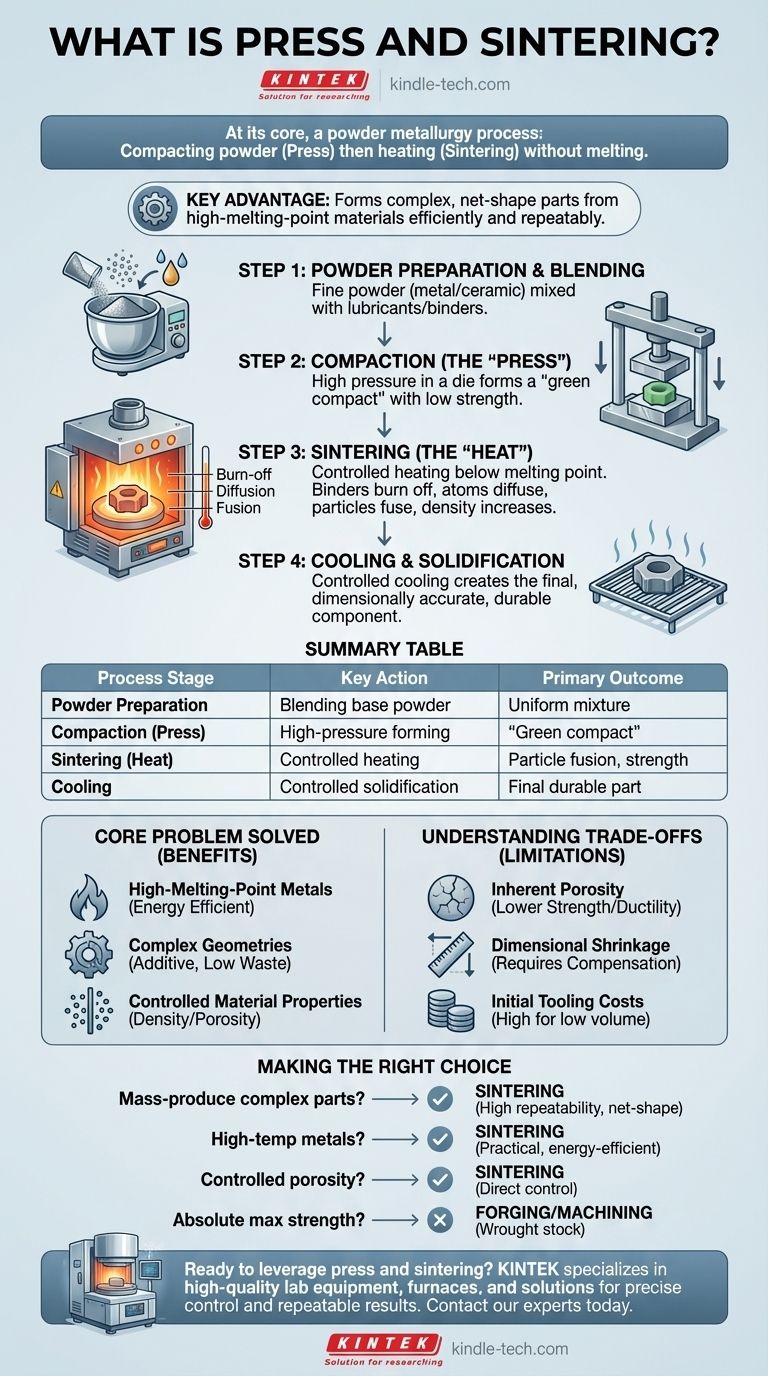
At its core, press and sintering is a powder metallurgy process used to create solid objects from powdered material without melting it. It consists of two primary stages: first, compacting the powder under high pressure into a desired shape (the "press" stage), and second, heating that shape in a controlled furnace to a temperature below its melting point, causing the individual particles to bond and fuse together (the "sintering" stage).
The fundamental advantage of press and sintering is its ability to form complex, net-shape parts from materials—especially those with very high melting points—in an energy-efficient and highly repeatable manner, making it a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
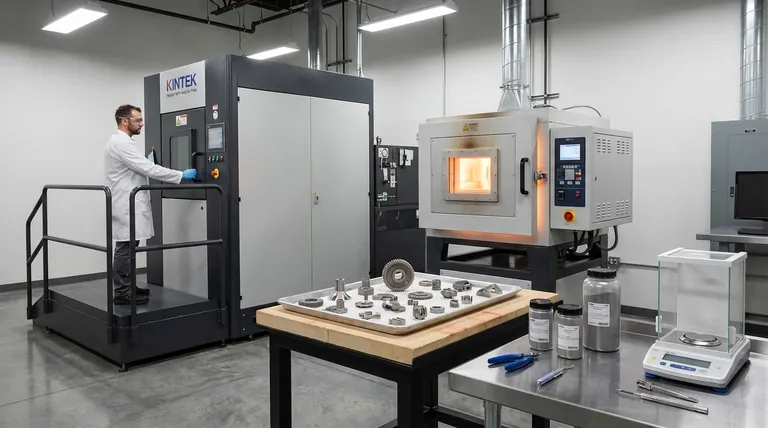

Deconstructing the Press and Sintering Process
To truly understand this technique, we must look at it as a sequence of carefully controlled steps, each contributing to the final properties of the component.
