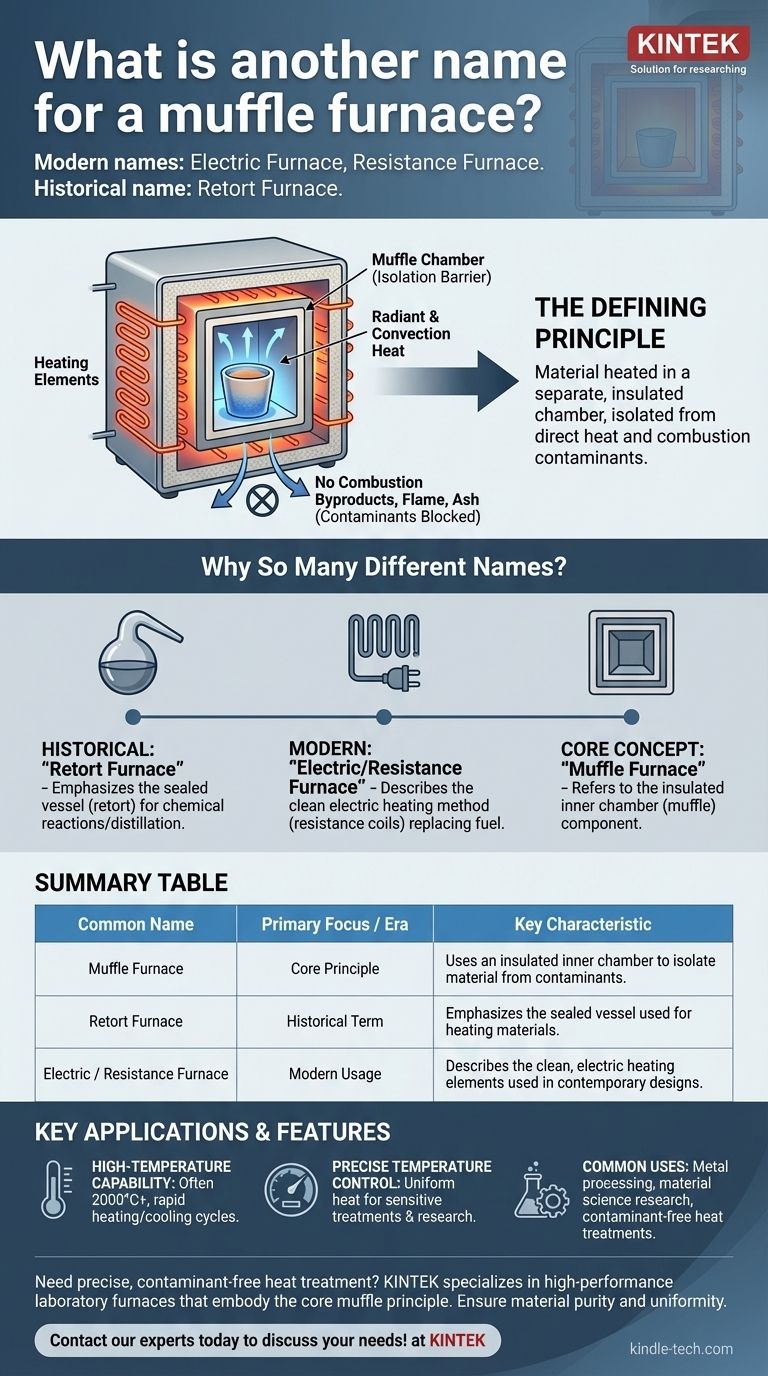
Historically, a muffle furnace was also known as a retort furnace, but in modern usage, it is most commonly referred to as an electric furnace or resistance furnace. These names all describe a furnace where the material being heated is isolated from the direct heat source and any byproducts of combustion.
The key takeaway is not the specific name but the defining principle: a muffle furnace uses a separate, insulated inner chamber (the "muffle") to heat a substance without exposing it to contaminants from fuel, flame, or ash.

What Truly Defines a Muffle Furnace?
