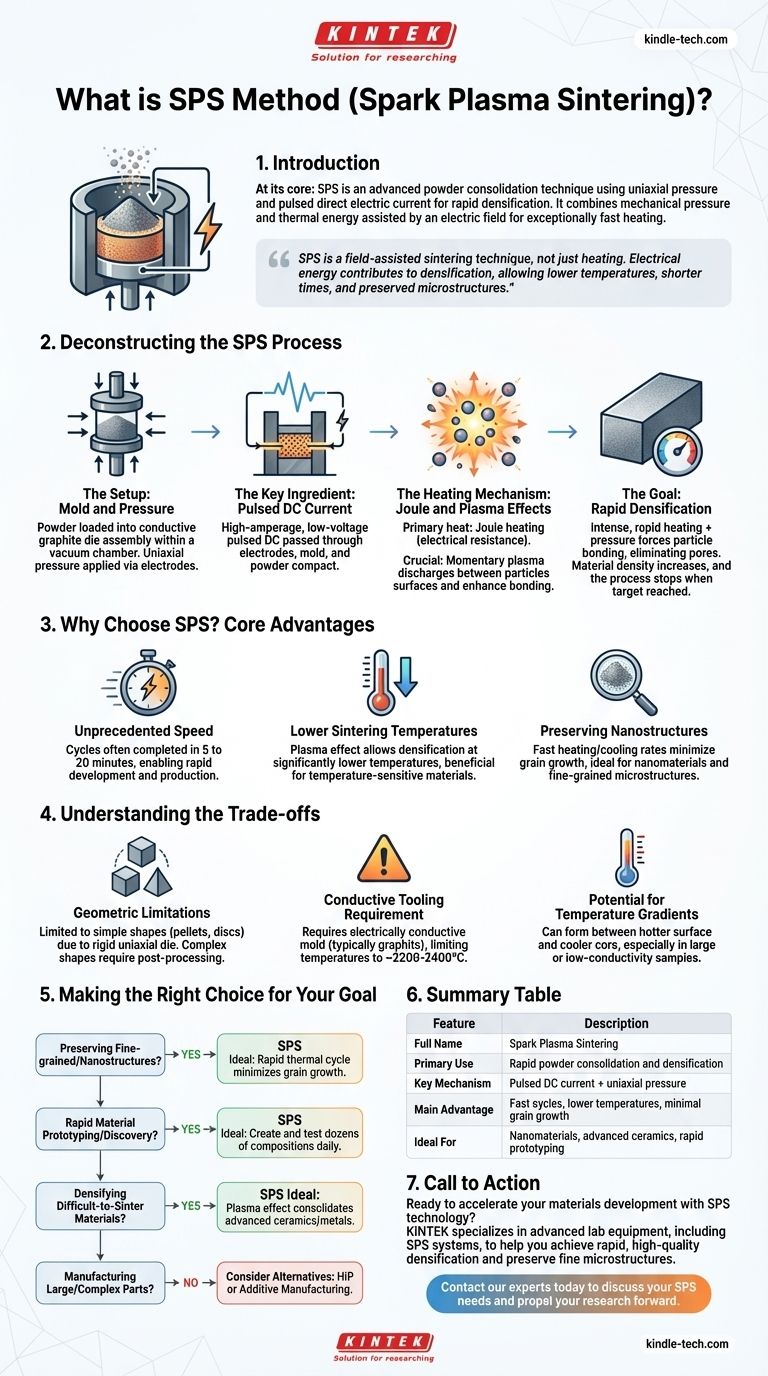
At its core, Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is an advanced powder consolidation technique that uses a combination of uniaxial pressure and a pulsed direct electric current to densify materials. The powder is loaded into a conductive graphite mold which is simultaneously heated by the current and used to apply pressure. This unique combination allows for exceptionally fast heating rates and sintering cycles, often reducing a process that takes hours in a conventional furnace to just a few minutes.
SPS is not merely a heating method; it is a field-assisted sintering technique where electrical energy directly contributes to densification. This allows for the consolidation of materials at lower temperatures and in significantly shorter times than traditional methods, preserving fine microstructures.
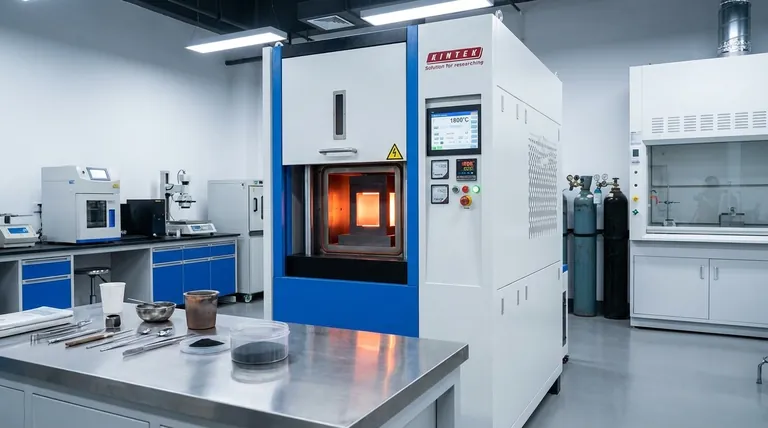

Deconstructing the SPS Process
To understand SPS, it's best to break it down into its key operational stages, from the initial setup to the final densified product.
