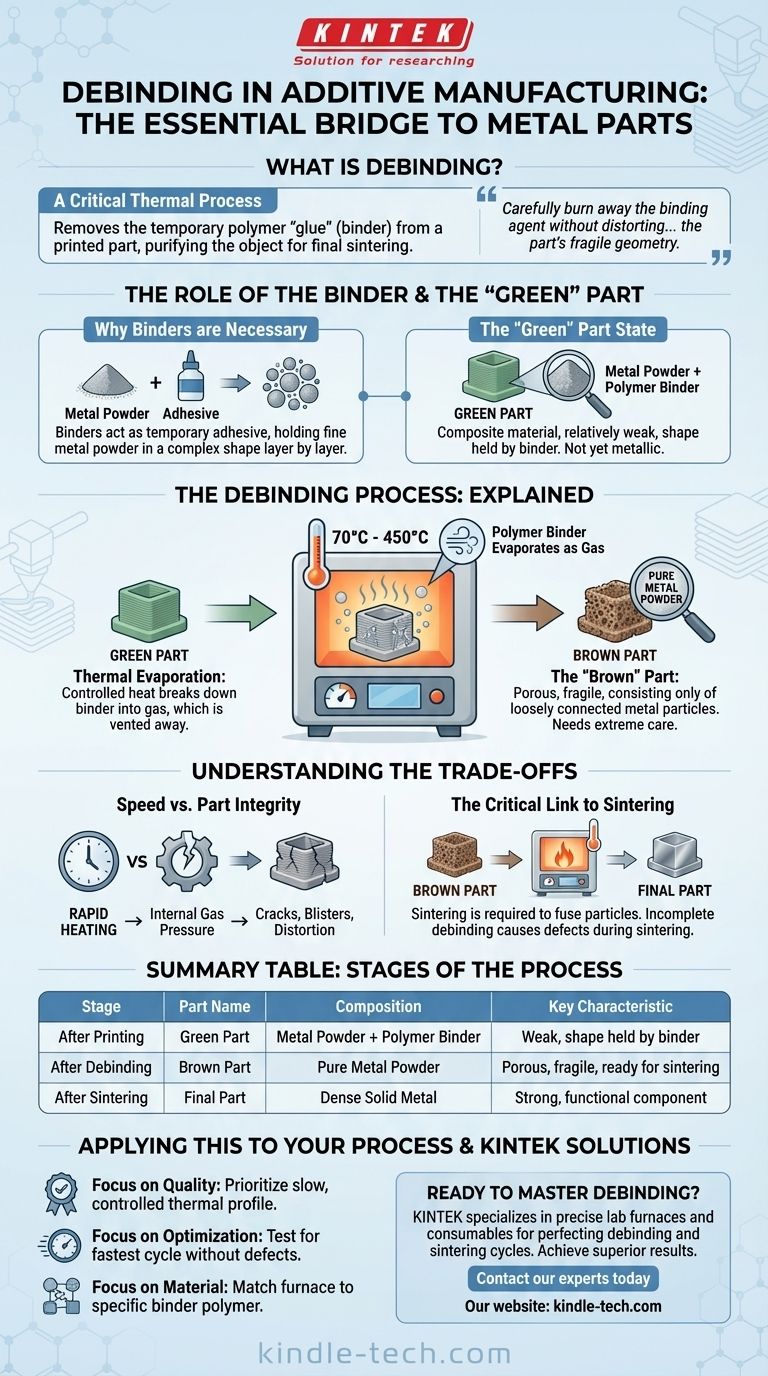
In additive manufacturing, debinding is a critical thermal process that removes the temporary polymer "glue," or binder, from a printed part. This step purifies the object, leaving behind a fragile structure of metal powder that is prepared for the final sintering stage, where it will be fused into a solid metal component.
Debinding is the essential and delicate bridge between printing a part and creating a solid metal object. Its purpose is to carefully burn away the binding agent without distorting or damaging the part's fragile geometry, setting the stage for final densification.

