At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a high-tech coating process performed in a vacuum that transfers material on an atomic level. It involves turning a solid source material into a vapor, which then travels across a chamber and condenses onto a target object—the substrate—to form an exceptionally thin, pure, and durable film. This method effectively builds a new surface, atom by atom.
PVD is less like painting and more like 3D printing a new surface at a microscopic scale. This precision allows for the creation of coatings that enhance a material's hardness, temperature resistance, or optical properties in ways that are impossible with traditional methods.
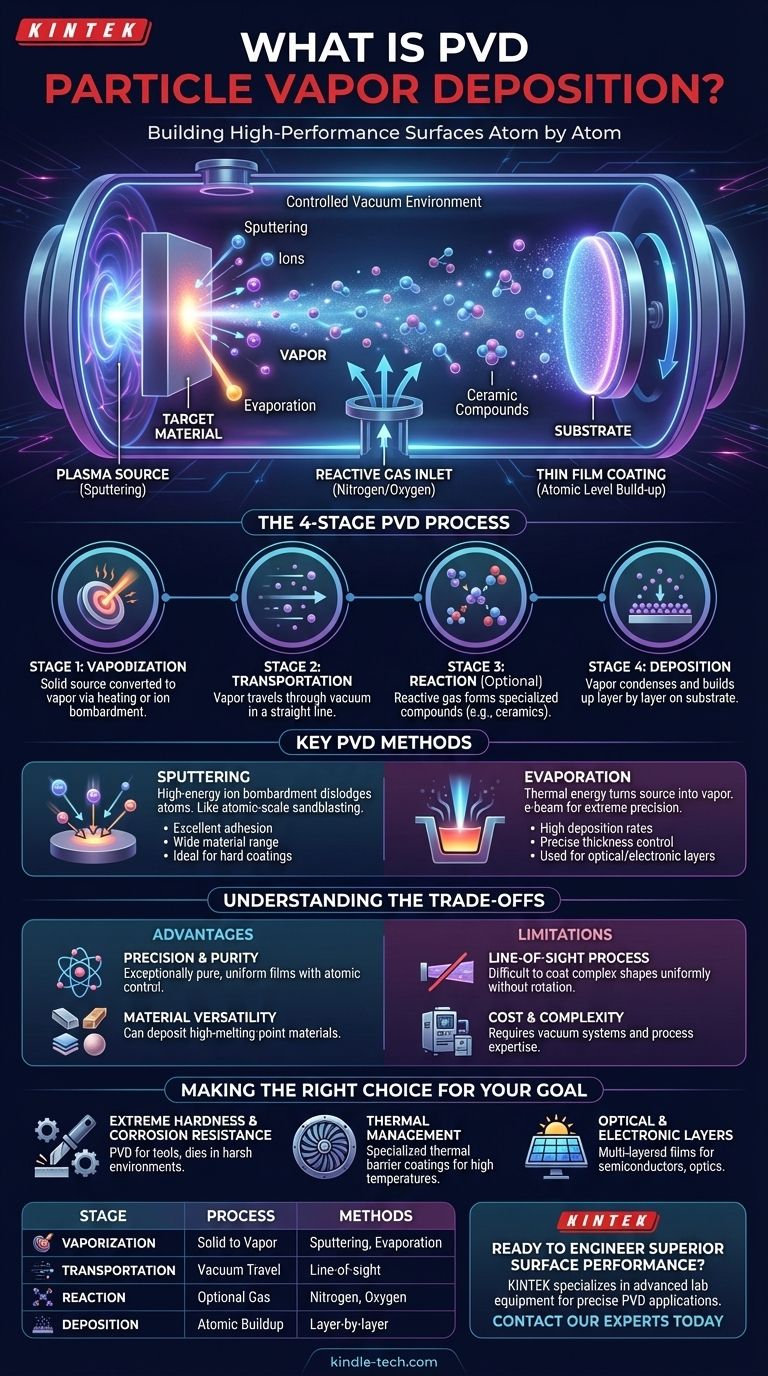
How PVD Builds a Coating Atom by Atom
The PVD process is best understood as a sequence of distinct physical stages that occur within a controlled vacuum environment. The vacuum is critical because it removes other atoms and molecules that could interfere with the process.
