In the pharmaceutical industry, an evaporator is a critical piece of equipment designed for thermal separation. Its primary function is to remove a liquid, typically a solvent or water, from a solution by boiling it. This process leaves behind a more concentrated form of the desired substance, such as the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API).
At its core, evaporation in pharmaceuticals is not simply about boiling off a liquid. It is a precisely controlled process for concentrating valuable products, recovering expensive solvents, and preparing solutions for crystallization, often performed under a vacuum to protect heat-sensitive compounds from degradation.

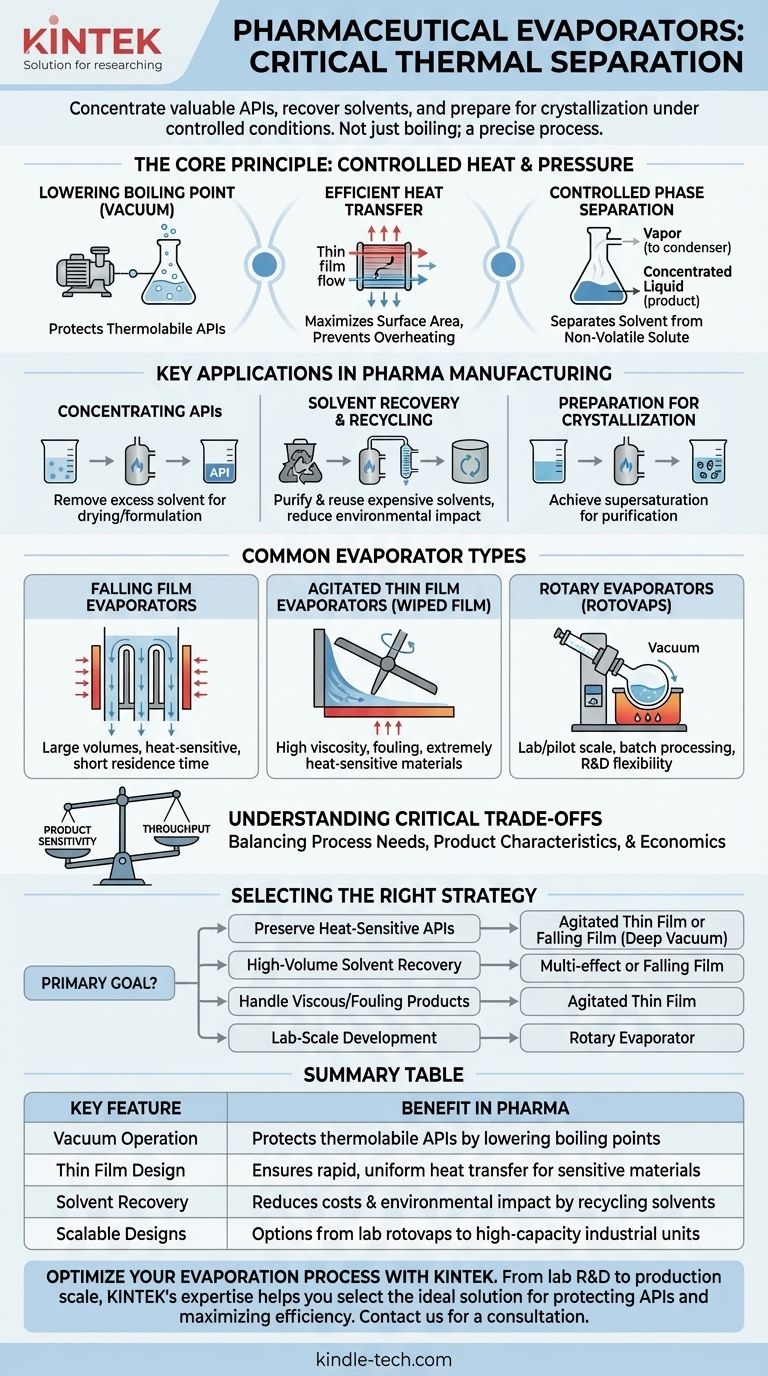
The Core Principle: More Than Just Boiling
Understanding pharmaceutical evaporation requires moving beyond the simple concept of heating a liquid. The process is governed by controlled heat transfer and pressure to ensure the final product meets stringent quality standards.
Lowering the Boiling Point with Vacuum
Many APIs and biological compounds are thermolabile, meaning they degrade or lose potency when exposed to high temperatures. By operating the evaporator under a vacuum, the pressure inside the system is lowered, which significantly reduces the boiling point of the solvent. This allows for rapid evaporation at much lower, safer temperatures, preserving the integrity of the product.
Efficient Heat Transfer
The goal is to transfer energy into the liquid as efficiently as possible to initiate boiling without overheating any portion of the product. Different evaporator designs achieve this by maximizing the surface area over which heat is exchanged, often by creating thin films of the liquid.
