In simple terms, a deposition process gas is a gas used in a controlled environment to create a solid thin film on a surface. These gases can serve two fundamentally different purposes: they can be the direct source of the material being deposited, or they can be an inert "working gas" used to physically transfer material from a solid source onto the surface. The specific gas and its role are entirely dependent on the deposition technique being used.
The critical takeaway is that "deposition process gas" is not one type of substance. Its function changes with the process: in Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the gas is a chemical reactant, while in Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), it is often an inert gas that acts as a physical tool.
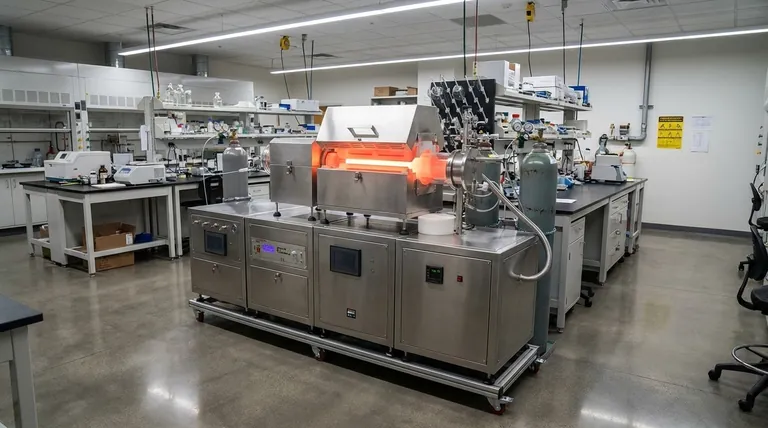

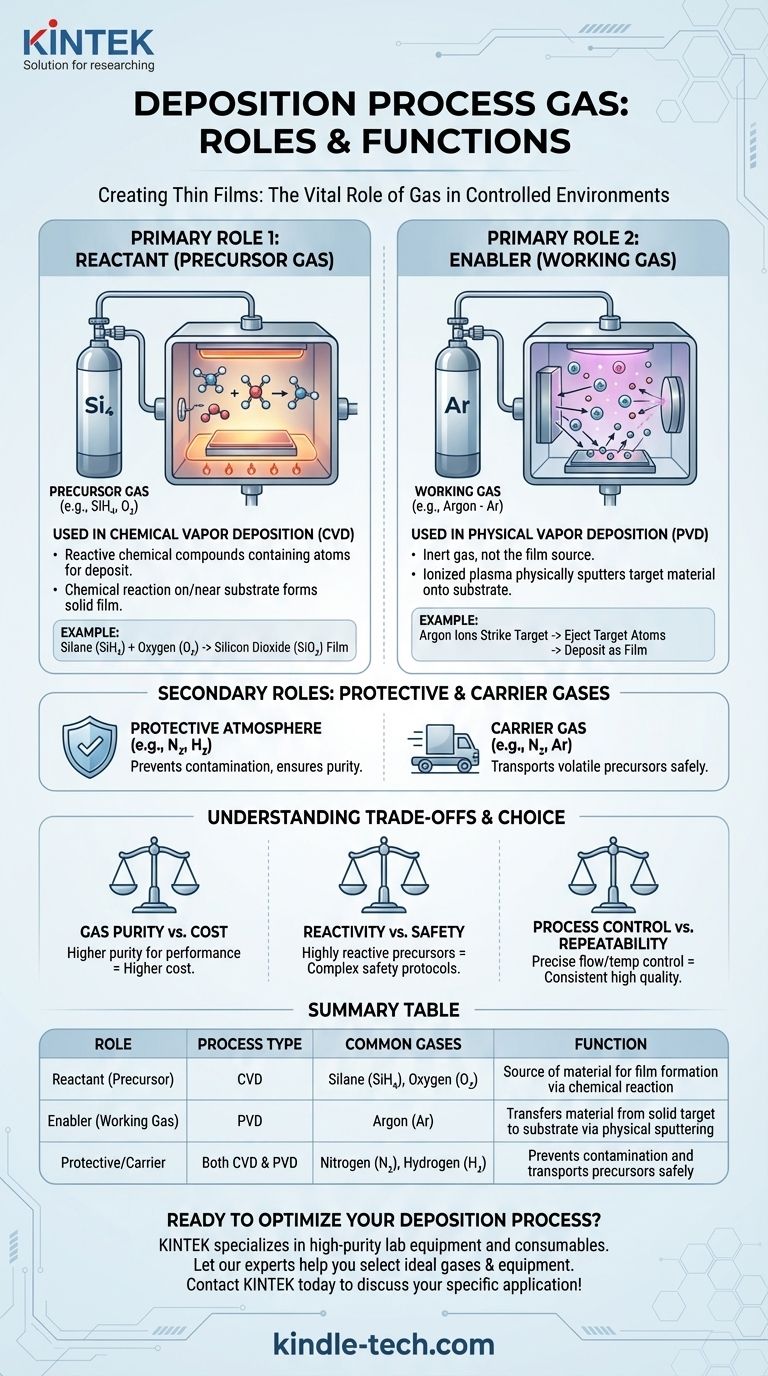
The Two Primary Roles of Process Gases
To truly understand deposition, you must distinguish between the two main functions a process gas can perform. The choice between them defines the entire category of the deposition process.
