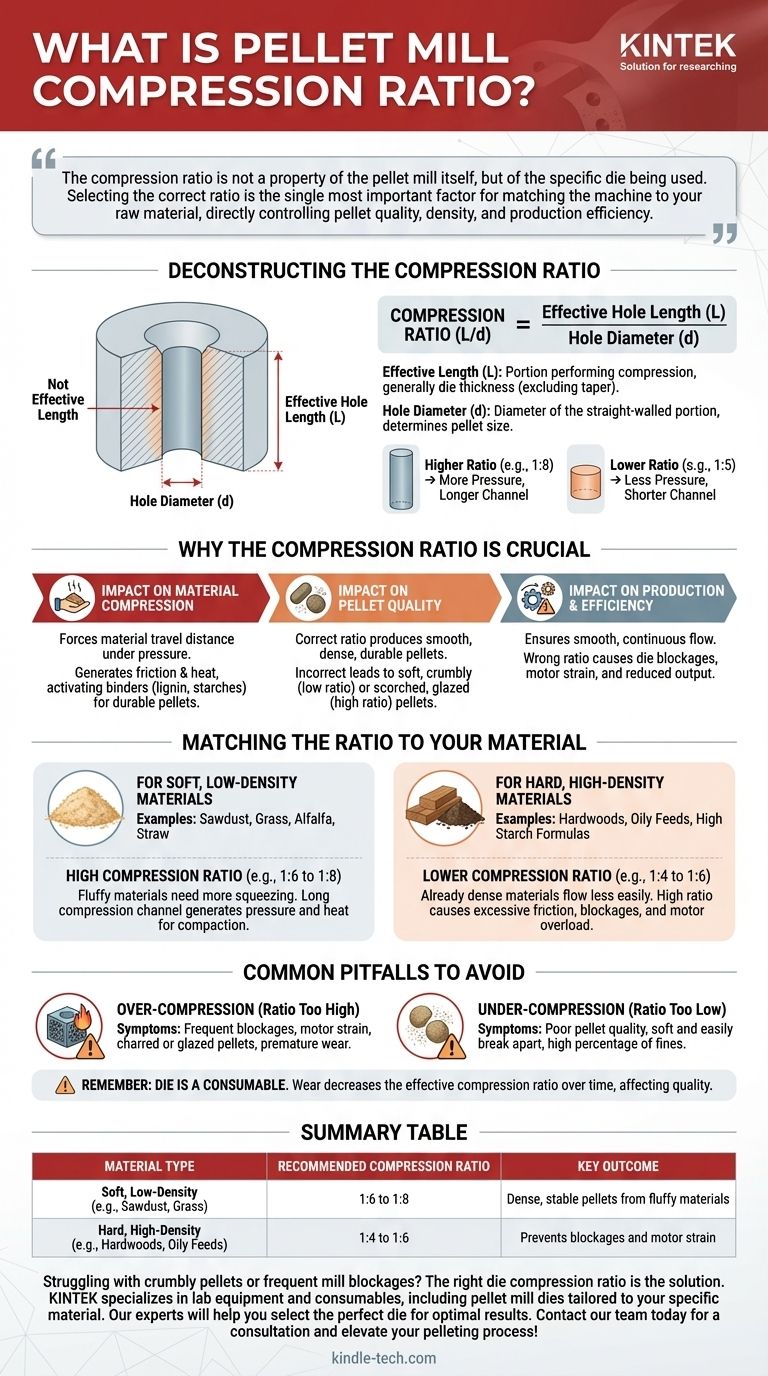
The compression ratio of a pellet mill die is a critical calculation that defines the relationship between the effective length of the die hole and its diameter. This ratio is not a single number for the mill itself, but a specific property of the interchangeable die plate. It determines the amount of pressure, friction, and time a raw material is subjected to during compression, which directly controls the quality and density of the final pellets.
The compression ratio is not a property of the pellet mill itself, but of the specific die being used. Selecting the correct ratio is the single most important factor for matching the machine to your raw material, directly controlling pellet quality, density, and production efficiency.
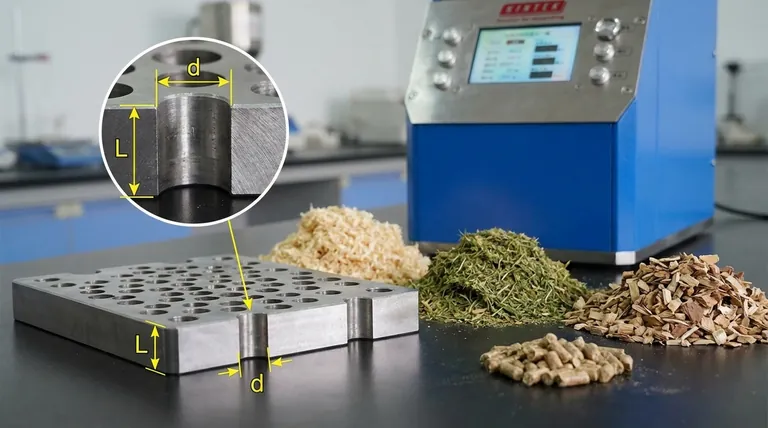

Deconstructing the Compression Ratio
To effectively use a pellet mill, you must first understand the two components that make up its most important specification.
The Core Formula
The compression ratio is calculated with a simple formula: Compression Ratio (L/d) = Effective Hole Length (L) / Hole Diameter (d).
