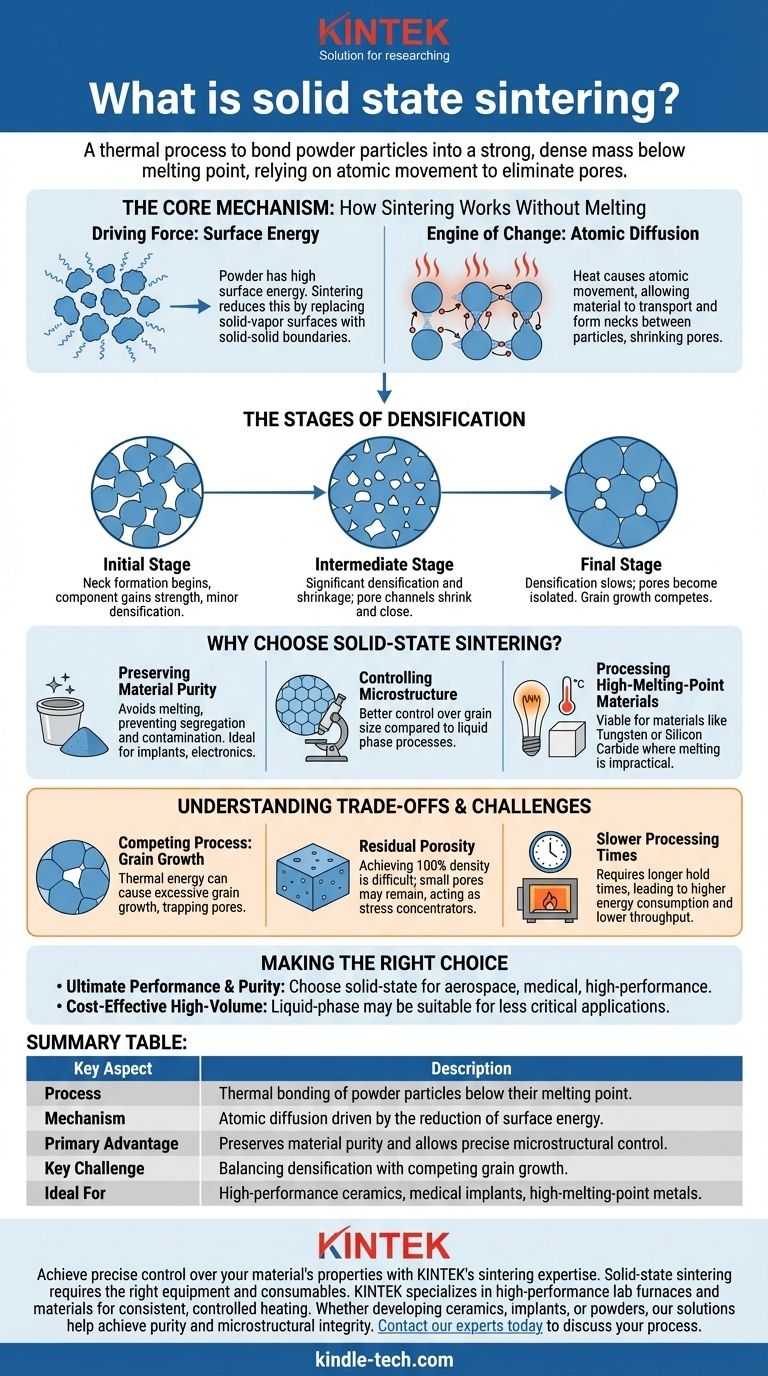
In essence, solid-state sintering is a thermal process used to bond a collection of powder particles into a strong, dense, solid mass. This is accomplished by applying heat at temperatures below the material's melting point, relying on atomic movement to eliminate the pores between particles and fuse them together. This method is fundamental to producing high-performance ceramics, like alumina, and consolidating metal powders where maintaining chemical purity is critical.
The core principle of solid-state sintering is achieving densification without liquefaction. By avoiding a liquid phase, this process offers unparalleled control over the final material's purity, chemical composition, and microscopic structure, making it essential for advanced engineering applications.

The Core Mechanism: How Sintering Works Without Melting
To grasp solid-state sintering, you must understand the two fundamental forces at play: the desire to reduce surface energy and the atomic motion that makes it possible.
The Driving Force: Surface Energy
A fine powder has an enormous amount of surface area relative to its volume. From a thermodynamic perspective, this high surface area represents a high-energy state. The material is inherently unstable and "wants" to reduce this energy.
