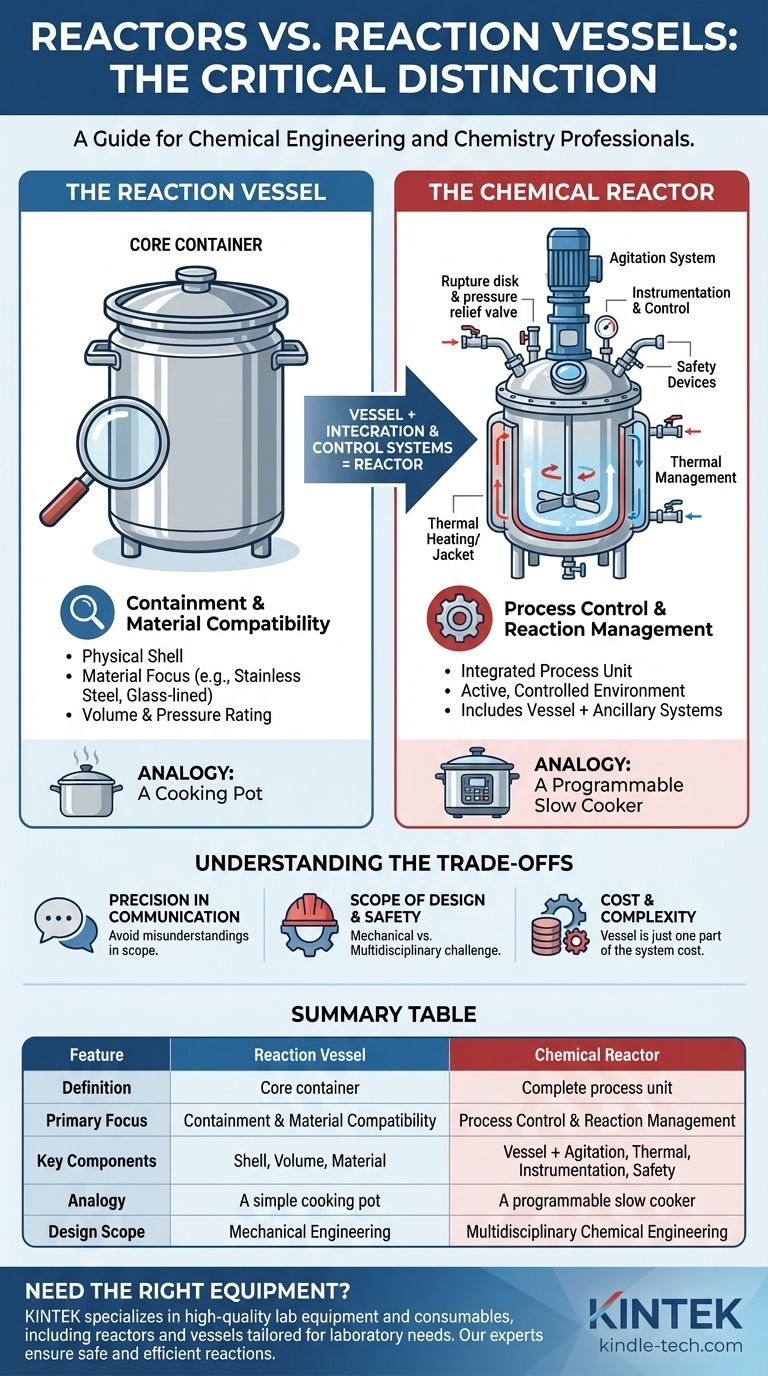
In chemical engineering and chemistry, the terms "reactor" and "reaction vessel" are often used interchangeably, but they have a distinct technical difference. A reaction vessel refers specifically to the container or shell where a chemical process takes place. A chemical reactor, on the other hand, is the complete, engineered system that includes the vessel plus all the ancillary equipment required to control the reaction.
The simplest way to understand the difference is that the reaction vessel is a core component, while the reactor is the entire functional system. Every reactor has a reaction vessel, but a simple container only becomes a reactor when integrated with control systems.

The Vessel vs. The System: A Deeper Look
To operate a chemical process safely and efficiently, you need far more than just a container. This is the fundamental distinction between a simple vessel and a fully engineered reactor.
The Reaction Vessel: The Core Container
A reaction vessel is the physical shell that contains the chemical reactants. Its primary design considerations are containment and material compatibility.