Stage 1: Vaporization
The process begins with a solid source material, often called the target. This target is converted into a vapor through high-energy means. The two most common methods are heating the material until it evaporates or bombarding it with high-energy ions, which physically knock atoms off its surface (a process known as sputtering).
Stage 2: Transportation
Once vaporized, the atoms or molecules from the target material travel through the vacuum chamber. Because there is virtually no air or other particles to collide with, they move in a straight line from the source to the object being coated.
Stage 3: Reaction
In some advanced PVD processes, a reactive gas like nitrogen or oxygen is introduced into the chamber. This gas reacts with the traveling metal vapor to form a ceramic compound, which is then deposited on the substrate. This allows for the creation of extremely hard or specialized coatings.
Stage 4: Deposition
When the vapor particles reach the substrate, they condense back into a solid state. They build up layer by layer, forming a thin, dense, and highly adherent film. This atomic-level build-up ensures the coating is uniform and tightly bonded to the surface.
Key PVD Methods Explained
While the principle remains the same, the method of vaporization defines the specific type of PVD process. The two dominant techniques offer different advantages.
Sputtering
In sputtering, the target material is bombarded with high-energy ions (usually of an inert gas like argon) generated by a plasma. Think of it as an atomic-scale sandblasting, where the ions dislodge individual atoms from the target. These ejected atoms then travel to and deposit onto the substrate.
Evaporation
This method uses thermal energy to turn the source material into a vapor. The solid material is heated in the vacuum until it evaporates or boils. A common technique is e-beam evaporation, which uses a powerful electron beam to melt and vaporize the source material with extreme precision.
Understanding the Trade-offs
PVD technology is powerful, but its suitability depends on understanding its inherent strengths and limitations.
Advantage: Precision and Purity
Because it occurs in a vacuum and builds the coating atom by atom, PVD produces exceptionally pure and uniform thin films. The thickness of the coating can be controlled with extreme accuracy.
Advantage: Material Versatility
PVD can be used to deposit materials that are very difficult to work with otherwise, including metals and ceramics with extremely high melting points. This makes it ideal for high-performance applications.
Limitation: Line-of-Sight Process
The vaporized material generally travels in a straight line. This means that PVD is a "line-of-sight" technique, and it can be difficult to uniformly coat complex shapes with deep grooves or internal surfaces without sophisticated part rotation.
Limitation: Cost and Complexity
PVD requires expensive vacuum equipment and a high degree of process control. While the systems are well-established, they represent a significant investment in both capital and operational expertise compared to simpler coating methods like painting or electroplating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying PVD is a strategic decision to engineer a material's surface for a specific performance outcome.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and corrosion resistance: PVD is the standard for applying thin, dense ceramic coatings to cutting tools, dies, and other components used in harsh environments.
- If your primary focus is thermal management: The precision of e-beam PVD is used to create specialized thermal barrier coatings essential for high-performance aerospace and automotive parts that must withstand extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is creating precise optical or electronic layers: The atomic-level control of PVD makes it indispensable for manufacturing the multi-layered films found in semiconductors, solar panels, and optical lenses.
Ultimately, PVD provides a powerful method for fundamentally changing the surface properties of an object, enhancing its performance from the outside in.
Summary Table:
| PVD Stage | Key Process | Common Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Vaporization | Solid source material is turned into vapor | Sputtering, Evaporation (e-beam) |
| Transportation | Vapor travels in a vacuum chamber | Line-of-sight travel in vacuum |
| Reaction (Optional) | Vapor reacts with gas to form compounds | Introduction of nitrogen, oxygen |
| Deposition | Vapor condenses on substrate, forming a thin film | Layer-by-layer atomic buildup |
Ready to Engineer Superior Surface Performance?
PVD technology can transform your components with ultra-hard, corrosion-resistant, or specialized optical coatings. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise PVD applications, helping laboratories achieve groundbreaking results in materials science, electronics, and aerospace.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PVD solutions can meet your specific coating challenges and enhance your project's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells



















