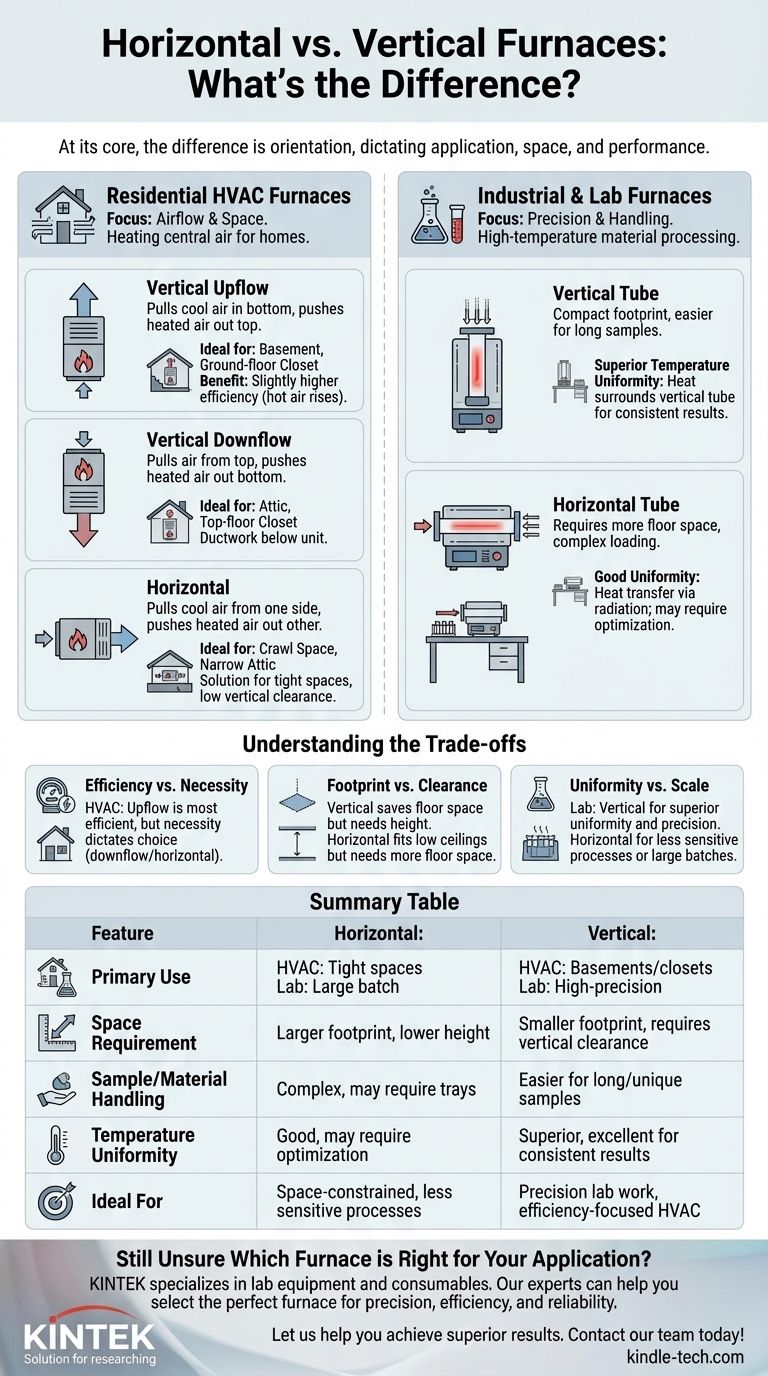
At its core, the difference is orientation. A vertical furnace stands upright, while a horizontal furnace lies on its side. This simple distinction dictates everything from its application and installation space to its performance characteristics and how it distributes heat. The term "furnace" can refer to a residential HVAC unit or a high-temperature industrial/lab furnace, and the implications of orientation are different for each.
The choice between a horizontal and vertical furnace is not about which is inherently better, but which is correct for the specific application. For home heating, the decision is dictated by installation space; for industrial processes, it's driven by precision and material handling.

The Two Worlds of Furnaces: Home vs. Industry
Before comparing orientations, it's critical to understand which type of furnace you are dealing with. The term is used in two very different contexts.
Residential HVAC Furnaces
These are the units that provide central heating for a home. Their primary job is to heat air and circulate it through ductwork. Here, the orientation—upflow, downflow, or horizontal—is all about airflow direction.
Industrial & Lab Furnaces
These are specialized, high-temperature ovens, often called tube furnaces, used for material processing, testing, and research. In this context, orientation affects sample loading, space requirements, and the precision of heat application.