The name "muffle furnace" comes from its core component. Understanding this component is the key to recognizing the furnace, regardless of what it's called.
The Principle of Isolation
The primary feature of a muffle furnace is its independent heating and combustion chambers. The material to be heated is placed inside an airtight inner chamber, shielding it completely.
This design prevents any byproducts from the heat source—such as gases or flying ash—from contaminating the material.
The Role of the "Muffle"
The "muffle" is the physical barrier itself. It is an interior chamber or vessel made from a heat-resistant material with high thermal conductivity.
This chamber houses the materials and allows heat to transfer evenly to the workpiece through a combination of radiant and convection heat, ensuring homogeneous treatment.
Modern Electric Designs
Today, most muffle furnaces use high-temperature electric heating elements. This design is inherently clean, as it produces no combustion byproducts.
Because of this, the terms electric furnace and resistance furnace (referring to the electric resistance coils) have become synonymous with modern muffle furnaces.
Why So Many Different Names?
The various names simply reflect an evolution in technology and a focus on different aspects of the furnace's design or function.
"Electric" or "Resistance" Furnace
These modern terms describe how the furnace generates heat. They emphasize the use of clean, controllable electric resistance heating coils that have replaced older fuel-based methods.
"Retort Furnace"
This is a historical term. A "retort" is a sealed vessel used for distillation or chemical reactions. The name highlights the furnace's function of heating a material in a sealed, isolated container.
Key Applications and Features
The unique design of a muffle furnace makes it essential for processes where purity and precision are critical.
High-Temperature Capability
Muffle furnaces are designed for high-temperature applications and can often reach over 2000°C. They allow for rapid heating, recovery, and cooling cycles.
Precise Temperature Control
Modern electric designs offer superior control over temperature uniformity. This makes them ideal for sensitive heat treatments and experimental research in laboratory settings.
Common Uses
These furnaces are widely used for processing various metals like low-carbon steel and copper, conducting material science research, and performing heat treatments that require a contaminant-free environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core function helps you identify the right tool for the job, no matter the label.
- If your primary focus is material purity: The isolated chamber of a muffle furnace is non-negotiable, as it guarantees protection from contamination.
- If your primary focus is precise, repeatable heat treatment: An electric muffle or resistance furnace offers the temperature control and uniformity you need.
- If you are interpreting historical or older technical documents: Recognize that "retort furnace" likely refers to the same fundamental design principle.
Ultimately, focusing on the principle of isolated heating will always lead you to the correct equipment for your work.
Summary Table:
| Common Name | Primary Focus / Era | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | Core Principle | Uses an insulated inner chamber to isolate material from contaminants. |
| Retort Furnace | Historical Term | Emphasizes the sealed vessel used for heating materials. |
| Electric / Resistance Furnace | Modern Usage | Describes the clean, electric heating elements used in contemporary designs. |
Need precise, contaminant-free heat treatment for your lab work?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance laboratory furnaces that embody the core principle of the muffle furnace: guaranteed material purity through isolated heating. Whether you are processing metals, conducting material science research, or require precise temperature control for sensitive experiments, our electric resistance furnaces deliver the uniformity and reliability your laboratory demands.
Let KINTEK provide the right heating solution for your critical applications. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature sintering furnace contribute to halide solid electrolyte testing? Ensure Battery Stability
- How does a constant temperature drying oven facilitate the CBD process of a SnO2 ETL? Optimize Your Film Morphology
- Why is it necessary to control the temperature program of a debinding furnace? Prevent Cracks in Ti/Al2O3 Composites
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and hot oven? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thermal Tool
- What are the advantages of using a tempering furnace for FATT50? Precision Control for Superior Steel Toughness
- What is the function of a box furnace in Li6PS5Cl synthesis? Master Post-Treatment for Solid-State Electrolytes
- How is ash content determined for a given food sample? A Guide to Accurate Mineral Analysis
- Why are 1500 K furnaces required for rare-earth perovskite synthesis? Overcome Kinetic Barriers for Phase Purity



















