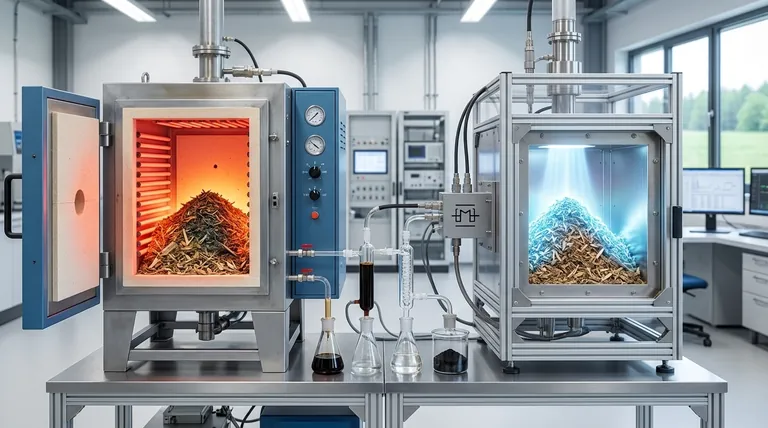
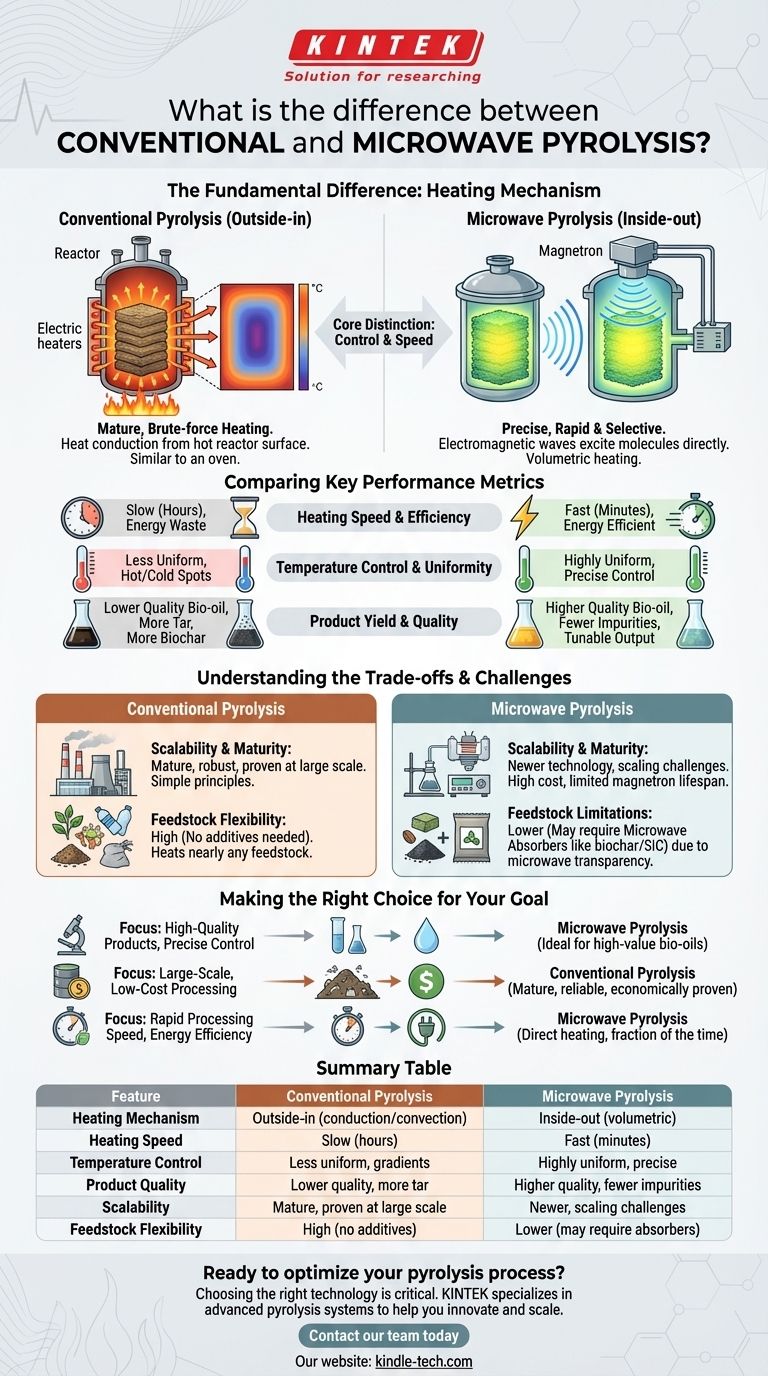
The fundamental difference lies in the heating mechanism. Conventional pyrolysis heats material from the outside-in via thermal conduction from a hot reactor surface, similar to an oven. In contrast, microwave pyrolysis heats material from the inside-out by using electromagnetic waves to directly excite molecules within the feedstock itself, a process known as volumetric heating.