As a Reactant (Precursor Gas)
In Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the process gases are precursors. This means they are reactive chemical compounds that contain the atoms you want to deposit.
These precursor gases are introduced into a chamber where they react on or near a heated substrate. The chemical reaction breaks the gases down, and the desired solid material "deposits" onto the substrate, forming a film.
A classic example is the deposition of silicon dioxide (SiO₂). This process uses a silicon precursor gas, like silane (SiH₄), and an oxygen precursor gas, like oxygen (O₂) or nitrous oxide (N₂O). The gases react to form solid SiO₂ on the surface.
As an Enabler (Working Gas)
In Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), such as sputtering, the process gas is typically an inert working gas, with Argon (Ar) being the most common choice.
This gas is not the source of the film material. Instead, it is ionized to create a plasma. The positively charged argon ions are then accelerated by a strong electric field and directed at a solid "target" made of the material you wish to deposit.
When the argon ions strike the target, they physically knock atoms off its surface. These ejected atoms then travel through the chamber and deposit onto the substrate, forming the film. Here, the argon gas is a physical tool for transferring material, not a chemical ingredient.
Beyond the Primary Roles: Protective and Carrier Gases
In addition to being reactants or enablers, gases can serve other critical functions that ensure the quality and success of the deposition process.
Creating a Protective Atmosphere
Many deposition processes are highly sensitive to contamination from the ambient atmosphere, especially oxygen, which can cause unwanted oxidation.
To prevent this, a protective or "shielding" gas like **nitrogen (N₂) or hydrogen (H₂) **is often used. This inert or reducing gas creates a controlled atmosphere inside the chamber, ensuring the purity of the deposited film.
Acting as a Carrier
Sometimes, a precursor material is difficult to handle as a gas on its own. In these cases, a stable, inert carrier gas (often nitrogen or argon) is used to safely transport the more volatile or reactive precursor gas to the substrate surface. This allows for precise control over the delivery of the reactants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of process gas is a critical engineering decision with significant consequences for cost, safety, and film quality.
Gas Purity vs. Cost
For high-performance applications like semiconductor manufacturing, extremely high-purity gases are required to avoid incorporating impurities into the film. This "ultra-high purity" (UHP) gas is significantly more expensive and requires specialized handling infrastructure.
Reactivity vs. Safety
Many of the most effective precursor gases for CVD are highly reactive, toxic, or flammable. Silane (SiH₄), for example, is pyrophoric, meaning it can ignite spontaneously in air. This necessitates complex and expensive safety protocols, ventilation, and monitoring systems.
Process Control and Repeatability
Different gases have unique physical and chemical properties. Achieving a high-quality, repeatable film requires precise control over gas flow rates, pressure, and temperature. The choice of gas directly impacts the complexity of the control system needed to master the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection of a process gas is dictated by the material you need to deposit and the properties you want it to have.
- If your primary focus is depositing a compound material (like an oxide or nitride): You will use a mixture of reactive precursor gases in a Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process.
- If your primary focus is depositing a pure element or alloy from a solid target: You will use an inert working gas, like Argon, in a Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) process such as sputtering.
- If your primary focus is ensuring film purity and preventing contamination: You will need to incorporate high-purity protective or carrier gases, such as nitrogen, regardless of the primary deposition method.
Understanding the specific role of the gas—reactant, enabler, or protector—is the key to mastering any deposition process.
Summary Table:
| Role | Process Type | Common Gases | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reactant (Precursor) | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Silane (SiH₄), Oxygen (O₂) | Source of material for film formation via chemical reaction |
| Enabler (Working Gas) | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) | Argon (Ar) | Transfers material from a solid target to the substrate via physical sputtering |
| Protective/Carrier | Both CVD & PVD | Nitrogen (N₂), Hydrogen (H₂) | Prevents contamination and transports precursors safely |
Ready to Optimize Your Deposition Process?
Choosing the right process gas is critical for achieving high-quality, repeatable thin films. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-purity lab equipment and consumables tailored to your deposition needs—whether you're working with CVD precursors, PVD sputtering gases, or protective atmospheres.
Let our experts help you select the ideal gases and equipment to enhance your film quality, improve process control, and ensure safety. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and discover how our solutions can drive your research or production forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of carbon nanotube purification? Achieve High-Purity CNTs for Your Application
- What are the key characteristics of Atomic Layer Chemical Vapour Deposition (ALCVD)? Precise Thin-Film Solutions
- What is a potential complication of using catalysts in the CVD process for graphene? Mastering Carbon Solubility
- What is chemical vapor deposition at atmospheric pressure? A High-Speed, Low-Cost Thin Film Solution
- Which deposition technique allows deposition of ultra-thin layers with atomic layer precision? Achieve Perfect Conformity with ALD
- What is the effect of pressure and ion energy in the sputtering process? Optimize Film Density & Step Coverage
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer
- What is the role of substrate in CVD? The Blueprint for High-Quality Thin Films



















