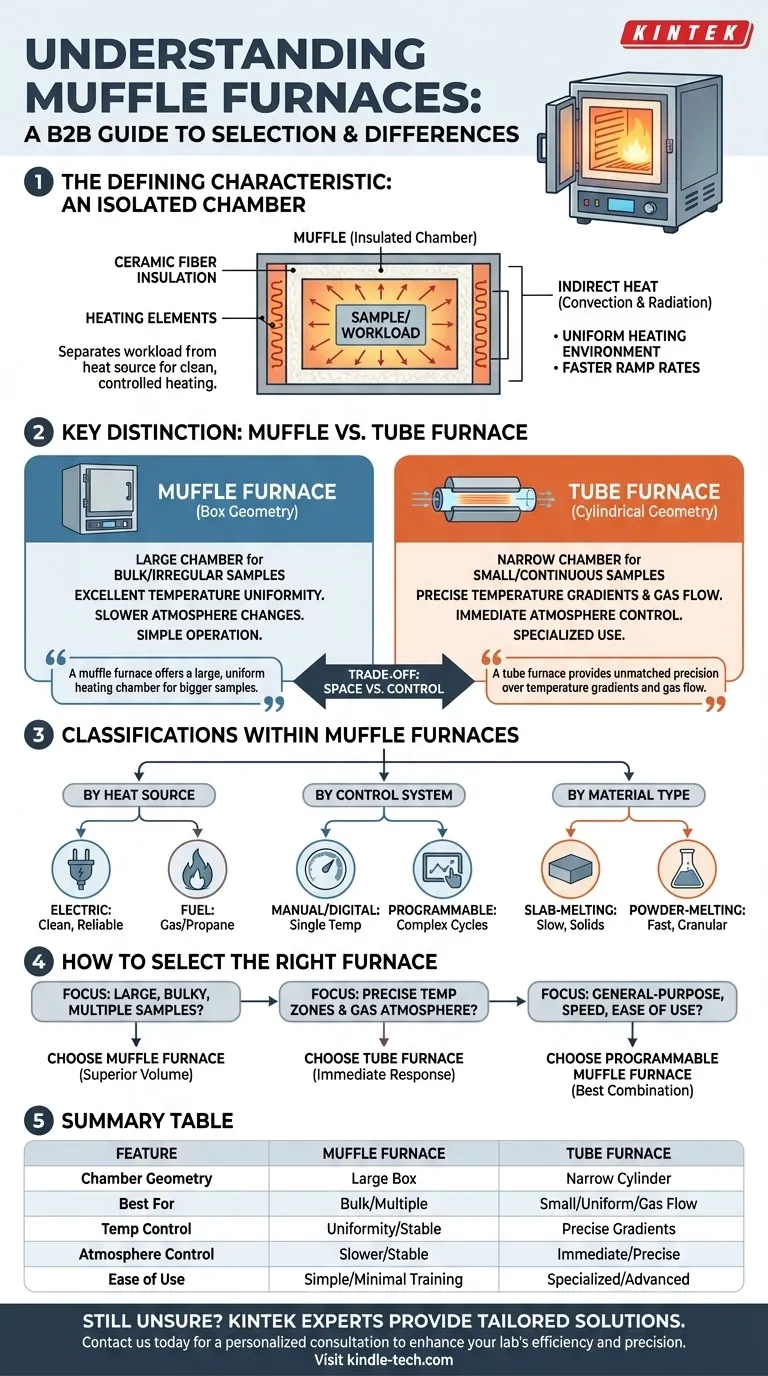
The term 'muffle furnace' defines a category of high-temperature ovens, distinguished primarily by an insulated inner chamber that separates the sample from the direct heat source. The key differences between them lie not just in their internal design—such as for melting solids versus powders—but more critically in how they compare to their main alternative, the tube furnace, especially regarding chamber size and atmospheric control.
The crucial difference when selecting a high-temperature furnace is not about maximum heat, but about the trade-off between space and control. A muffle furnace offers a large, uniform heating chamber for bigger samples, while a tube furnace provides unmatched precision over temperature gradients and gas flow for sensitive, smaller-scale processes.

The Defining Characteristic: An Isolated Chamber
A muffle furnace's core design principle is the separation of the workload from the heating elements. This "muffle" creates a controlled, uniform, and clean heating environment.
The Role of Modern Insulation
Modern muffle furnaces are equipped with advanced ceramic fiber insulation. This material has low thermal mass, allowing for significantly faster heating and cooling ramp rates compared to older furnaces built with firebricks.
