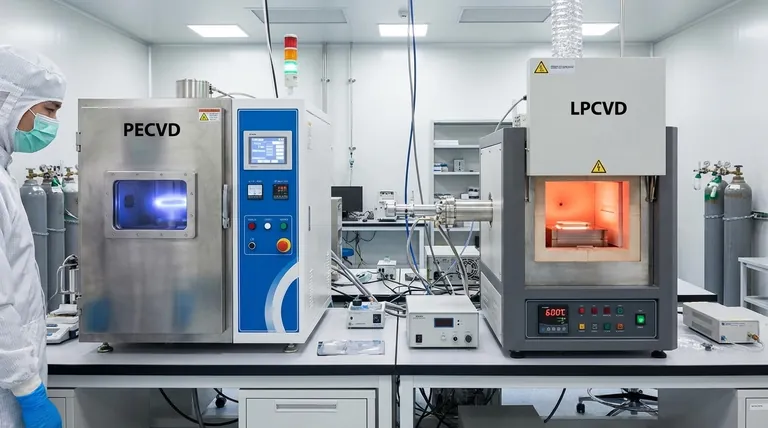
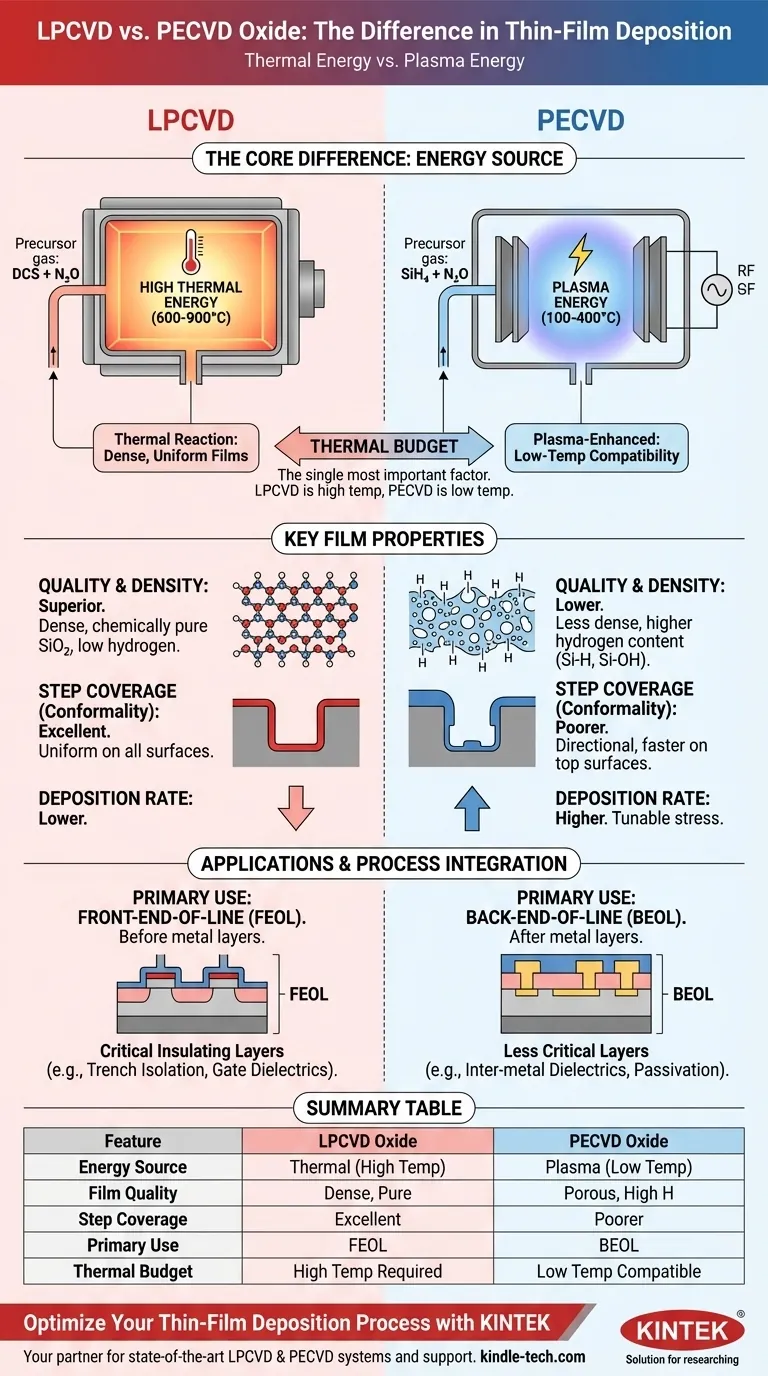
The fundamental difference between LPCVD and PECVD oxide lies in the energy source used for deposition. Low-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (LPCVD) uses high thermal energy (600-900°C) to create dense, highly uniform films. In contrast, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) uses plasma at much lower temperatures (100-400°C), making it suitable for temperature-sensitive devices but typically resulting in lower-quality films.
The choice between these two methods is almost always dictated by the thermal budget of your process. LPCVD offers superior film quality at the cost of high heat, while PECVD enables deposition on completed devices by substituting that heat with plasma energy.