The core distinction is not just about the heat source, but about control. Conventional pyrolysis is a mature, brute-force heating method, while microwave pyrolysis is a precise, rapid, and selective technology that offers greater control over the final products.

The Fundamental Difference: How Heat is Delivered
To understand the practical implications, you must first grasp how each method transfers energy to the target material (the feedstock). This core difference in heat transfer dictates everything from process speed to product quality.
Conventional Pyrolysis: The "Oven" Analogy
Conventional pyrolysis uses an external heat source, like electric heaters or fuel burners, to heat the walls of a reactor.
This heat is then transferred slowly to the feedstock through conduction and convection. The material on the outer edges heats up first, and that heat gradually penetrates toward the core.
This process inevitably creates temperature gradients, where the outside of the material is much hotter than the inside. This is a major limitation, often leading to inefficient reactions.
Microwave Pyrolysis: The "Microwave" Analogy
Microwave pyrolysis uses a magnetron to generate microwaves that are directed into the reactor chamber.
These waves pass through the material and directly transfer energy to polar molecules (like water) or conductive materials (like carbon). This causes the material to heat itself uniformly and volumetrically.
Because the heat is generated internally, the process is incredibly fast and avoids the significant temperature gradients seen in conventional methods.
Comparing Key Performance Metrics
The differences in heating mechanisms lead to dramatically different outcomes in efficiency, control, and the quality of the final products (bio-oil, syngas, and biochar).
Heating Speed and Efficiency
Microwave pyrolysis is significantly faster, often reducing reaction times from hours to mere minutes.
It is also more energy-efficient because the energy is targeted directly into the feedstock. Conventional methods waste a substantial amount of energy heating the reactor chamber and the surrounding environment.
Temperature Control and Uniformity
Microwave heating is far more uniform, eliminating the hot spots and cold spots that plague conventional reactors.
This precise temperature control prevents unwanted secondary reactions and thermal cracking of valuable products, leading to a more consistent and higher-quality output. Conventional methods struggle with this, often over-cooking the outer layers of the feedstock.
Product Yield and Quality
The superior control of microwave pyrolysis often results in a higher yield of high-quality bio-oil with fewer undesirable compounds like tar.
By tuning the process, operators can selectively favor the production of either liquid (bio-oil), gas (syngas), or solid (biochar) products. The slow, uneven heating of conventional methods typically produces more lower-value biochar.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While microwave pyrolysis offers significant advantages in performance, it is not without its own set of challenges, particularly concerning scalability and material compatibility.
Scalability and Maturity
Conventional pyrolysis is a mature, robust, and well-understood technology. Its principles are simple, and it has been successfully implemented in large-scale industrial operations for decades.
Microwave pyrolysis is a newer technology. Scaling it up presents technical hurdles, such as ensuring even microwave distribution in a large reactor and the high cost and limited lifespan of industrial magnetrons.
Feedstock Limitations
A critical challenge for microwave pyrolysis is that many raw materials, such as dry biomass or most plastics, are microwave-transparent—they don't absorb microwave energy well.
To process these materials, a microwave absorber (like biochar or silicon carbide) must be mixed in with the feedstock to initiate heating. This adds complexity and cost to the process. Conventional methods can heat nearly any type of feedstock without additives.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice between conventional and microwave pyrolysis depends entirely on your project's specific priorities, balancing product quality against operational simplicity and scale.
- If your primary focus is high-quality products and precise process control: Microwave pyrolysis is the superior choice for creating high-value bio-oils with minimal contamination.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, low-cost processing of diverse waste: Conventional pyrolysis remains the more mature, reliable, and economically proven technology.
- If your primary focus is rapid processing speed and energy efficiency: Microwave pyrolysis offers clear advantages by heating the material directly and completing reactions in a fraction of the time.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental heating mechanism is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific chemical conversion goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Conventional Pyrolysis | Microwave Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Outside-in (conduction/convection) | Inside-out (volumetric) |
| Heating Speed | Slow (hours) | Fast (minutes) |
| Temperature Control | Less uniform, temperature gradients | Highly uniform, precise control |
| Product Quality | Lower quality bio-oil, more tar | Higher quality bio-oil, fewer impurities |
| Scalability | Mature, proven at large scale | Newer technology, scaling challenges |
| Feedstock Flexibility | High (no additives needed) | Lower (may require microwave absorbers) |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process?
Choosing the right pyrolysis technology is critical for achieving your target product yields and quality. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory equipment, including pyrolysis systems, to help you innovate and scale your processes efficiently.
Our experts can help you determine the best solution for your specific feedstock and goals, whether you're focused on high-value bio-oil production or large-scale waste conversion.
Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is an electric muffle furnace? Achieve Unmatched Thermal Purity and Uniformity
- What is the annealing temperature of quartz? Achieve Optimal Thermal Stability for Your Components
- What is the use of a digital muffle furnace? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the use of electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- How do high-temperature furnaces and ceramic crucibles impact Li-ion battery stability? Master Precision Synthesis



