The Setup: Mold and Pressure
The process begins by loading the powder material into a graphite die. This entire assembly is placed between two electrodes within a vacuum chamber.
A mechanical or hydraulic system applies uniaxial pressure (pressure along a single axis) to the powder through the electrodes and graphite punches.
The Key Ingredient: Pulsed DC Current
Once the chamber is evacuated and pressure is applied, a high-amperage, low-voltage pulsed Direct Current (DC) is passed through the electrodes, the graphite mold, and often, the sample itself.
This direct application of current is the defining feature of SPS and the source of its efficiency.
The Heating Mechanism: Joule and Plasma Effects
The primary heating source is Joule heating—the heat generated as the electric current passes through the resistive graphite mold and powder compact.
Crucially, at the microscopic level between powder particles, the pulsed current can generate momentary sparks or plasma discharges. This plasma helps to clean the surfaces of the powder particles, removing oxides and contaminants, which dramatically enhances the bonding between them.
The Goal: Rapid Densification
The combination of intense, rapid heating and applied pressure forces the powder particles to bond together, eliminating the pores between them.
The material shrinks in real-time as its density increases. The process is typically stopped once the target temperature is reached and the rate of densification slows, indicating the material has reached near-full density.
Why Choose SPS? The Core Advantages
SPS is not just a faster version of conventional heating; its unique mechanism offers distinct benefits for materials science and engineering.
Unprecedented Speed
SPS cycles are remarkably short, often completed in 5 to 20 minutes. This allows for rapid material development, screening, and production compared to the hours or even days required for conventional furnace sintering.
Lower Sintering Temperatures
The surface activation effect from the plasma allows for densification to occur at significantly lower temperatures than in methods that rely purely on thermal energy. This is a major advantage for temperature-sensitive materials.
Preserving Nanostructures
The extremely fast heating and cooling rates, combined with short processing times, effectively prevent grain growth. This makes SPS the premier technique for producing fully dense materials while preserving nanoscale or fine-grained microstructures, which are critical for achieving superior mechanical or functional properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, SPS is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Geometric Limitations
The reliance on a rigid, uniaxial die means that SPS is primarily suited for producing simple shapes like pellets, discs, or rectangular bars. Complex, three-dimensional shapes are not feasible without significant post-processing.
Conductive Tooling Requirement
The process fundamentally requires an electrically conductive mold, which is almost always graphite. This limits the maximum achievable temperature to around 2200-2400°C, as graphite begins to degrade at higher temperatures.
Potential for Temperature Gradients
Since heating is generated by current flowing through the die, a temperature gradient can form between the hotter surface and the cooler core of the sample. This effect is more pronounced in larger samples or materials with low thermal conductivity and requires careful process optimization to manage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
SPS is a specialized tool. Use this guide to determine if it aligns with your objective.
- If your primary focus is preserving fine-grained or nanostructures: SPS is the ideal choice due to its rapid thermal cycle that minimizes grain growth.
- If your primary focus is rapid material prototyping or discovery: The speed of the SPS process enables you to quickly create and test dozens of material compositions in a single day.
- If your primary focus is densifying difficult-to-sinter materials: The plasma effect in SPS can consolidate advanced ceramics or refractory metals that resist conventional sintering methods.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing large or complex-shaped parts: SPS is not the best method; consider alternatives like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) or additive manufacturing.
When applied correctly, Spark Plasma Sintering is one of the most powerful and efficient tools available for creating next-generation bulk materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Spark Plasma Sintering |
| Primary Use | Rapid powder consolidation and densification |
| Key Mechanism | Pulsed DC current + uniaxial pressure |
| Main Advantage | Fast cycles, lower temperatures, minimal grain growth |
| Ideal For | Nanomaterials, advanced ceramics, rapid prototyping |
Ready to accelerate your materials development with SPS technology?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including SPS systems, to help you achieve rapid, high-quality densification of your powder materials. Our expertise ensures you can preserve fine microstructures and develop next-generation materials efficiently.
Contact our experts today to discuss how an SPS system can meet your specific laboratory needs and propel your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of spark plasma sintering? Fast, Low-Temp Fabrication of Advanced Materials
- What is the plasma sintering method? Unlock Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What is the difference between spark plasma sintering and conventional sintering? A Guide to Faster, Better Materials
- What are the applications of spark plasma sintering? Fabricate High-Performance Materials with Precision
- What is the difference between spark plasma sintering and flash sintering? A Guide to Advanced Sintering Methods



