The Benefit of Indirect Heat
By isolating the sample from the heating elements, the furnace prevents contamination from any combustion byproducts (in fuel-fired models) and ensures heat is transferred evenly through convection and radiation. This results in excellent temperature uniformity across the entire chamber.
Key Distinction: Muffle Furnace vs. Tube Furnace
While both furnace types can reach similar temperatures and be equipped for vacuum or inert gas use, their fundamental geometry dictates their ideal applications.
Chamber Geometry and Sample Size
A muffle furnace is a box furnace. Its large, open chamber is perfectly suited for heating multiple samples at once, bulky or irregularly shaped objects, or materials placed in crucibles.
A tube furnace, by contrast, features a narrow cylindrical chamber. This design severely limits sample size but is ideal for processes involving continuous material flow or small, uniform substrates.
Temperature and Atmosphere Control
The large volume of a muffle furnace makes it excellent for batch processing at a stable, uniform temperature. However, changing the atmosphere or creating precise temperature zones is slow and difficult.
The small, enclosed volume of a tube furnace allows for precise and immediate control over gas flow and temperature. Its exposed ends make it easy to establish specific temperature gradients, which is critical for specialized applications.
Classifications Within Muffle Furnaces
Beyond the comparison to tube furnaces, muffle furnaces themselves can be categorized by their internal mechanics and control systems.
By Heat Source
The most common type is the electric muffle furnace, which uses resistive heating elements integrated into the chamber walls for clean, reliable heat. Less common are fuel muffle furnaces that run on natural gas or propane.
By Control System
Furnaces can have simple manual or digital controls for setting a single temperature. More advanced programmable muffle furnaces allow users to define complex work cycles with multiple heating, soaking, and cooling steps.
By Material Processing Type
For specific high-temperature melting, furnaces can be specialized. Slab-melting units are designed for solid materials and operate more slowly, while powder-melting units are optimized for faster performance with granular materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the correct furnace requires acknowledging the inherent advantages and limitations of each design.
Muffle Furnace: Volume vs. Precision
The primary benefit of a muffle furnace—its large chamber—is also its main drawback. It is inefficient for processes that require rapid atmospheric changes or tightly controlled temperature gradients along a sample.
Tube Furnace: Control vs. Capacity
A tube furnace offers superior control but at the expense of throughput and sample size. It is a specialized tool that is unsuitable for bulk processing or large objects.
Ease of Operation
Muffle furnaces are generally considered simple to use and require minimal operator training. Their straightforward controls for setting temperature and time profiles make them a user-friendly and reliable workhorse in most laboratory settings.
How to Select the Right Furnace
Your decision should be guided by the physical nature of your sample and the specific requirements of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is processing large, bulky, or multiple samples at once: A muffle furnace is the superior choice due to its larger chamber volume.
- If your primary focus is precise control over temperature zones and gas atmosphere: A tube furnace provides the immediate response and gradient management required for sensitive processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating, ashing, or sintering: A modern, programmable electric muffle furnace offers the best combination of speed, uniformity, and ease of use.
Ultimately, your choice depends on a clear understanding of your sample's geometry and your process's specific atmospheric and thermal requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Tube Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Chamber Geometry | Large, open box | Narrow cylinder |
| Best For | Bulk samples, multiple items | Small, uniform substrates, gas flow processes |
| Temperature Control | Excellent uniformity, stable for batch processing | Precise gradients, ideal for sensitive processes |
| Atmosphere Control | Slower gas changes, suited for stable environments | Immediate, precise control over gas flow |
| Ease of Use | Simple operation, minimal training required | More specialized, may require advanced knowledge |
Still unsure which furnace is right for your application? The experts at KINTEK can help! We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored solutions for your laboratory's unique thermal processing challenges. Whether you need the large chamber of a muffle furnace for bulk samples or the precise control of a tube furnace for specialized processes, we have the expertise to guide you to the perfect equipment. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let KINTEK enhance your lab's efficiency and precision.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages and limitations of heat treatment? Tailor Material Properties for Peak Performance
- What are the applications of muffle furnaces? Essential Tools for High-Temperature Processes
- What is the temperature of a muffle furnace for ash determination? Key Insights for Accurate Results
- What is the most common form of heat treatment? Mastering Annealing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What is the optimal temperature for ashing in a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise and Efficient Results



