The Core Mechanism: Thermal vs. Plasma Energy
Understanding how each method energizes the precursor gases is key to understanding the difference in the final silicon dioxide (SiO₂) film.
How LPCVD Works: High Temperature, Low Pressure
LPCVD relies purely on thermal energy to initiate the chemical reaction. Precursor gases, such as dichlorosilane (DCS) and nitrous oxide (N₂O) or TEOS, are introduced into a hot-wall furnace.
The high temperature provides the activation energy needed for the gas molecules to react on the wafer surface and form a solid SiO₂ film. The process is run at low pressure to ensure a long mean free path for gas molecules, which promotes highly uniform deposition across many wafers at once.
How PECVD Works: Plasma-Enhanced Deposition
PECVD fundamentally changes the energy input. Instead of relying on heat, it applies a radio frequency (RF) electromagnetic field to the precursor gases (like silane, SiH₄, and N₂O).
This RF field ignites a plasma, a state of matter containing highly energetic ions and free radicals. These reactive species can then form SiO₂ on the wafer surface at significantly lower temperatures, as the required energy comes from the plasma, not from heat.
Comparing Key Film Properties
The difference in energy source directly impacts the characteristics of the deposited oxide film.
Film Quality and Density
LPCVD oxide is very dense, stoichiometric (chemically pure SiO₂), and has a very low hydrogen content. This results in superior electrical properties, such as high dielectric strength and low leakage current, making it an excellent insulator.
PECVD oxide is generally less dense and can contain a significant amount of incorporated hydrogen from the silane (SiH₄) precursor. This hydrogen can lead to Si-H and Si-OH bonds in the film, which can degrade its electrical performance.
Step Coverage (Conformality)
LPCVD provides excellent, highly conformal step coverage. Because the reaction is limited by the surface reaction rate (not by how fast the gas gets there), the film deposits at a nearly equal thickness on all surfaces, including vertical sidewalls of trenches.
PECVD deposition is often more directional and results in poorer conformality. The reactive species in the plasma have a shorter lifetime, leading to faster deposition on top surfaces than on the bottom or sidewalls of features.
Deposition Rate and Stress
PECVD typically offers a higher deposition rate than LPCVD, which is advantageous for depositing thick films, such as final passivation layers.
Furthermore, the film stress in PECVD can be tuned from compressive to tensile by adjusting process parameters. LPCVD films generally have a fixed, low tensile stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
The choice between LPCVD and PECVD is rarely about which is "better" in a vacuum; it's about which is appropriate for a specific step in the fabrication sequence.
The Thermal Budget Constraint
This is the single most important factor. The high temperatures of LPCVD would destroy metal layers (like aluminum) or other temperature-sensitive structures.
Therefore, LPCVD is used in the front-end-of-line (FEOL), before metal is deposited. PECVD is the dominant method for depositing dielectrics in the back-end-of-line (BEOL), after transistors and metal interconnects are already in place.
Electrical Performance vs. Process Integration
For critical insulating layers where performance cannot be compromised—such as trench isolation or gate dielectrics—the superior quality of LPCVD oxide makes it the clear choice.
For less critical applications like inter-metal dielectrics or scratch-protection passivation layers, the lower quality of PECVD oxide is an acceptable trade-off for its low-temperature process compatibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by your specific requirements for film quality and the temperature limitations of your substrate.
- If your primary focus is the highest quality electrical insulation: LPCVD is the superior choice, provided your device can withstand the high process temperature.
- If your primary focus is depositing an oxide on a temperature-sensitive device: PECVD is your only viable option due to its low-temperature processing.
- If your primary focus is filling deep trenches or coating complex topography uniformly: LPCVD provides significantly better conformality.
- If your primary focus is rapidly depositing a thick passivation or inter-metal layer: PECVD is often preferred for its higher deposition rate and BEOL compatibility.
Ultimately, the decision between LPCVD and PECVD is dictated by your thermal budget—let the temperature tolerance of your substrate guide your choice.
Summary Table:
| Feature | LPCVD Oxide | PECVD Oxide |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Thermal (600-900°C) | Plasma (100-400°C) |
| Film Quality | Dense, stoichiometric, low hydrogen | Less dense, higher hydrogen content |
| Step Coverage | Excellent conformality | Poorer conformality |
| Primary Use | Front-end-of-line (FEOL) | Back-end-of-line (BEOL) |
| Thermal Budget | High temperature required | Low temperature compatible |
Optimize Your Thin-Film Deposition Process with KINTEK
Choosing between LPCVD and PECVD is critical for your semiconductor fabrication success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables that meet the precise demands of both deposition methods.
Why partner with KINTEK for your deposition needs?
- Access to state-of-the-art LPCVD and PECVD systems tailored to your specific thermal budget requirements
- Expert guidance on selecting the right equipment for FEOL or BEOL applications
- Comprehensive support for achieving optimal film quality, conformality, and electrical performance
- Reliable consumables that ensure consistent deposition results
Whether you're working on front-end transistor isolation or back-end inter-metal dielectrics, KINTEK has the solutions to enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Contact our deposition experts today to discuss how we can support your specific LPCVD or PECVD requirements and help you achieve superior thin-film results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process



