Sintering provides a pathway for the system to reach a lower, more stable energy state by eliminating the solid-vapor interfaces (the surfaces of the powder particles) and replacing them with solid-solid interfaces (grain boundaries).
The Engine of Change: Atomic Diffusion
Heat provides the energy for atoms to move. At temperatures well below melting, atoms within the crystal lattice are not static; they can jump from one position to another. This movement is called atomic diffusion.
During sintering, this diffusion allows material to be transported to the points of contact between particles, forming "necks" that grow over time. As these necks expand, the centers of the particles move closer together, the pores between them shrink, and the entire component becomes denser.
The Stages of Densification
The process generally unfolds in three overlapping stages:
- Initial Stage: Particles that are touching begin to form necks. The component gains significant strength, but the overall densification (shrinkage) is minor.
- Intermediate Stage: The necks grow substantially, and the pores form a continuous, interconnected network. This is where the majority of densification and shrinkage occurs as the pore channels shrink and close off.
- Final Stage: The pores become isolated and spherical. Densification slows dramatically, and the primary competing mechanism, grain growth, begins to dominate.
Why Choose Solid-State Sintering?
Engineers select this method when the properties of the final component are non-negotiable and depend entirely on the integrity of the starting material.
Preserving Material Purity
This is the primary advantage. By never melting the material, you avoid issues like segregation, where different elements in an alloy might separate. It also prevents contamination that can occur when a liquid phase reacts with the furnace atmosphere or crucible. This is crucial for medical implants, electronic substrates, and optical components.
Controlling Microstructure
The mechanical properties of a material, such as hardness and strength, are highly dependent on its microstructure, particularly the size of its crystalline grains. Solid-state sintering provides better control over final grain size compared to processes involving a liquid phase, which can lead to rapid and undesirable grain growth.
Processing High-Melting-Point Materials
For materials like tungsten (melting point 3422°C) or advanced ceramics like silicon carbide, reaching their melting point for casting is often impractical or technologically prohibitive. Solid-state sintering allows these materials to be consolidated into dense parts at more achievable temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Despite its advantages, solid-state sintering is not without its difficulties. The process is a delicate balance between competing phenomena.
The Competing Process: Grain Growth
The same thermal energy that drives the diffusion needed for densification also drives grain growth. If grains grow too large too quickly, they can trap pores inside them, making it impossible to achieve full density. The ultimate goal is to maximize densification while minimizing grain growth.
The Problem of Residual Porosity
Achieving 100% theoretical density via solid-state sintering is extremely difficult. Small amounts of residual porosity are often unavoidable. These pores can act as stress concentrators and crack initiation sites, potentially compromising the mechanical reliability of the final part.
Slower Processing Times
Because it relies on the relatively slow mechanism of atomic diffusion through a solid, this process requires longer hold times at high temperatures compared to liquid-phase sintering. This translates to higher energy consumption and lower production throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right sintering process depends entirely on the end goal for your material.
- If your primary focus is ultimate performance and purity: Solid-state sintering is the superior choice for applications like aerospace components, medical-grade ceramics, and high-performance cutting tools where material integrity cannot be compromised.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: Liquid-phase sintering may be a better alternative for applications where minor variations in composition and a larger grain structure are acceptable.
- If you are working with extremely high-melting-point materials: Solid-state sintering is often the only technologically viable consolidation method available.
Ultimately, mastering solid-state sintering is about precisely controlling heat and time to win the race between densification and grain growth.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Thermal bonding of powder particles below their melting point. |
| Mechanism | Atomic diffusion driven by the reduction of surface energy. |
| Primary Advantage | Preserves material purity and allows precise microstructural control. |
| Key Challenge | Balancing densification with competing grain growth. |
| Ideal For | High-performance ceramics, medical implants, and high-melting-point metals. |
Achieve precise control over your material's properties with KINTEK's sintering expertise.
Solid-state sintering is a delicate process where the right equipment and consumables are critical for success. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and materials that provide the consistent, controlled heating essential for maximizing densification and minimizing grain growth.
Whether you are developing advanced ceramics, medical implants, or consolidating metal powders, our solutions are designed to help you achieve the purity and microstructural integrity your application demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your sintering process and help you create stronger, more reliable materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials
- What are the factors influencing shrinkage during sintering? Control Dimensional Changes for Precision Parts
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?



















