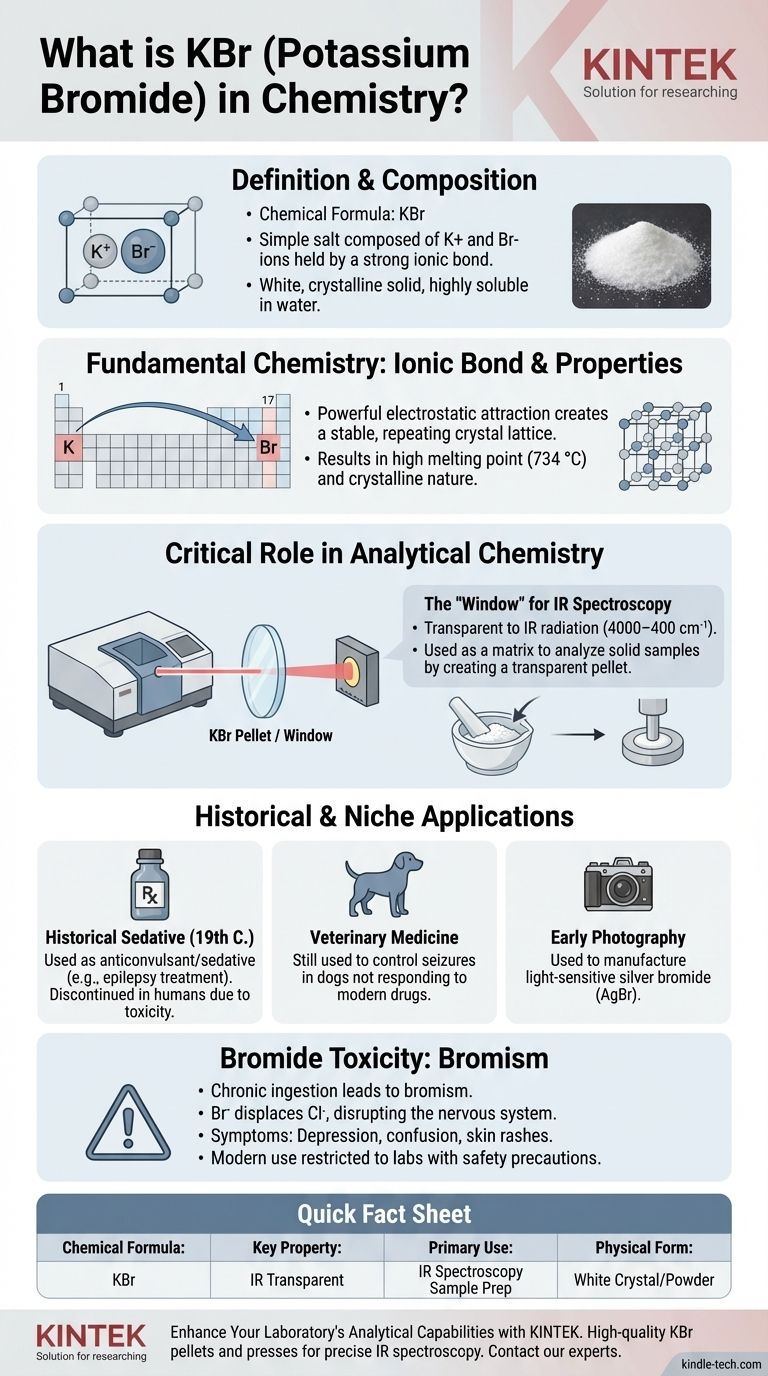
In the world of chemistry, KBr is the chemical formula for Potassium Bromide. It is a simple salt composed of a potassium ion (K+) and a bromide ion (Br−) held together by a strong ionic bond. This white, crystalline solid is highly soluble in water and is a staple compound found in most chemical laboratories.
While easily defined as a simple salt, Potassium Bromide's true significance lies in its unique physical properties. Its transparency to infrared light makes it an indispensable tool in modern chemical analysis, a role that has far outlasted its historical, and riskier, use in medicine.

The Fundamental Chemistry of KBr
Potassium Bromide is a quintessential example of an ionic compound, formed by elements from opposite ends of the periodic table. Its properties are a direct result of this chemical structure.
An Iconic Ionic Bond
Potassium (K) is an alkali metal in Group 1, which readily loses one electron to form a positively charged ion (a cation), K+. Bromine (Br) is a halogen in Group 17, which readily accepts one electron to form a negatively charged ion (an anion), Br−.
The powerful electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions creates a stable, repeating crystal lattice structure. This strong bond is responsible for KBr's high melting point (734 °C or 1353 °F) and its crystalline nature.
