extreme high-temp vacuum furnaces |
| Silicon Carbide | SiC | Up to 1800°C | Air | High-temp furnaces in air |
| Molybdenum Disilicide | MoSi₂ | Up to 1800°C | Air | High-temp furnaces in air |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your lab furnace or industrial process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you choose the optimal material—whether it's durable Nichrome for standard applications or high-performance Molybdenum and Silicon Carbide for extreme temperatures—ensuring efficiency, longevity, and cost-effectiveness for your specific environment. Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application
- What are the uses of silicon carbide rod? The Ultimate Heating Solution for Extreme Temperatures
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution











