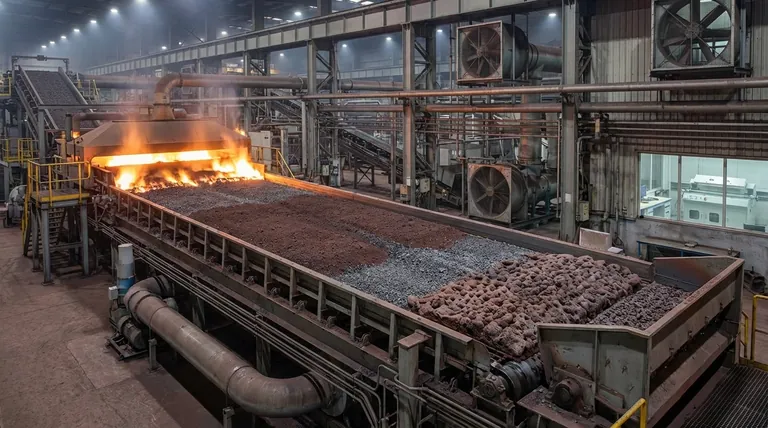
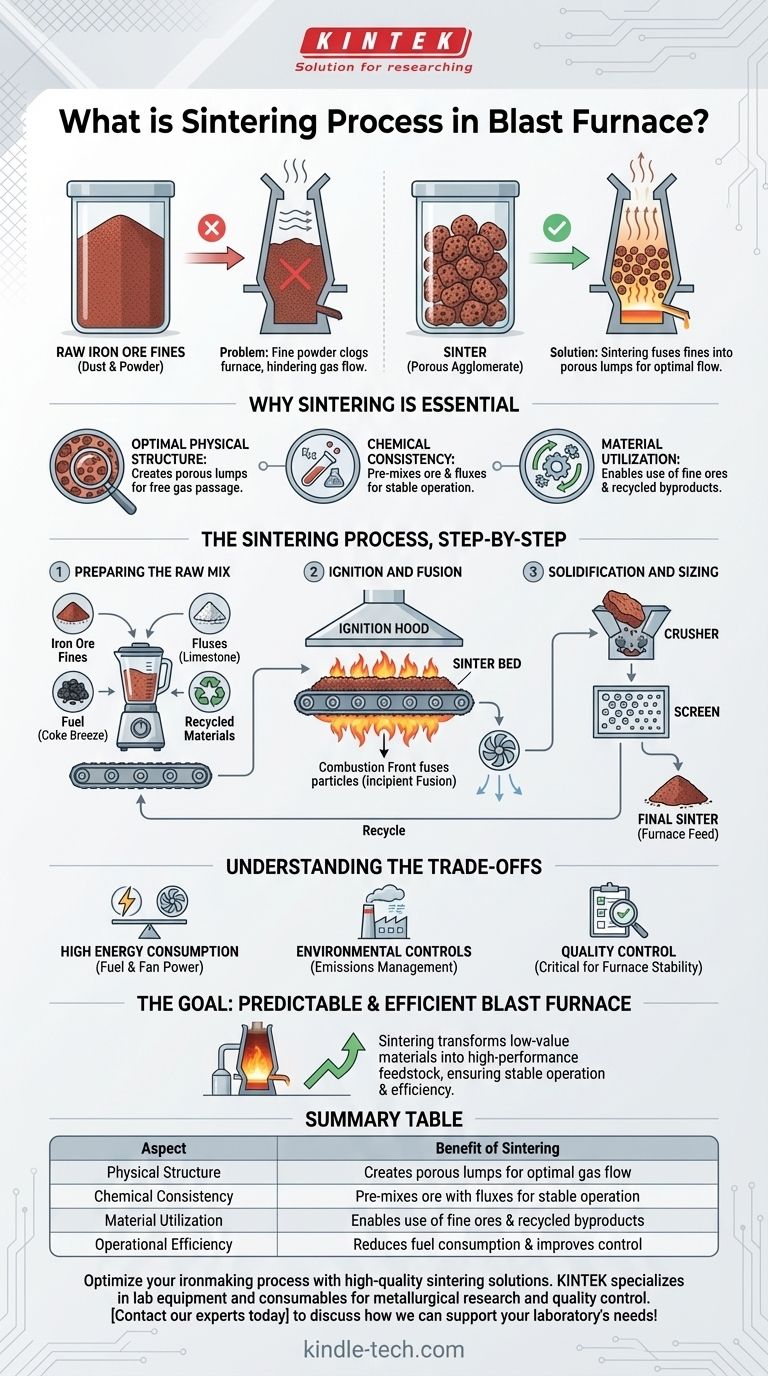
In the context of ironmaking, the sintering process is a crucial pre-treatment step that agglomerates fine iron ore particles with fluxes and other materials into a single, porous mass called "sinter." This high-temperature fusion process transforms dusty, inconsistent raw materials into an ideal, uniform feedstock that is physically and chemically optimized for the blast furnace.
The core problem is that fine, raw iron ore powder would clog a blast furnace, severely hindering its operation. Sintering solves this by converting that unusable powder into a strong, porous, and chemically consistent product, ensuring a predictable and highly efficient iron production process.

Why Sintering is Essential for Iron Production
To understand sintering, you must first understand the problem it solves. A blast furnace operates like a massive chemical reactor that requires hot gases to flow evenly up through a column of raw materials.
The Problem with Raw Iron Ore Fines
Fine materials, like iron ore dust or powder, are detrimental to this process. If fed directly into the furnace, they would block the spaces between larger chunks of material, much like sand filling the gaps in a bucket of gravel.
This blockage prevents the even distribution of reducing gases, leading to inefficient chemical reactions, unstable furnace conditions, and a significant loss of operational control.
Creating an Optimal Physical Structure
Sintering fuses these fine particles into larger, open-grained lumps. This porous structure is the key benefit.
The porosity allows hot gases to pass through the furnace burden freely and uniformly, maximizing contact with the iron ore and ensuring the efficient reduction of iron oxides into liquid iron.
Achieving Chemical Consistency
The sintering process is also an opportunity to pre-mix the iron ore with other essential ingredients.
By blending in fluxes (like limestone) and recycled materials from the steel plant, the resulting sinter has a highly consistent and predictable chemical composition. This standardization makes the blast furnace operation far more stable.
The Sintering Process, Step-by-Step
The conversion of raw materials into sinter occurs in a dedicated facility called a sinter plant, typically located adjacent to the blast furnace.
Preparing the Raw Mix
The process begins by creating a homogenous mixture of several key ingredients:
- Iron Ore Fines: The primary iron-bearing material.
- Fluxes: Materials like limestone or dolomite that will later help form slag in the blast furnace.
- Fuel: A fine carbon source, typically coke breeze, which provides the heat for the process.
- Recycled Materials: Dust and other iron-rich byproducts from the steel plant.
Ignition and Fusion
This prepared mix is spread onto a moving grate, forming a bed. The top surface of the bed passes under an ignition hood, which combusts the fuel in the uppermost layer.
As the grate moves along, powerful fans pull air down through the bed. This creates a narrow, high-temperature combustion front that slowly travels downward. In this hot zone, the particle surfaces soften and fuse together, a process known as incipient fusion.
Solidification and Sizing
Once the combustion front has passed through the entire depth of the bed, the fused material cools and solidifies into a large, brittle cake.
This cake is then discharged, crushed into smaller pieces, and screened to specific size requirements. The correctly sized product is the final sinter, which is then sent to the blast furnace. Undersized particles are recycled back into the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential, the sintering process is not without its challenges. It represents a complex balance of operational benefits and inherent costs.
High Energy Consumption
Sintering is an energy-intensive operation. The combustion of coke breeze and the power required for the large fans represent a significant portion of the energy costs in an integrated steel plant.
Environmental Controls are Non-Negotiable
The process generates significant emissions, including dust, sulfur oxides (SOx), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). Modern sinter plants require extensive and sophisticated gas cleaning systems to capture these pollutants and comply with environmental regulations.
Quality Control is Paramount
The performance of the blast furnace is directly tied to the quality of the sinter it receives. Inconsistent chemical composition, poor physical strength, or incorrect sizing can quickly undo all the benefits of the process, leading to operational instability and reduced efficiency.
The Goal: A Predictable and Efficient Blast Furnace
Sintering is best understood not as an isolated process, but as the critical first step in creating a stable and high-performing blast furnace operation.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: View sintering as the essential pre-processing step that guarantees a standardized furnace feed, leading to a more stable operation and lower fuel consumption.
- If your primary focus is raw material flexibility: Sintering is the key to effectively using fine iron ores and recycling in-plant waste, which would otherwise be unusable.
- If your primary focus is product quality: The chemical consistency engineered during the sintering process directly contributes to the final quality and composition of the hot metal produced by the blast furnace.
Ultimately, sintering transforms low-value raw materials into a high-performance product engineered specifically for the demanding environment of the blast furnace.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Benefit of Sintering |
|---|---|
| Physical Structure | Creates porous lumps for optimal gas flow in the blast furnace |
| Chemical Consistency | Pre-mixes ore with fluxes for stable, predictable furnace operation |
| Material Utilization | Enables use of fine ores and recycled plant byproducts |
| Operational Efficiency | Reduces fuel consumption and improves furnace control |
Optimize your ironmaking process with high-quality sintering solutions. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for metallurgical research and quality control. Whether you're developing sinter recipes or analyzing raw materials, our reliable tools help you achieve precise, efficient results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data



