For Residential HVAC: It's All About Airflow and Space
In a home heating system, the furnace's orientation is chosen to match the installation location. All three configurations are priced similarly, but the layout of your home dictates the correct choice.
Vertical Upflow Furnaces
An upflow furnace is the most common type. It pulls cool air in through the bottom and pushes heated air out the top, sending it into ductwork. This design is ideal for installation in a basement or a ground-floor closet.
Because hot air naturally rises, this configuration works with physics, not against it. This can lead to slightly higher energy efficiency compared to other orientations.
Vertical Downflow Furnaces
A downflow furnace operates in the reverse. It pulls air from the top and pushes heated air out the bottom. This is the required configuration for installations in an attic or a top-floor utility closet, where the ductwork is located below the unit.
Horizontal Furnaces
A horizontal furnace is installed on its side. It pulls cool air from one side and pushes heated air out the other. This design is the solution for tight spaces with low vertical clearance, such as a crawl space or a narrow attic.
For Lab & Industrial Use: It's About Precision & Handling
In a technical setting, the orientation of a tube furnace directly impacts the quality of the work and the ease of the process.
Vertical Tube Furnaces
These units have a compact footprint, making them ideal for labs with limited space. Samples are loaded vertically, which is far easier for long or uniquely shaped materials.
Most importantly, vertical furnaces provide superior temperature uniformity. The heating element surrounds the vertical tube, and heat transfers efficiently via convection and radiation, ensuring the entire length of the sample is heated consistently.
Horizontal Tube Furnaces
Horizontal furnaces require more floor space. Loading samples horizontally can be more complex, sometimes requiring specialized trays or positioning mechanisms, especially for multiple samples.
While highly effective, they can experience slight temperature variations along the length of the tube. Heat transfer occurs primarily through radiation, which may require careful optimization to ensure the entire sample receives uniform heat distribution.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an orientation is a matter of weighing priorities based on your specific goal.
Efficiency vs. Necessity
For home HVAC, an upflow furnace is generally the most energy-efficient. However, this small gain is irrelevant if your home’s layout requires a downflow or horizontal unit. The correct fit is always the primary concern.
Footprint vs. Clearance
This trade-off applies to both worlds. Vertical furnaces save valuable floor space but demand vertical height. Horizontal furnaces can fit in spaces with low ceilings but require a larger overall footprint.
Uniformity vs. Scale
For lab work, the decision is critical. The exceptional temperature uniformity of a vertical furnace is essential for reliable, repeatable results. A horizontal furnace may be suitable for less sensitive processes or when handling very large sample batches that are impractical to load vertically.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
- If your primary focus is heating your home: Your decision is determined entirely by the installation location—basement (upflow), attic (downflow/horizontal), or crawl space (horizontal).
- If your primary focus is high-precision lab work: A vertical tube furnace is the superior choice for its temperature uniformity and ease of loading.
- If your primary focus is fitting a unit in a space with low ceilings: A horizontal furnace is your only practical option, whether for HVAC or industrial use.
Ultimately, the correct furnace orientation is the one that best serves the unique demands of your space and your objective.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Horizontal Furnace | Vertical Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | HVAC: Tight spaces (attics, crawl spaces) Lab: Large batch processing |
HVAC: Basements/standard closets Lab: High-precision applications |
| Space Requirement | Larger footprint, lower height | Smaller footprint, requires vertical clearance |
| Sample/Material Handling | Can be complex; may require trays | Easier for long or uniquely shaped samples |
| Temperature Uniformity | Good; may require optimization | Superior; excellent for consistent results |
| Ideal For | Space-constrained installations, less sensitive processes | Precision lab work, efficiency-focused HVAC |
Still Unsure Which Furnace is Right for Your Application?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Whether you're setting up a new lab or optimizing an existing process, our experts can help you select the perfect furnace for your specific requirements—ensuring you get the precision, efficiency, and reliability your work demands.
Let us help you achieve superior results. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a tube furnace play in the synthesis of MCM? Master Carbonization for Magnetic Microspheres
- What are ceramic tubes used for? Essential Components for Extreme Heat & Electrical Insulation
- What is pyrolysis in biogas? A High-Temperature Process for Syngas, Bio-Oil, and Bio-Char
- What is the function of a high-vacuum tube furnace in graphene CVD? Optimize Synthesis for High-Quality Nanomaterials
- What are the three types of pyrolysis? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process for Your Output
- What is the role of a high-temperature tube furnace in the synthesis of Mo2C catalysts? Achieve Precise Carbonization
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the solid-state synthesis of niobate mixed crystals? Precision Phase Control
- What conditions does a tube carbonization furnace provide for stabilized fibers? Master the Carbonization Process



















