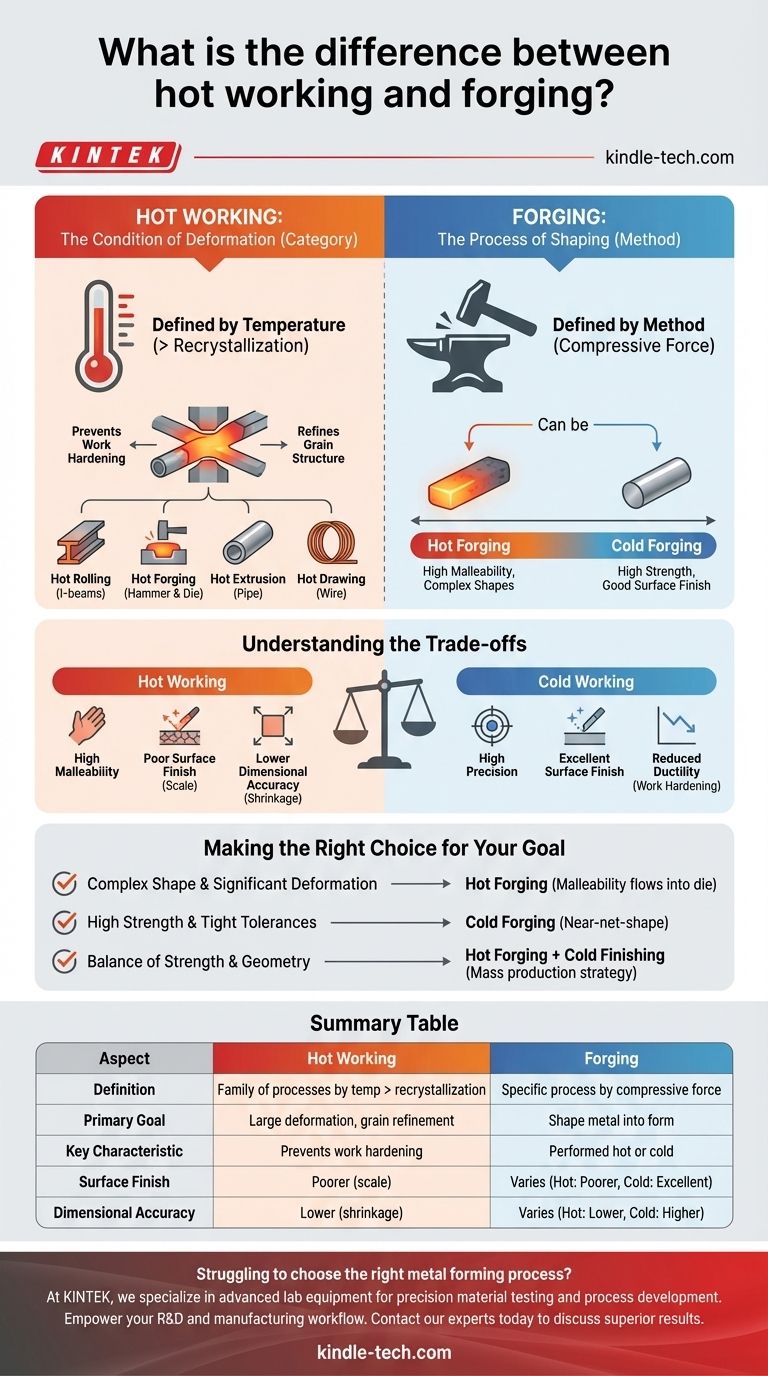
At a fundamental level, hot working is a broad category of metal deformation processes, while forging is a specific manufacturing technique within that category. The key distinction is that hot working is defined by temperature—working a metal above its recrystallization point—whereas forging is defined by method—shaping metal using localized compressive forces. Therefore, forging can be a type of hot working, but it can also be performed cold.
The critical distinction is one of category versus process. Hot working describes the condition under which metal is shaped—specifically, above its recrystallization temperature. Forging is a specific process of shaping metal with compressive force, which can be done either hot or cold.

What is Hot Working? The Condition of Deformation
Hot working is not one single process, but rather a family of processes unified by a single principle: deforming metal at a temperature high enough to prevent it from strain-hardening.
Defined by Temperature, Not Method
The defining characteristic of any hot working process is that the metal's temperature is maintained above its recrystallization temperature.
At this temperature, the metal's crystalline grain structure is continuously reformed and refined as it is being deformed. This is analogous to working with warm clay; it remains pliable and doesn't crack under pressure.
