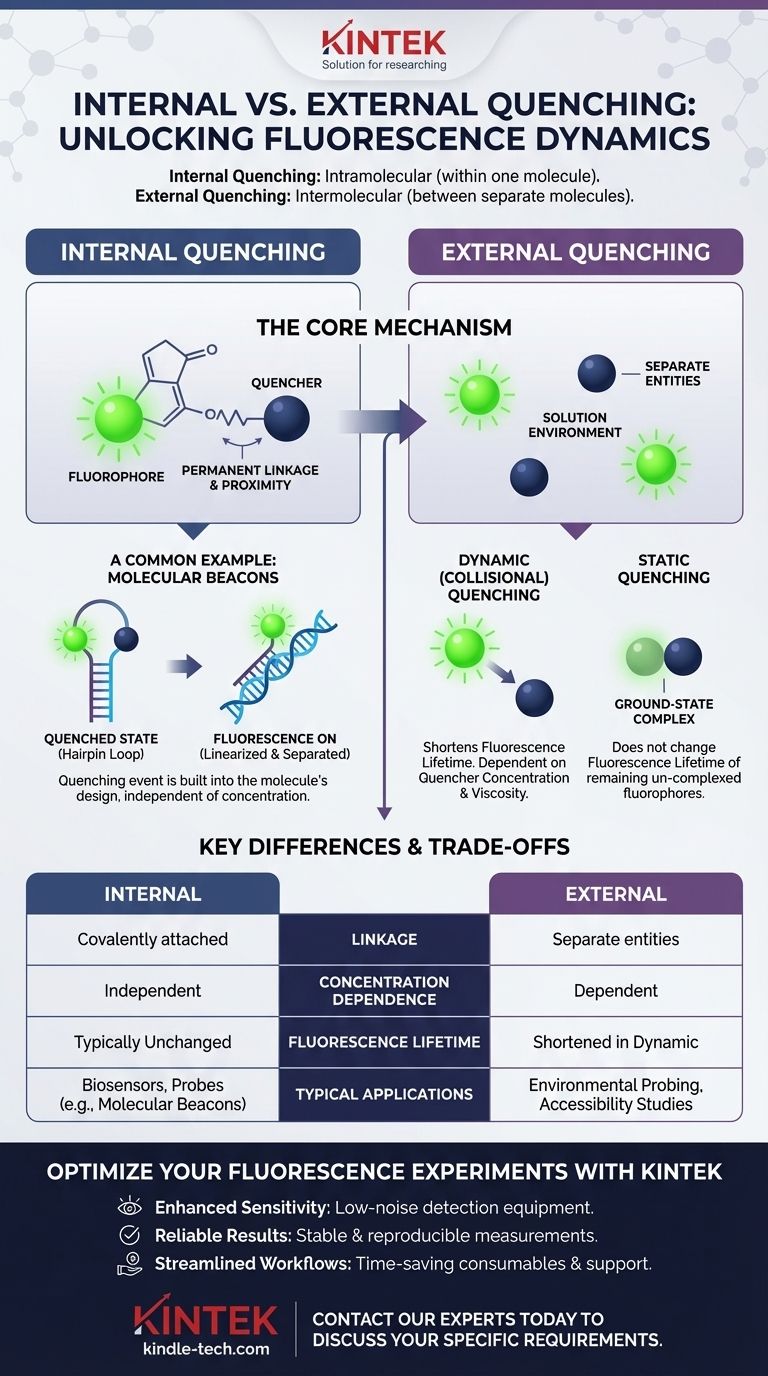
The fundamental difference is that internal quenching occurs when the quenching agent and the fluorescent molecule (fluorophore) are part of the same molecule, while external quenching happens when they are two separate, independent molecules that must interact in a solution. Internal quenching is an intramolecular process (within one molecule), whereas external quenching is an intermolecular process (between two or more molecules).
The core distinction lies in proximity and linkage. Internal quenching involves a fluorophore and quencher permanently tethered together, while external quenching relies on random collisions or complex formation between separate molecules in a solution.

A Closer Look at Internal Quenching (Intramolecular)
The Core Mechanism
In internal quenching, the quencher is physically and covalently attached to the fluorophore. This creates a single molecular system where the two components are always in close proximity.
The quenching process is built into the molecule's design and is therefore independent of the molecule's concentration.
How it Works
The most common mechanisms are Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) or contact quenching. In these systems, the excited fluorophore transfers its energy to the nearby quencher without emitting a photon, effectively "turning off" the fluorescence.
This energy transfer is efficient precisely because the quencher is held close by the molecular structure itself.
A Common Example: Molecular Beacons
Molecular beacons are a perfect illustration of internal quenching. They are single-stranded DNA probes with a fluorophore on one end and a quencher on the other.
