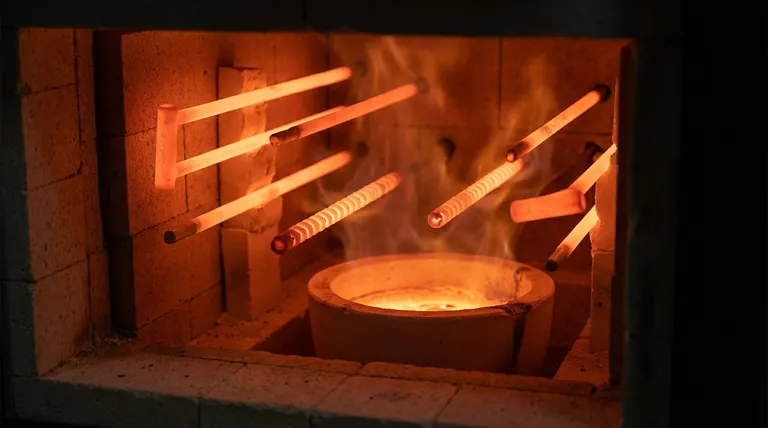
At its core, a silicon carbide rod heated to a high temperature functions as a robust, non-metallic electric heating element. It is the material of choice for creating and precisely controlling extreme heat in various industrial furnaces and other electric heating devices.
Silicon carbide is not just a simple heating source; it is a specialized material engineered to perform reliably in extreme temperature and chemically harsh environments where conventional metallic elements would fail. Its primary use is to enable precise, high-temperature control for advanced manufacturing processes.

What Makes Silicon carbide a Premier Heating Element?
The effectiveness of silicon carbide (SiC) as a heating element stems directly from its unique material properties and the demanding process used to create it.
The Manufacturing Process
A SiC heating element begins as a billet made from high-purity silicon carbide. This billet is then sintered through a process of high-temperature siliconization and recrystallization at over 2200°C.
This intense process creates a highly stable, durable material designed specifically for high-heat applications.
Exceptional Performance at High Temperatures
The primary purpose of a SiC rod is to serve as an electric heating element in high-temperature furnaces. They are essential components in machinery used for metallurgy, ceramics, and glass manufacturing.
Their function is to generate and maintain the high temperatures required for processes like sintering, melting, and heat treatment.
Resistance to Harsh Environments
Beyond just heat, silicon carbide exhibits excellent resistance to thermal shock. This means it can withstand rapid changes in temperature without cracking or failing.
It also shows a strong resistance to erosion from high-energy plasmas, making it a critical component in the semiconductor industry for applications like Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) and oxide etch chambers.
Key Industrial Applications
The unique properties of SiC heating elements make them indispensable across several advanced industries that rely on precise thermal management.
Metallurgy and Ceramics
In industries like powder metallurgy, magnet production, and ceramics, SiC elements provide the stable and uniform high temperatures necessary for sintering and firing materials. This control is critical to achieving the desired material properties.
Glass Manufacturing
Within glass production, SiC heaters are used in electric heating feed channels. Here, their purpose is to precisely control the temperature of each section of the channel.
This ensures the molten glass in the material basin reaches the correct molding temperature, effectively managing the critical cooling process.
Semiconductor Processing
The semiconductor industry uses a specialized form, CVD silicon carbide, for components inside processing chambers. Its ability to resist plasma erosion and thermal shock is vital for maintaining a pure and stable environment during chip fabrication.
The Broader Context of Silicon Carbide
While its modern, high-tech application is as a heating element, the inherent durability of silicon carbide has been recognized for a long time.
Historical Uses
Historically, the hardness and abrasive nature of silicon carbide led to its widespread use in products like sandpapers and industrial cutting tools.
This legacy underscores the fundamental toughness of the material, which is the same property that allows it to function so reliably under the extreme stress of modern industrial heating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the primary strengths of silicon carbide allows you to see why it is chosen for specific, demanding tasks.
- If your primary focus is stable, high-temperature industrial heating: Silicon carbide elements are the industry standard for furnaces used in metallurgy, ceramics, and glass production.
- If your primary focus is performance in a chemically aggressive environment: SiC's resistance to plasma and thermal shock makes it essential for components in semiconductor manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and durability: The same properties that make SiC a great heating element also make it a superior material for abrasives and cutting tools.
Ultimately, silicon carbide is a cornerstone material that enables the high-temperature processes driving modern advanced manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temperature Stability | Reliable performance up to 1600°C+ | Industrial Furnaces (Sintering, Melting) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid temperature changes | Glass Manufacturing, Semiconductor Processing |
| Plasma & Chemical Resistance | Long-lasting in harsh environments | Semiconductor Etch Chambers, RTP Systems |
Need a reliable heating solution for your high-temperature process?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces and consumables designed for demanding environments. Our expertise ensures you get the precise thermal control and durability your laboratory or production line requires.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our silicon carbide heating solutions can enhance your manufacturing efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum temperature for silicon carbide heating element? The Real Limit for Your High-Temp Furnace
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application
- What are the uses of silicon carbide rod? The Ultimate Heating Solution for Extreme Temperatures
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance



















