The fundamental difference between a muffle furnace and a blast furnace lies in their core function and method of heating. A muffle furnace uses indirect heat to treat materials in a controlled, contaminant-free environment, while a blast furnace uses direct, intense heat from combusting fuel to chemically reduce ore into molten metal. One is a tool for precision treatment; the other is an engine for raw production.
At its core, the choice between these furnaces is a choice between process goals. A muffle furnace is designed to protect a material while heating it, whereas a blast furnace is designed to transform a material by forcing it to react with fuel and flux.

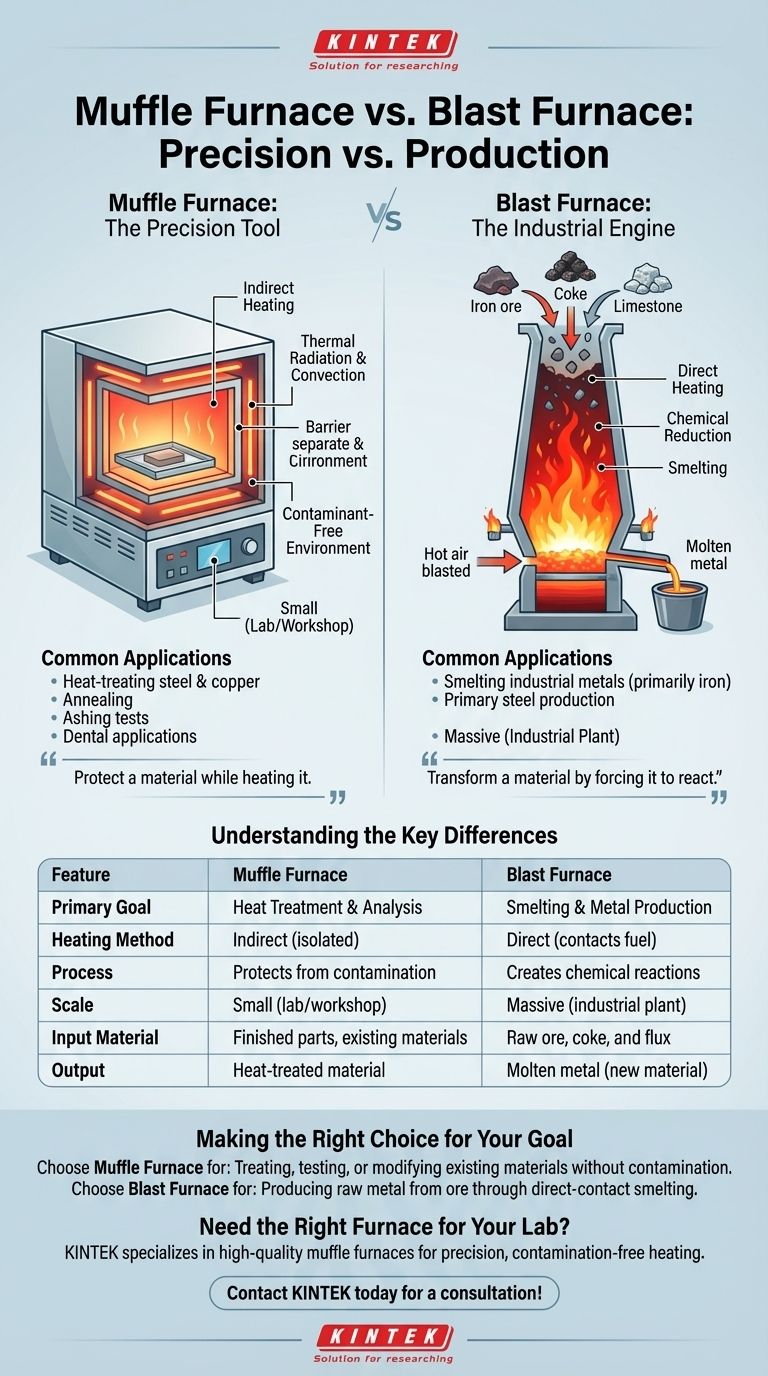
What is a Muffle Furnace? The Precision Tool
A muffle furnace is a chamber furnace designed for high-temperature applications where isolating the sample from combustion contaminants is critical. It is a common tool in laboratories and workshops.
