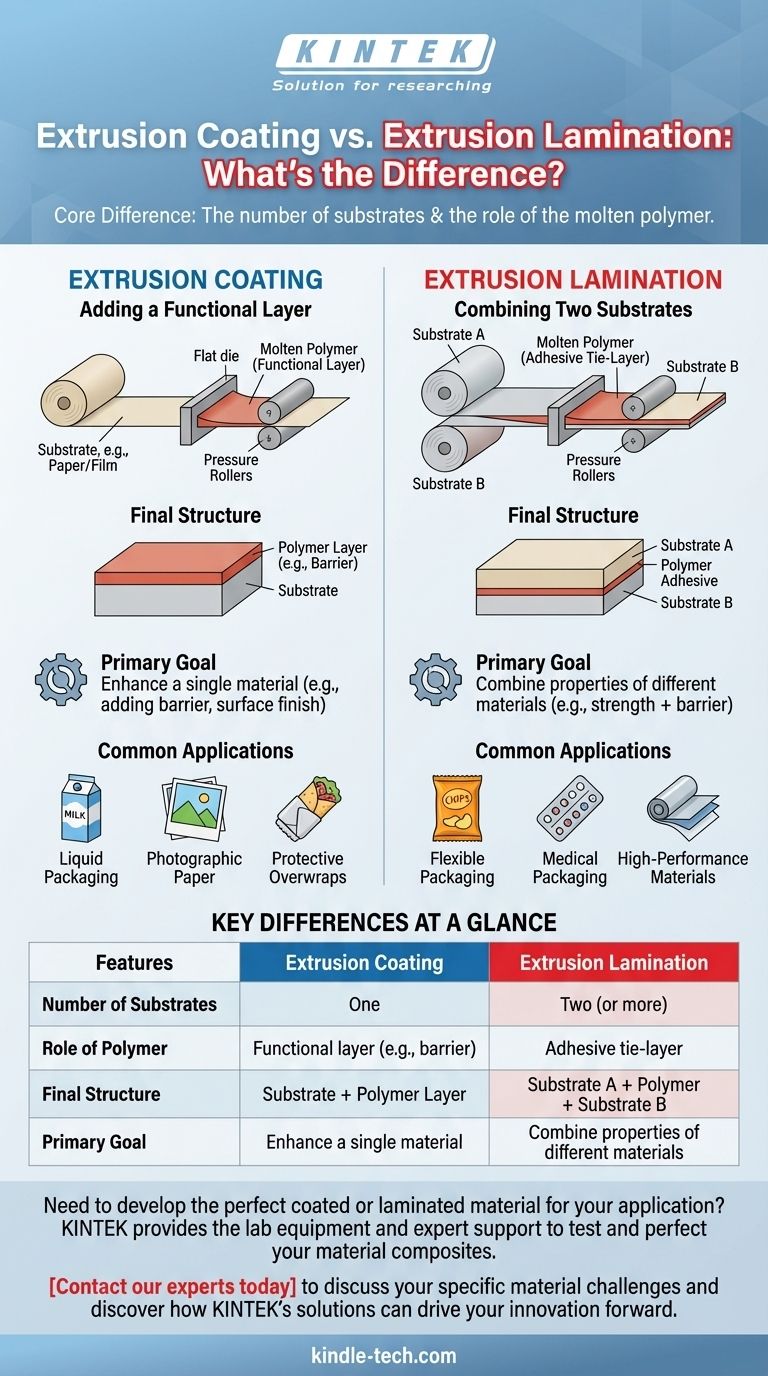
At its core, the difference between extrusion coating and extrusion lamination is the number of substrates involved. Extrusion coating applies a molten thermoplastic material directly onto a single substrate web, like paper or film. In contrast, extrusion lamination uses that molten thermoplastic as an adhesive layer to bond two separate substrate webs together.
