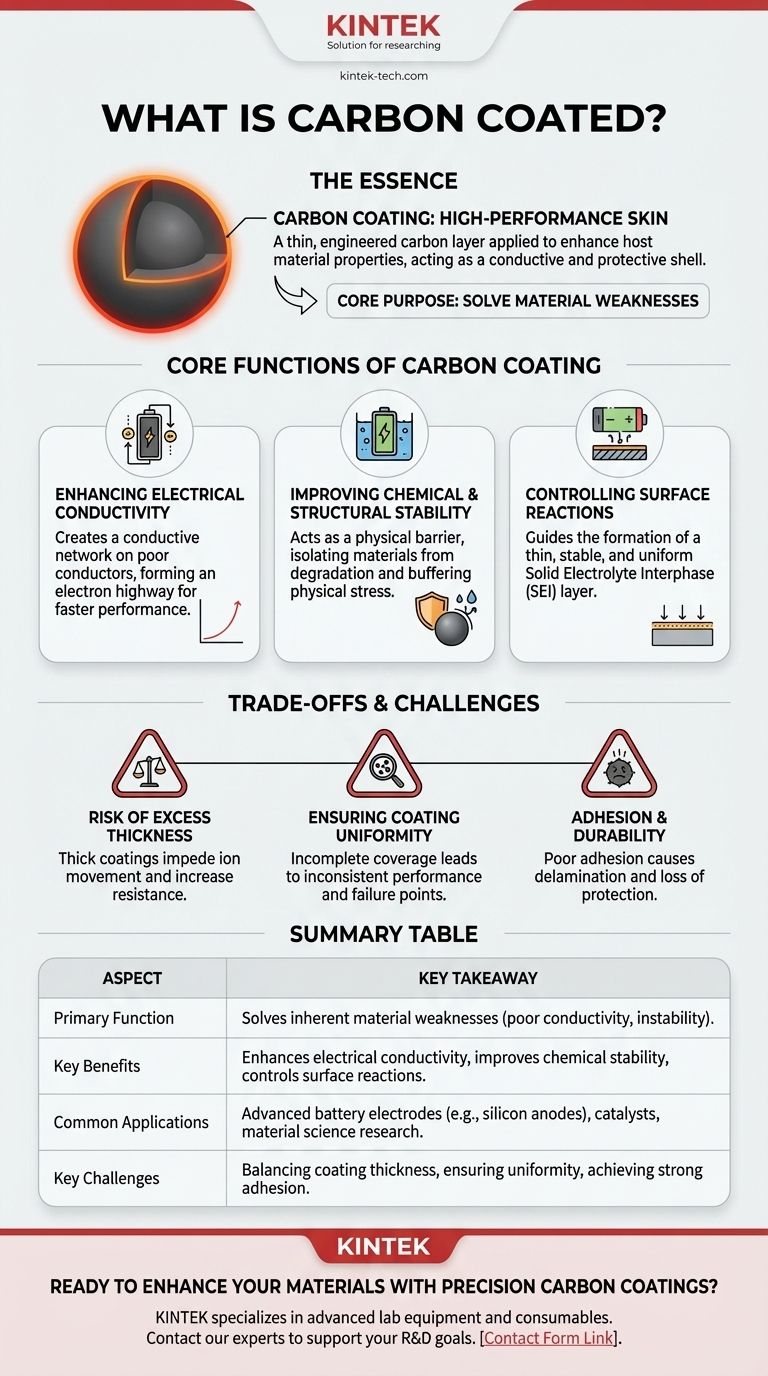
In essence, a carbon coating is a thin, engineered layer of carbon applied to the surface of another material. This is not done for aesthetic reasons, but to fundamentally enhance the host material's properties, most notably its electrical conductivity and chemical stability. It acts as a high-performance "skin" that unlocks or improves the functionality of the core material.
The central purpose of carbon coating is to solve a material's inherent weaknesses. By creating a conductive and protective carbon shell, engineers can make poor conductors electronically active and shield unstable materials from chemical degradation, especially in demanding applications like advanced batteries.