Key Physical Characteristics
As a standard laboratory reagent, KBr is a white, odorless powder or crystal. Its most important physical property for many chemists is its high solubility in water, where it dissociates completely into its constituent K+ and Br− ions.
KBr's Critical Role in Analytical Chemistry
The most significant modern application of Potassium Bromide is not in chemical reactions, but as a medium for analysis, particularly in infrared (IR) spectroscopy.
The "Window" for Infrared Spectroscopy
IR spectroscopy works by shining infrared light through a sample to see which frequencies are absorbed. This absorption pattern reveals the types of chemical bonds present in a molecule.
KBr is exceptionally useful here because it is transparent to IR radiation across a very wide frequency range (4000–400 cm⁻¹). Its simple ionic lattice has no covalent bonds that would vibrate and absorb IR light in this region, so it doesn't create interfering signals.
How KBr Pellets Are Made
To analyze a solid sample, a tiny amount is ground into a fine powder with dry KBr. This mixture is then put into a die and compressed with several tons of pressure.
The soft, salt-like nature of KBr allows it to flow under pressure, forming a thin, transparent or translucent disc, often called a KBr pellet or window. The sample is trapped within this KBr matrix, allowing the IR beam to pass through for analysis.
Historical and Niche Applications
Before becoming a cornerstone of spectroscopy, KBr had a long and varied history, most notably in medicine.
A Sedative of the Past
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, Potassium Bromide was widely used as an anticonvulsant and sedative. It was one of the first effective treatments for epilepsy.
Veterinary Medicine
While its use in humans has been discontinued due to toxicity, KBr is still used in veterinary medicine, primarily to control seizures in dogs that do not respond to more modern drugs.
Role in Early Photography
Potassium Bromide was also used in the manufacturing of silver bromide (AgBr), a light-sensitive compound that is the fundamental component of black-and-white photographic films and papers.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Issue of Bromide Toxicity
The very reason KBr worked as a sedative is also the source of its danger. Understanding this trade-off is key to appreciating its shift in application.
The Mechanism of "Bromism"
The bromide ion (Br−) is chemically similar to the chloride ion (Cl−), which is essential for nerve function. When ingested in high doses, bromide can displace chloride in the body, disrupting the central nervous system.
This chronic intoxication, known as bromism, can cause a range of neurological and psychological symptoms, including depression, confusion, psychosis, and skin rashes. The long half-life of bromide in the body makes it easy to accumulate to toxic levels.
Modern Safety Precautions
Due to the risk of bromism, KBr is no longer used in human medicine. In the lab, it is considered a standard, relatively safe chemical for its intended purpose but must be handled with appropriate care. Ingestion should always be avoided, and standard personal protective equipment like gloves and safety glasses should be worn.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your perspective on KBr will depend entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is analytical chemistry: View KBr as a fundamental and indispensable tool for preparing solid samples for IR spectroscopy.
- If your primary focus is synthesis: Consider KBr mainly as a stable, inexpensive, and water-soluble source of bromide ions for aqueous reactions.
- If your primary focus is the history of science: Recognize KBr as a classic example of how a compound's use evolves as our understanding of its properties and biological risks deepens.
Ultimately, understanding Potassium Bromide is to see how a simple compound's story is shaped by its unique chemical and physical properties.
Summary Table:
| Property/Application | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | KBr |
| Chemical Name | Potassium Bromide |
| Key Property | Transparent to IR light (4000–400 cm⁻¹) |
| Primary Use | Sample preparation for IR spectroscopy |
| Physical Form | White, crystalline solid |
| Solubility | Highly soluble in water |
| Historical Uses | Sedative, anticonvulsant, photography |
Enhance Your Laboratory's Analytical Capabilities with KINTEK
KBr is a fundamental tool for precise infrared spectroscopy, enabling accurate chemical analysis. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables, including reliable KBr pellets and presses, to support your research and analytical needs.
Our products are designed to ensure consistency, clarity, and accuracy in your spectroscopic applications. Whether you're in pharmaceuticals, materials science, or academic research, KINTEK delivers the dependable supplies you need to achieve superior results.
Ready to optimize your IR spectroscopy workflow? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How does sample size affect analysis? Maximize the Reliability of Your Research
- What are the advantages of an electrolytic polishing device for EK-181 steel TEM samples? Ensure Peak Sample Integrity
- What is the purpose of using electrolytic polishing on copper foils? Optimize Your CVD Graphene & hBN Growth Surface
- Why are an electrolytic polishing system and specific electrolytes necessary for Inconel 625? Expert Analysis
- How long does it take to solder? A guide to timing and technique for perfect joints



