Key aspects of the vessel include its volume, the material it's made from (e.g., stainless steel, glass-lined steel, Hastelloy), and its ability to withstand the required pressure and temperature of the process.
The Reactor: The Integrated Process Unit
A reactor is the complete operational unit designed to execute and control a chemical transformation. It encompasses the vessel and integrates it with other critical subsystems.
These subsystems turn a passive container into an active, controlled environment and typically include:
- Agitation System: A motor, gearbox, shaft, and impeller (agitator) to ensure proper mixing.
- Thermal Management: A heating/cooling jacket or internal coils to add or remove heat and control the reaction temperature.
- Inlet/Outlet Nozzles: Ports for adding reactants, removing products, and connecting instrumentation.
- Instrumentation: Sensors for monitoring temperature, pressure, pH, and other critical process variables.
- Safety Devices: Equipment like rupture disks and pressure relief valves to prevent over-pressurization.
An Analogy: A Cooking Pot vs. a Slow Cooker
Thinking about the difference in kitchen terms can provide immediate clarity.
The Pot as the Vessel
A simple stainless steel pot is a vessel. You can put ingredients in it, but it does nothing on its own. Its job is just to hold the contents.
The Slow Cooker as the Reactor
A slow cooker is a reactor system. It includes the ceramic pot (the vessel), a heating element (thermal management), and a control dial (instrumentation). It is an integrated system designed for a specific process: cooking food slowly at a controlled temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why the Distinction Matters
Using the correct term is not just academic; it has significant implications for design, communication, and safety in a professional environment.
Precision in Communication
When you say "reactor," you are communicating that you are considering the entire controlled process, including kinetics, heat transfer, and mass transfer. When you say "vessel," the focus is narrowed to the physical container, its material, and its pressure rating. This precision prevents costly misunderstandings.
Scope of Design and Safety
Designing a "vessel" is primarily a mechanical engineering challenge focused on structural integrity. Designing a "reactor" is a multidisciplinary chemical engineering challenge that involves process control, reaction engineering, and comprehensive safety analysis (like HAZOP studies).
Cost and Complexity
The reaction vessel is only one part of the total cost of a reactor system. The agitator, instrumentation, and control systems often represent a significant portion of the overall investment and complexity. Referring to the entire unit as a "vessel" can grossly underrepresent its scope.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use the term that most accurately reflects the scope of your discussion. Clear language demonstrates technical expertise and ensures everyone is on the same page.
- If your primary focus is the physical container: Use reaction vessel when discussing material selection, volume, pressure ratings, or fabrication details.
- If your primary focus is the overall chemical process: Use reactor when discussing reaction kinetics, control strategies, heat management, or the complete operational unit.
- If you are discussing different process types: Use reactor to specify the configuration, such as a Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor (CSTR), a Plug Flow Reactor (PFR), or a Batch Reactor.
Mastering this distinction ensures precision in your technical communication, reflecting a deeper understanding of the engineering involved.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Reaction Vessel | Chemical Reactor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The core container holding reactants | The complete, integrated process unit |
| Primary Focus | Containment & Material Compatibility | Process Control & Reaction Management |
| Key Components | Shell, Volume, Material of Construction | Vessel + Agitation, Heating/Cooling, Instrumentation, Safety Devices |
| Analogy | A simple cooking pot | A programmable slow cooker |
| Design Scope | Mechanical Engineering (Structural Integrity) | Multidisciplinary Chemical Engineering |
Need the right equipment for your chemical process?
Understanding the distinction between a vessel and a reactor is the first step. The next is selecting the right integrated system for your specific application, whether it's a standard design or a custom solution.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reactors and vessels tailored for laboratory needs. We provide the engineered systems and expert support to ensure your reactions run safely and efficiently.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your requirements and let our experts help you build the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Cylindrical Press Mold with Scale for Lab
People Also Ask
- Does pressure affect melting and boiling? Master Phase Changes with Pressure Control
- What are the advantages of a chemical reactor? Unlock Precision, Efficiency, and Safety in Your Process
- What is the pressure in a batch reactor? A Guide to Dynamic Control and Safety
- What are autoclaves used in the chemical industry? High-Pressure Reactors for Synthesis & Curing
- What is a high pressure high temperature autoclave reactor? Unlock Extreme Chemical Synthesis



