The Principle of Indirect Heating
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is its "muffle"—an inner chamber that contains the material being heated. The heating elements or flames are outside this chamber.
Heat is transferred to the material through thermal radiation and convection, but the material never comes into direct contact with the fuel or its byproducts.
A Contaminant-Free Environment
This indirect heating method is crucial for processes that require purity. By isolating the workload, the furnace prevents contamination from gases and particulates generated during fuel combustion.
This makes it ideal for processes like air calcination, annealing, or ashing samples for analysis, where the chemical integrity of the material must be maintained.
Common Applications and Scale
Muffle furnaces are typically smaller, box-shaped units used for batch processing. Their larger heating zone makes placing and removing individual samples straightforward.
Common uses include heat-treating steel and copper components, hardening tools, performing ashing tests in a lab, and in dental applications for creating crowns.
What is a Blast Furnace? The Industrial Engine
A blast furnace is a massive, vertical shaft furnace used for smelting industrial metals, primarily iron. It is the foundational piece of equipment in primary steel production.
The Principle of Direct Heating and Smelting
Unlike a muffle furnace, a blast furnace operates by mixing the material directly with fuel and other reactants. Iron ore, coke (a high-carbon fuel), and limestone (a flux) are loaded together into the top of the furnace.
Hot air is then "blasted" into the bottom, causing the coke to combust at extreme temperatures. This direct contact is not only intentional but essential to the process.
Designed for Chemical Reduction
The goal of a blast furnace is not just to heat ore, but to trigger a chemical reaction. The burning coke produces carbon monoxide, which acts as a reducing agent, stripping oxygen atoms from the iron ore.
This process, known as smelting, transforms the solid ore into molten iron, often called "pig iron." The purpose is raw material creation, not sample purification.
Massive Scale and Singular Purpose
Blast furnaces are enormous industrial structures that often run continuously for years. Their singular purpose is the high-volume, bulk production of molten metal from raw ore, which is then transferred for further processing into steel.
Understanding the Key Differences
The choice between these two furnaces is never ambiguous because they solve completely different problems. Their designs reflect these opposing goals.
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Blast Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Heat Treatment & Analysis | Smelting & Metal Production |
| Heating Method | Indirect (material is isolated) | Direct (material contacts fuel) |
| Process | Protects material from contamination | Intentionally creates chemical reactions |
| Scale | Small (lab/workshop) | Massive (industrial plant) |
| Input Material | Finished parts, existing materials | Raw ore, coke, and flux |
| Output | A heat-treated version of the input | Molten metal (a new material) |
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on whether you are trying to modify an existing material or create a new one from ore.
- If your primary focus is producing raw metal from ore: You need a blast furnace for its direct-contact smelting process and chemical reduction capabilities.
- If your primary focus is treating, testing, or modifying an existing material without contamination: You need a muffle furnace for its isolated, controlled, and clean heating environment.
Ultimately, understanding the core purpose—protection versus transformation—is the key to distinguishing these essential industrial tools.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Blast Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Heat Treatment & Analysis | Smelting & Metal Production |
| Heating Method | Indirect (material isolated) | Direct (material contacts fuel) |
| Process | Protects from contamination | Creates chemical reactions |
| Scale | Small (lab/workshop) | Massive (industrial plant) |
| Output | Heat-treated material | Molten metal (new material) |
Need the Right Furnace for Your Lab?
Understanding the difference is the first step. Choosing the right equipment is the next. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality muffle furnaces and other lab equipment designed for precision, contamination-free heating—perfect for ashing, annealing, heat-treating, and more.
Let our experts help you select the perfect furnace to enhance your lab's efficiency and accuracy.
Contact KINTALK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a furnace used in the lab? Your Guide to High-Temperature Precision
- What affects melting range? Understand the Critical Role of Purity and Structure
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and hot air oven? Choose the Right Heating Tool for Your Lab
- What temperature causes melting? Debinding vs. Melting in Metal Fabrication
- What is the use of muffle furnace in chemistry laboratory? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Material Processing



