Controlled Phase Separation
The fundamental goal is to separate the volatile solvent from the non-volatile solute (the product). The solvent turns into a vapor, which is then removed from the system and often condensed back into a liquid for recovery and reuse, while the concentrated product is collected.
Key Applications in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Evaporators are not a niche tool; they are a workhorse unit operation central to several key stages of drug production.
Concentrating Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
After synthesis, an API often exists in a dilute solution. Evaporation is used to remove the excess solvent, increasing the concentration of the API to the required level for subsequent steps like drying or formulation.
Solvent Recovery and Recycling
Pharmaceutical-grade solvents are expensive and their disposal is environmentally regulated. Evaporators are essential for recovering these solvents from waste streams, allowing them to be purified and reused. This dramatically reduces both operational costs and environmental impact.
Preparation for Crystallization
Crystallization is a common method for purifying APIs. To initiate this process, the solution must be supersaturated, meaning it contains more dissolved solute than it normally could. Evaporation is the primary method used to carefully remove the solvent until this precise point of supersaturation is reached.
Common Types of Evaporators in Pharma
The choice of evaporator depends entirely on the product's characteristics, such as its viscosity and heat sensitivity, as well as the required production scale.
Falling Film Evaporators
In this design, the liquid is fed to the top of vertical tubes and flows downward as a thin film, with heat applied to the outside of the tubes. This provides a very short residence time, making it ideal for processing large volumes of heat-sensitive materials.
Agitated Thin Film Evaporators
Also known as wiped film evaporators, these are the solution for the most challenging products. A rotating wiper system continuously spreads a very thin film of the liquid on a heated surface. This design is excellent for highly viscous, fouling, or extremely heat-sensitive materials that would be damaged in other systems.
Rotary Evaporators (Rotovaps)
Commonly seen in laboratory and pilot-plant settings, a rotovap consists of a rotating flask partially submerged in a heated bath. The rotation creates a thin film on the interior surface of the flask, and a vacuum is applied to lower the boiling point. They are ideal for small-scale batch processing and development work.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting an evaporator is a balancing act between process needs, product characteristics, and economic realities.
Product Sensitivity vs. Throughput
The gentlest processing methods, like those in agitated thin film evaporators, are often not the highest-capacity systems. A key decision is balancing the need to protect a fragile product with the need to meet production volume targets.
Viscosity and Fouling Tendencies
As a solution becomes more concentrated, its viscosity often increases dramatically, and it may have a tendency to foul (coat) the heated surfaces. A simple falling film evaporator that works well for a dilute solution may fail entirely once the product becomes thick and sticky, necessitating a more robust design like an agitated thin film unit.
Capital Cost vs. Operating Efficiency
More complex and energy-efficient systems, such as multi-effect evaporators that reuse heat, have a higher initial purchase price. However, they can offer significant long-term savings on energy consumption, a major operational expense.
Selecting the Right Evaporation Strategy
Your choice must be driven by the primary goal of the specific process step.
- If your primary focus is preserving highly heat-sensitive APIs: An agitated thin film or falling film evaporator operating under a deep vacuum is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is high-volume solvent recovery: A multi-effect or falling film evaporator offers the best balance of throughput and energy efficiency.
- If your primary focus is handling viscous or fouling products: An agitated thin film evaporator is specifically designed to manage these challenging materials without compromising performance.
- If your primary focus is lab-scale development: A rotary evaporator provides the necessary flexibility and control for research and small-scale batches.
Ultimately, selecting the correct evaporator is a strategic decision that directly impacts product quality, process efficiency, and operational costs in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit in Pharma |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Operation | Protects thermolabile APIs by lowering boiling points |
| Thin Film Design | Ensures rapid, uniform heat transfer for sensitive materials |
| Solvent Recovery | Reduces costs and environmental impact by recycling expensive solvents |
| Scalable Designs | Options from lab rotovaps to high-capacity industrial units |
Optimize Your Pharmaceutical Evaporation Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right evaporation technology is critical for protecting your valuable APIs, maximizing solvent recovery, and ensuring process efficiency. Whether you are developing a new drug in the lab or scaling up production, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help you select the ideal solution—from rotary evaporators for R&D to advanced agitated thin film systems for challenging production materials.
Let our specialists help you enhance product quality and reduce operational costs. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation on your laboratory's evaporation needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Benchtop Water Circulating Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What determines the vacuum degree achievable by a water circulating vacuum pump? Unlock the Physics of Its Limits
- What factors affect evaporation and condensation? Master the Science of Water's Phase Changes
- How does the impeller rotation affect the gas flow in a water circulating vacuum pump? A Guide to the Liquid Ring Principle
- Why must a laboratory vacuum pump be used to evacuate a PM-HIP capsule before it is sealed? Ensure Material Integrity
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments



