The Core Functions of a Carbon Coating
Understanding why a carbon coating is applied requires looking at the problems it is designed to solve. Its benefits are primarily functional, targeting specific performance bottlenecks in a material.
Enhancing Electrical Conductivity
Many materials with otherwise desirable properties, such as high energy storage capacity, are poor electrical conductors. This is a critical failure point in applications like battery electrodes.
A carbon coating creates a conductive network directly on the surface of these materials. This layer acts like a highway, allowing electrons to move quickly to and from the active material, which dramatically improves the rate of performance and overall efficiency.
Improving Chemical and Structural Stability
Materials used in harsh chemical environments, like the inside of a battery, are prone to degradation from unwanted side reactions.
The carbon layer serves as a physical barrier. It isolates the core material from its surroundings (e.g., the liquid electrolyte in a battery), preventing reactions that would otherwise consume the material and shorten the device's lifespan.
This coating can also help buffer physical stress. For example, some battery materials swell and shrink significantly during charging and discharging. A flexible carbon coating can help hold the particle together, preventing it from cracking and falling apart over repeated cycles.
Controlling Surface Reactions
In many electrochemical systems, the initial reactions at the material's surface are critical for long-term performance. A well-known example is the formation of the Solid Electrolyte Interphase (SEI) layer in lithium-ion batteries.
A precisely engineered carbon coating can promote the formation of a thin, stable, and uniform SEI layer. An uncontrolled reaction can lead to a thick, resistive layer that chokes the battery, but a carbon coating guides this process, ensuring low resistance and long-term stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While highly effective, applying a carbon coating is a delicate balancing act. The process is not without its own set of engineering challenges that must be overcome for the coating to be beneficial.
The Risk of Excess Thickness
A carbon coating must be thick enough to provide continuous conductive pathways, but not so thick that it impedes other critical functions.
If the layer is too thick, it can block the movement of ions (like lithium ions in a battery). This increases the internal resistance of the device, cancelling out the benefits of improved electronic conductivity and ultimately harming performance.
Ensuring Coating Uniformity
An incomplete or non-uniform coating is a major point of failure. Any exposed areas of the underlying material remain vulnerable to side reactions and degradation.
Achieving a perfectly uniform shell around every single microscopic particle, especially in a large-batch industrial process, is a significant manufacturing challenge. Inconsistent coverage leads to inconsistent performance and faster failure.
Adhesion and Durability
The coating is only useful if it stays attached to the host material. It must withstand the physical stresses of manufacturing and operation, including expansion, contraction, and abrasion.
Poor adhesion means the coating can delaminate or flake off, instantly losing its protective and conductive benefits and leaving the core material exposed.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The significance of carbon coating depends entirely on your field and objectives. Its application is a solution to a specific set of material limitations.
- If your primary focus is advanced batteries: View carbon coating as an essential enabling technology for next-generation anode and cathode materials like silicon, LFP (lithium iron phosphate), and LMFP, which require it to achieve high performance and long cycle life.
- If your primary focus is materials science: See this as a versatile surface modification technique to impart conductivity and chemical inertness onto a wide range of materials, from ceramics to polymers.
- If your primary focus is catalysis: Consider carbon coating a method to support catalytic nanoparticles, preventing them from agglomerating while providing a stable, conductive substrate for electrochemical reactions.
Ultimately, carbon coating is a critical tool for overcoming the natural limitations of a material, allowing us to engineer better performance at the atomic scale.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Solves inherent material weaknesses (poor conductivity, instability). |
| Key Benefits | Enhances electrical conductivity, improves chemical stability, controls surface reactions. |
| Common Applications | Advanced battery electrodes (e.g., silicon anodes), catalysts, material science research. |
| Key Challenges | Balancing coating thickness, ensuring uniformity, achieving strong adhesion. |
Ready to enhance your materials with precision carbon coatings?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for materials engineering. Whether you are developing next-generation batteries, catalysts, or novel materials, our solutions can help you achieve the uniform, durable coatings essential for peak performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your research and development goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the disadvantages of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Managing the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition
- What is the temperature of PECVD deposition? Achieve High-Quality Films at Low Temperatures
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems


