The fundamental distinction lies in the role of the molten polymer. In extrusion coating, the polymer is the functional layer being added. In extrusion lamination, the polymer is the adhesive that joins two different functional layers.
Understanding Extrusion Coating: Adding a Functional Layer
Extrusion coating is a process designed to enhance the properties of a single existing material. It's about adding a new capability, such as a barrier or a specific surface finish.
The Process
A thin layer of molten polymer is extruded through a flat die. This hot polymer curtain is then applied directly onto a moving web of a substrate material, such as paper, paperboard, or foil. Pressure rollers then press the polymer onto the substrate to ensure a strong bond as it cools.
The Resulting Structure
The final product is a two-layer composite material. Its structure is simply Substrate + Polymer Layer. The original substrate provides the bulk properties like strength or form, while the new polymer layer adds a specific function.
Common Applications
This process is ideal for creating materials that need a barrier against moisture, grease, or gas. Common examples include liquid packaging like milk or juice cartons (polyethylene coated on paperboard), photographic paper, and protective overwraps for food.
Understanding Extrusion Lamination: Combining Two Substrates
Extrusion lamination is a process for creating a more complex, multi-layered material. The goal is to combine the unique, desirable properties of two different materials into a single structure.
The Process
Similar to coating, a molten polymer is extruded through a flat die. However, it is extruded directly into the nip point between two moving substrate webs. The hot polymer acts as a glue, and pressure rollers immediately bond the three layers together.
The Resulting Structure
The final product is a three-layer (or more) composite. Its basic structure is Substrate A + Polymer Adhesive + Substrate B. This allows for the creation of high-performance materials that couldn't exist otherwise.
Common Applications
This is common in flexible packaging where multiple performance characteristics are required. A classic example is a potato chip bag, which might combine a printed outer film (Substrate A) with an inner aluminum foil layer (Substrate B) for an ultimate oxygen and light barrier.
Key Differences at a Glance
Breaking the processes down by their core function clarifies their distinct purposes.
Role of the Polymer
In coating, the polymer itself serves as the functional barrier or surface. In lamination, the polymer serves as the adhesive tie-layer, and its primary function is to bond the two substrates.
Number of Substrates
This is the simplest differentiator. Coating always involves one primary substrate. Lamination always involves two or more substrates being joined.
Final Product Goal
The goal of coating is to enhance a single material. The goal of lamination is to combine two different materials to create a new composite structure with synergistic properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice is dictated entirely by the desired properties of your final material.
- If your primary focus is adding a single property (like a moisture barrier) to one material: Extrusion coating is the direct and efficient solution.
- If your primary focus is creating a composite that combines the distinct properties of two substrates (like the strength of paper and the barrier of foil): Extrusion lamination is the necessary process.
Understanding this core difference empowers you to select the precise process for creating materials with the exact performance characteristics you require.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Extrusion Coating | Extrusion Lamination |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Substrates | One | Two (or more) |
| Role of Polymer | Functional layer (e.g., barrier) | Adhesive tie-layer |
| Final Structure | Substrate + Polymer Layer | Substrate A + Polymer + Substrate B |
| Primary Goal | Enhance a single material | Combine properties of different materials |
Need to develop the perfect coated or laminated material for your application?
The choice between extrusion coating and lamination is critical for achieving the desired barrier properties, strength, and functionality in your final product. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and expert support you need to test, develop, and perfect your material composites.
Whether you're enhancing a single substrate or creating a complex multi-layer structure, our team can help you optimize your process. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific material challenges and discover how KINTEK's solutions can drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot pressing? Choose the Right Powder Metallurgy Process
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot stamping? Unlock Ultra-High Strength for Automotive Parts
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use
- Which features of vacuum hot pressing equipment are utilized by the dual-step vacuum hot press process? Optimize AlMgTi
- Why is a vacuum hot-pressing furnace preferred for C_fiber/Si3N4 composites? Achieve High Density & Fiber Protection


