A higher ratio (e.g., 1:8) means the compression channel is long relative to its width, creating more pressure. A lower ratio (e.g., 1:5) indicates a shorter channel, resulting in less pressure.
What is 'Effective Length' (L)?
The effective length is the portion of the die hole that performs the actual compression. It is generally the thickness of the flat die.
Some dies have a countersink or taper at the entrance of the hole to help guide material in. The effective length does not include this tapered portion.
What is 'Hole Diameter' (d)?
This is the straightforward diameter of the straight-walled portion of the die hole.
This measurement directly corresponds to the final diameter of the pellet you intend to produce. As noted, a single mill can use multiple dies to create pellets of various sizes.
Why the Compression Ratio is Crucial
The entire success of the pelleting operation hinges on selecting a die with the correct compression ratio for the specific material being processed.
Impact on Material Compression
A high compression ratio forces the material to travel a longer distance under immense pressure. This generates significant friction and heat.
This heat is essential for activating natural binders like lignin in wood or gelatinizing starches in animal feed, which helps form a durable, dense pellet.
Impact on Pellet Quality
The correct ratio produces smooth, dense, and durable pellets.
An incorrect ratio results in poor quality. If the ratio is too low, pellets will be soft, crumbly, and dusty. If it's too high, the pellets may be scorched or "glazed" from excessive heat and friction.
Impact on Production and Efficiency
Matching the ratio to the material ensures a smooth, continuous flow.
Using the wrong ratio leads to operational problems. A ratio that is too high for a material will cause blockages in the die, place extreme strain on the motor, and drastically reduce output.
Matching the Ratio to Your Material
Different types of raw material require vastly different compression ratios for successful pelleting. The core principle is simple: fluffy materials need more squeezing, while dense materials need less.
For Soft, Low-Density Materials
Materials like sawdust, grass, alfalfa, and straw are fluffy and resist compression. They require a high compression ratio (e.g., 1:6 to 1:8).
The long compression channel is necessary to generate enough pressure and heat to compact the material into a dense, stable pellet.
For Hard, High-Density Materials
Materials like hardwoods or formulas with high oil or starch content are already dense and flow less easily. They require a lower compression ratio (e.g., 1:4 to 1:6).
Using a high ratio on these materials would create excessive friction, leading to blockages, motor overload, and potential damage to the die and rollers.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes in selecting a die are common and lead to frustration and poor results. Understanding these pitfalls is key to troubleshooting your process.
Over-Compression: A Frequent Mistake
This occurs when the compression ratio is too high for the material.
Symptoms include frequent die blockages, the motor straining or shutting down, and pellets emerging charred or with a shiny, glazed surface. This also causes premature wear on the die and rollers.
Under-Compression: The Cause of Poor Quality
This occurs when the compression ratio is too low for the material.
The primary symptom is poor pellet quality. Pellets will be soft, easily break apart, and the final output will contain a high percentage of un-pelleted dust or "fines."
Forgetting the Die is a Consumable
The die is a wearing part. Over time, the inside of the holes will wear, slightly increasing their diameter.
This gradual wear slowly decreases the effective compression ratio, which can lead to a decline in pellet quality over the life of the die.
Selecting the Right Die for Your Application
Your choice of die should always be driven by the specific characteristics of your raw material. Testing small batches with different dies is often necessary to find the optimal ratio.
- If your primary focus is processing softwoods, grasses, or agricultural straw: You will require a die with a high compression ratio (e.g., 1:6 to 1:8) to achieve proper density.
- If your primary focus is processing dense hardwoods or difficult materials: You should select a die with a lower compression ratio (e.g., 1:4 to 1:6) to prevent blockages and reduce machine strain.
- If you are experiencing high levels of dust or crumbly pellets: Your current compression ratio is likely too low for your material and is not generating enough pressure.
- If your mill is frequently blocking or the motor is overloading: Your compression ratio is almost certainly too high, creating excessive friction and resistance.
Understanding and mastering the compression ratio transforms pelletizing from a process of trial-and-error into a predictable and efficient operation.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Recommended Compression Ratio | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Soft, Low-Density (e.g., Sawdust, Grass) | 1:6 to 1:8 | Dense, stable pellets from fluffy materials |
| Hard, High-Density (e.g., Hardwoods, Oily Feeds) | 1:4 to 1:6 | Prevents blockages and motor strain |
Struggling with crumbly pellets or frequent mill blockages? The right die compression ratio is the solution. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including pellet mill dies tailored to your specific material—from biomass and feed to pharmaceuticals. Our experts will help you select the perfect die to achieve optimal pellet density, durability, and production efficiency. Contact our team today for a consultation and elevate your pelleting process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- kbr pellet press 2t
- XRF & KBR plastic ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a hydraulic press with precise pressure control for LPSCl0.3F0.7 electrolyte molding?
- What is the use of KBr in FTIR? A Key Technique for Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What is a hydraulic forging press used for? Harnessing Controlled Power for Complex Metal Forming
- What are the potential hazards in a hydraulic press? Understanding the Risks of Crushing, Injection, and Failure
- What are 3 important maintenance procedures for hydraulic systems? Prevent Costly Failures & Downtime
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press ensure product quality in NFPC preparation? Achieve Superior Composite Strength
- What is the difference between injection molding and pressure molding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process
- What does the efficiency of the hydraulic system depend on? Minimize Volumetric & Mechanical Losses



