Step 1: Powder Preparation and Blending
The process begins not with a solid block of material, but with a fine powder. This primary material, often a metal or ceramic, is mixed with other elements.
These additives can include lubricants to aid in compaction or bonding agents (like wax or polymers) that temporarily hold the powder together.
Step 2: Compaction (The "Press")
The prepared powder blend is loaded into a precision mold, or die. A powerful press then applies immense pressure, typically at room temperature.
This pressure compacts the powder, forcing the particles into intimate contact and forming a solid but fragile object known as a "green compact." This part has the desired shape but possesses low mechanical strength.
Step 3: Sintering (The "Heat")
The green compact is carefully removed from the die and placed into a sintering furnace with a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation. The heating process occurs in distinct phases.
First, the temperature is raised to burn away the binding agents added in the initial step. Then, the temperature is increased further to just below the melting point of the primary material.
At this elevated temperature, a process of atomic diffusion occurs at the contact points between particles. The atoms migrate across particle boundaries, causing the individual grains to fuse into a solid, unified mass and significantly increasing the part's density and strength.
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
After being held at the sintering temperature for a specific duration, the component is cooled in a controlled manner. It solidifies into its final, durable state.
The final part is a solid object that is dimensionally very close to the intended shape, often requiring little to no subsequent machining.
The Core Problem Sintering Solves
Press and sintering is not just an alternative manufacturing method; it is a solution for specific engineering challenges where traditional methods like casting or machining fall short.
Manufacturing High-Melting-Point Metals
For materials like tungsten, molybdenum, and other refractory metals, reaching their melting point requires enormous amounts of energy. Sintering bypasses this entirely, allowing parts to be formed at much lower temperatures, saving significant energy and cost.
Creating Complex Geometries Efficiently
Creating a small, intricate part by machining it from a large block of metal (subtractive manufacturing) is slow and generates significant waste. Sintering is an additive process, using only the material needed to form the part.
This makes it exceptionally efficient for the mass production of complex components like gears, bushings, and structural automotive parts with high consistency.
Controlling Material Properties
The sintering process allows for precise control over the final density of the part. By adjusting time, temperature, and pressure, manufacturers can create components with a specific level of porosity.
This is undesirable for a structural part but is the primary goal when creating products like sintered bronze bearings (which hold oil) or metallic filters.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is without limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging the inherent trade-offs of press and sintering.
Inherent Porosity
Unless secondary operations are performed, sintered parts almost always retain some level of microscopic porosity. This means they are typically not as strong or ductile as parts made from fully dense wrought or forged metal.
Dimensional Shrinkage
As the particles fuse and the part densifies during sintering, it shrinks. This shrinkage must be precisely calculated and compensated for in the initial design of the compaction die. Unpredictable shrinkage can lead to parts that are out of tolerance.
Initial Tooling Costs
The hardened steel dies required for the compaction stage are expensive to design and manufacture. This high initial investment means that press and sintering is most cost-effective for medium to high-volume production runs where the tooling cost can be amortized over many thousands of parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing complex metal parts: Sintering is an excellent choice due to its high repeatability, low material waste, and net-shape capabilities.
- If your primary focus is working with high-temperature metals: Sintering is often the most practical and energy-efficient method available.
- If your primary focus is creating materials with controlled porosity (like filters): This process offers direct control over the final density and pore structure of the part.
- If your primary focus is absolute maximum strength and fatigue resistance: You should investigate forging or machining from wrought bar stock, as the inherent porosity of standard sintered parts can be a limiting factor.
Ultimately, press and sintering empowers engineers to turn simple powder into complex, functional components with remarkable efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Preparation | Blending base powder with additives | Uniform mixture ready for compaction |
| Compaction (Press) | High-pressure forming in a die | Creation of a fragile "green compact" |
| Sintering (Heat) | Controlled heating below melting point | Particle fusion, increased strength and density |
| Cooling | Controlled solidification | Final, durable net-shape part |
Ready to leverage press and sintering for your lab or production needs? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including sintering furnaces and powder metallurgy solutions. Whether you're developing new materials or optimizing mass production, our expertise ensures precise temperature control, repeatable results, and energy-efficient performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application and help you achieve superior component quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
People Also Ask
- What is HIP treatment for metal? Eliminate Internal Defects for Superior Part Performance
- What is HIP in material processing? Achieve Near-Perfect Density for Critical Components
- What are the components of a hot isostatic pressing system? A Guide to Core HIP Equipment
- How much energy does hot isostatic pressing consume? Unlock Net Energy Savings in Your Process
- What pressure is hot isostatic press? Achieve Full Density & Superior Material Performance



