The Role of the Binder and the "Green" Part
Many metal additive manufacturing processes, such as binder jetting, don't melt metal powder directly. Instead, they use a different strategy to build the initial object.
Why Binders are Necessary
Fine metal powders cannot hold a complex shape on their own. A binder, typically a polymer, is mixed with the metal powder or selectively deposited to act as a temporary adhesive, gluing the metal particles together layer by layer.
The "Green" Part State
The object that comes directly off the printer is known as a "green" part. It is a composite material, consisting of metal powder held in its desired shape by the polymer binder. At this stage, the part is relatively weak and has not yet achieved its final metallic properties.
The Debinding Process Explained
To transform the green part into a solid metal object, the binder must be completely removed. This is the sole purpose of the debinding stage.
The Goal: Pure Metal Powder
The objective is to eliminate all organic compounds (the binder) from the part, leaving only the metal powder behind. This is a crucial purification step.
How It Works: Thermal Evaporation
The green part is placed in a specialized furnace. The temperature is then carefully and slowly raised, typically to a range between 70°C and 450°C. This controlled heat breaks down the polymer binder, causing it to evaporate as a gas. This gas is then vented away, often condensed and captured to avoid contamination.
The "Brown" Part State
After the binder has been fully removed, the part is referred to as a "brown" part. It is now extremely porous and fragile, consisting only of loosely connected metal particles. It must be handled with extreme care before it moves to the final step.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Debinding is a delicate balancing act. Rushing the process or failing to control the parameters can easily ruin the part.
Speed vs. Part Integrity
The most significant trade-off is between process speed and the structural integrity of the part. If the part is heated too quickly, the binder will evaporate rapidly, creating internal gas pressure. This pressure can cause cracks, blisters, or complete distortion, rendering the part useless. A slow, precise heating ramp is essential for success.
The Critical Link to Sintering
Debinding does not create the final part; it only prepares it. The fragile "brown" part has no functional strength. It must immediately undergo sintering, where it is heated to a much higher temperature (just below the metal's melting point) to fuse the metal particles together into a dense, strong component. Incomplete debinding will lead to contamination and defects during the sintering phase.
Applying This to Your Process
The success of your final metal part is heavily dependent on a properly executed debinding cycle.
- If your primary focus is part quality and yield: Prioritize a slow, controlled thermal profile to ensure the binder can escape without causing internal stress or cracking.
- If your primary focus is process optimization: Your goal should be to find the fastest possible debinding cycle that does not introduce defects, which requires careful testing and validation.
- If your primary focus is material compatibility: Always ensure your debinding furnace and temperature profile are correctly matched to the specific polymer binder used in your printing material.
Ultimately, mastering debinding is fundamental to producing reliable and high-quality metal parts through binder-based additive manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Part Name | Composition | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| After Printing | Green Part | Metal Powder + Polymer Binder | Weak, shape held by binder |
| After Debinding | Brown Part | Pure Metal Powder | Porous, fragile, ready for sintering |
| After Sintering | Final Part | Dense Solid Metal | Strong, functional component |
Ready to Master the Debinding Process?
Producing high-quality metal parts requires precise thermal processing. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables you need to perfect your debinding and sintering cycles. Our furnaces offer the precise temperature control essential for removing binders without damaging your parts.
Let us help you achieve superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and ensure your additive manufacturing process is a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is RF sputtering? A Guide to Depositing Non-Conductive Thin Films
- What is the process of thin film in semiconductor? Build the Layers of Modern Electronics
- What temperature do you vacuum cast? Master the 3 Key Temperatures for Perfect Results
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What happens in a pyrolysis reactor? Unlocking Value from Organic Waste
- What is sputtering techniques of thin film deposition? Achieve Superior Coatings with Material Versatility
- What is the purpose of the wiped film evaporator? Purify Heat-Sensitive Compounds Efficiently
- What is the function of a constant temperature magnetic stirrer in the synthesis of SO3H-functionalized ionic liquids?



