The Metallurgical Advantage
Working metal above its recrystallization temperature prevents work hardening, allowing for very large amounts of deformation without the risk of fracture.
This process also breaks down coarse grain structures and refines them into smaller, more uniform grains, which generally improves the material's toughness and ductility.
Examples of Hot Working Processes
To understand hot working as a category, consider its members. Forging is just one of many.
- Hot Rolling: Squeezing metal billets through rollers to create long products like I-beams or sheet metal.
- Hot Forging: Hammering or pressing metal into a desired shape.
- Hot Extrusion: Pushing metal through a die to create parts with a constant cross-section, like a pipe or aluminum window frame.
- Hot Drawing: Pulling metal through a die to reduce its diameter, like in wire manufacturing.
What is Forging? The Process of Shaping
Forging is one of the oldest metalworking processes, defined by the act of shaping metal using compressive forces, delivered either with a hammer or a press.
The Spectrum of Forging
The confusion between hot working and forging arises because forging can be performed across a range of temperatures, which dramatically changes its characteristics and outcomes.
Hot Forging This is where the two concepts intersect. Hot forging is the process of shaping metal via compressive force while it is above its recrystallization temperature.
Because it is a hot working process, hot forging can produce complex shapes and achieve significant changes in geometry in a single step.
Cold Forging This is the process of shaping metal at or near room temperature. Because it is a cold working process, it requires much higher forces and induces significant work hardening.
Cold forging increases the metal's strength and hardness at the expense of its ductility. It is typically used for finishing steps or for less complex shapes where high strength is required.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between hot and cold forming methods involves a clear set of engineering trade-offs. The right choice depends entirely on the goals for the final component.
Hot Working: Malleability vs. Precision
The primary benefit of hot working is the metal's high malleability. However, this comes at a cost.
High temperatures cause the formation of an oxide layer (scale) on the surface, leading to a poor surface finish. Furthermore, as the part cools, it shrinks and can warp, resulting in lower dimensional accuracy.
Cold Working: Precision vs. Deformability
The main advantage of cold working (including cold forging) is control. It produces parts with a smooth surface finish and excellent dimensional tolerances because there is no heat-related scale or shrinkage.
The trade-off is a massive reduction in ductility. Cold working requires significantly more force and is limited in the amount of deformation it can achieve before the material becomes too brittle and risks cracking.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's requirements for strength, dimensional accuracy, and cost will determine the ideal process.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex shape or achieving significant deformation: Hot forging is the correct path, as the material's high malleability allows it to flow easily into the die.
- If your primary focus is achieving high strength, a smooth surface finish, and tight dimensional tolerances: Cold forging or a secondary cold working process (like coining) is the superior choice for a near-net-shape part.
- If your primary focus is a balance of strength and complex geometry for mass production: A common strategy is to hot forge the initial shape and then use a cold finishing operation to achieve final dimensions and surface properties.
Understanding this hierarchy between condition and process empowers you to specify manufacturing methods with precision and intent.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hot Working | Forging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A family of processes defined by temperature (above recrystallization) | A specific process defined by method (compressive force) |
| Primary Goal | Achieve large deformations, refine grain structure | Shape metal into a desired form |
| Key Characteristic | Prevents work hardening, improves ductility | Can be performed hot or cold |
| Surface Finish | Poorer (due to scale) | Varies (Hot: Poorer, Cold: Excellent) |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Lower (due to shrinkage) | Varies (Hot: Lower, Cold: Higher) |
Struggling to choose the right metal forming process for your application?
The distinction between hot working and forging is critical for achieving the desired material properties, strength, and dimensional accuracy in your components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise material testing and process development.
Whether you are developing new alloys, optimizing forging parameters, or ensuring quality control, our solutions support your entire R&D and manufacturing workflow.
Let KINTEK empower your precision manufacturing. Contact our experts today to discuss how our equipment can help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Are biomass and biodiesel truly sustainable? The Surprising Truth Behind Their 'Green' Label
- What is heat treatment for small parts? Achieve Superior Strength and Durability
- What are the uses of oven in food chemistry laboratory? Achieve Precise Sample Preparation and Analysis
- How is a sputtering target made? A Guide to Manufacturing High-Performance Thin Film Sources
- What is the minimum melting-temperature for brazing material? The 450°C Threshold Explained
- How accurate is the XRF analysis? Achieve Lab-Quality Results with the Right Methodology
- What are the different types of heat treatment process? A Guide to Hardening, Softening & Brazing
- What is the difference between thermal decomposition and pyrolysis? A Guide to Controlled Heat Processes

