In their native state, they form a hairpin-loop structure that brings the fluorophore and quencher into direct contact, silencing the signal. When the beacon binds to its target sequence, it linearizes, separating the two and causing a dramatic increase in fluorescence.
Understanding External Quenching (Intermolecular)
The Core Mechanism
External quenching involves a fluorophore and a quencher existing as separate entities in a solution. Quenching only occurs when they happen to interact.
The efficiency of this process is highly dependent on factors like the concentration of the quencher and the viscosity of the environment, which control how often they encounter each other.
Dynamic (Collisional) Quenching
This is the most common form of external quenching. An excited fluorophore is deactivated when a quencher molecule collides with it.
This process reduces the fluorescence lifetime—the average time the molecule stays in its excited state. The relationship is described by the Stern-Volmer equation.
Static Quenching
In static quenching, the quencher forms a stable, non-fluorescent complex with the fluorophore while it's in its ground state (before it has been excited).
This reduces the total number of fluorophores available to emit light but does not change the fluorescence lifetime of the remaining, un-complexed fluorophores.
Key Differences and Trade-offs
Proximity and Linkage
Internal quenching relies on a permanent, covalent link ensuring the quencher is always nearby. This provides a reliable on/off switching mechanism.
External quenching depends on random diffusion and collisions. The components are not linked, making the process sensitive to environmental conditions.
Impact of Concentration
The efficiency of internal quenching is a property of the individual molecule and is not dependent on its concentration.
The efficiency of external quenching, however, is directly proportional to the concentration of the quencher. More quencher molecules mean more frequent collisions and more quenching.
Diagnostic Tool: Fluorescence Lifetime
This is a critical distinguishing factor. Dynamic external quenching is unique in that it actively shortens the measured fluorescence lifetime.
Internal quenching and static external quenching both reduce fluorescence intensity but typically do not affect the lifetime of the fluorophores that are still able to emit light.
Typical Applications
Internal quenching is the principle behind engineered biosensors, probes, and reporters like molecular beacons, where a specific event (like binding) is designed to trigger a fluorescence change.
External quenching is often used as an experimental tool to study the environment around a fluorophore, such as determining if a fluorescently-labeled part of a protein is exposed to the solvent or buried inside.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this distinction allows you to design and interpret fluorescence experiments with precision.
- If your primary focus is designing a specific biosensor for detection: Internal quenching provides the robust, built-in switching mechanism necessary for a reliable probe.
- If your primary focus is studying the accessibility of a labeled site on a macromolecule: External quenching is the ideal tool, as the quenching rate will report on how exposed that site is to quenchers in the solution.
- If your primary focus is confirming the formation of a ground-state complex: Static external quenching, which reduces intensity without changing lifetime, is a direct indicator of this phenomenon.
Ultimately, choosing between these frameworks depends entirely on whether you need the quenching event to be a pre-programmed molecular function or an indicator of environmental interaction.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Internal Quenching | External Quenching |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Intramolecular (within one molecule) | Intermolecular (between separate molecules) |
| Linkage | Covalently attached quencher & fluorophore | Separate entities in solution |
| Concentration Dependence | Independent | Dependent on quencher concentration |
| Fluorescence Lifetime | Typically unchanged | Shortened in dynamic quenching |
| Common Applications | Biosensors, molecular beacons | Environmental probing, accessibility studies |
Optimize Your Fluorescence Experiments with KINTEK
Understanding quenching mechanisms is crucial for accurate fluorescence analysis. Whether you're developing sensitive biosensors or studying molecular interactions, having the right equipment is key to success.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables designed to meet the precise needs of fluorescence researchers. We provide reliable instruments that deliver the performance and consistency required for your critical experiments.
Let us help you achieve:
- Enhanced Sensitivity: With equipment optimized for low-noise detection.
- Reliable Results: Through instruments that ensure stable and reproducible measurements.
- Streamlined Workflows: With consumables and support that save you time and effort.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What should be considered when comparing ultra-low freezer models? A Guide to Sample Security, Cost, and Usability
- How do baffled flasks and orbital shaker incubators facilitate yeast screening? Optimize Oxygen for Lipid Production
- What are the precautions to be taken for heating of a substance in the laboratory? Ensure Safety and Prevent Accidents
- Can THC distillate be vaporized? The Ultimate Guide to Vaping Potent Concentrates
- What is direct current pulse magnetron sputtering? Achieve Superior Thin Film Deposition for Insulating Materials
- At what temperature do terpenes evaporate? Unlock the Full Flavor and Effects of Your Cannabis
- What is the range of sputtering? Achieve High-Quality Thin Films for Any Application
- What is the significance of a constant temperature drying oven in high-pressure CO2 reduction? Ensure Stable Results


















