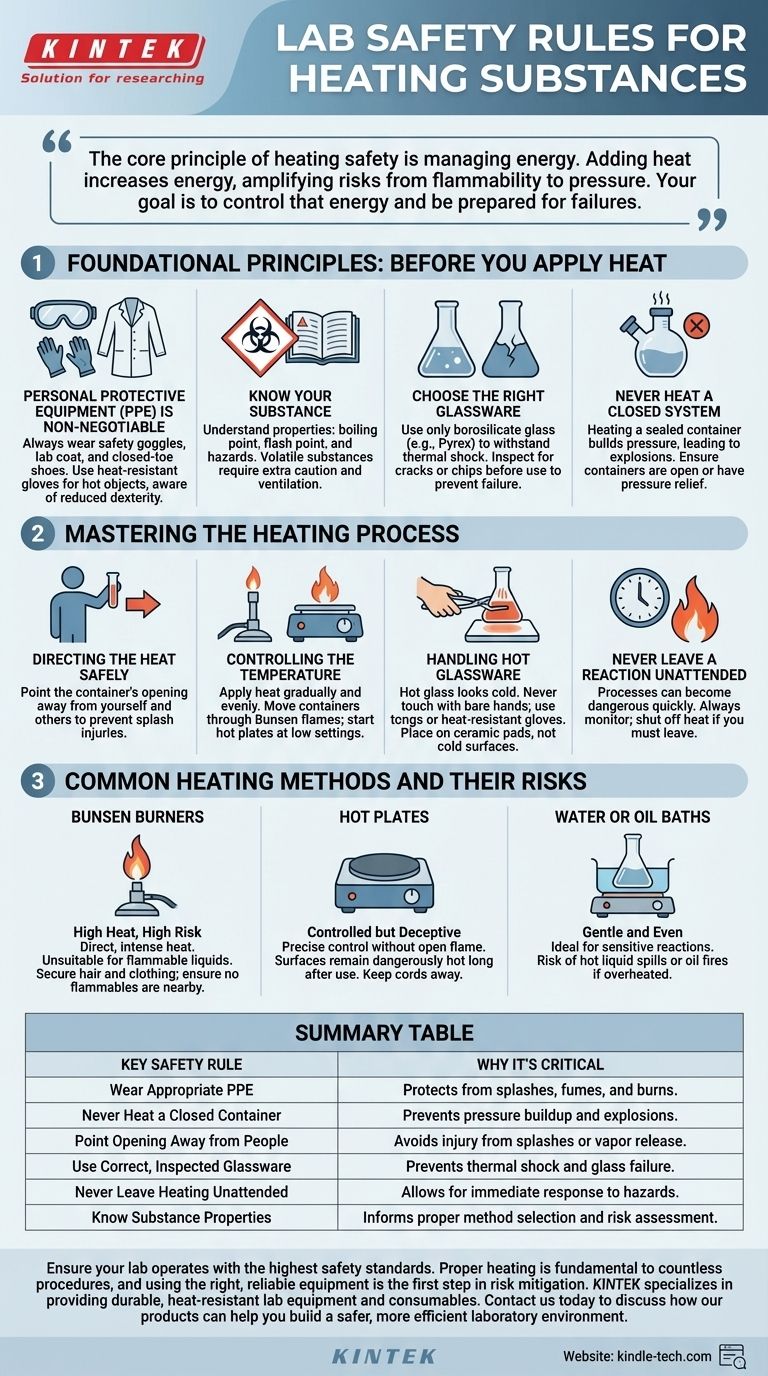
The fundamental rules for heating substances in a lab are to always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), never heat a closed container, and always point the opening of the container away from yourself and others. You must use the correct equipment for the task, such as heat-resistant glassware, and never leave a heating process unattended. Understanding the properties of the substance you are heating is critical to preventing fires, explosions, or the release of toxic fumes.
The core principle of heating safety is managing energy. Adding heat to a system increases its energy, which amplifies every potential risk, from flammability to pressure buildup. Your primary goal is not just to heat the substance, but to control that energy and be prepared for what happens if you lose control.

Foundational Principles: Before You Apply Heat
Proper preparation is the most critical phase of heating safety. The choices you make before you begin directly determine the level of risk you will face.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is Non-Negotiable
Always wear safety goggles to protect your eyes from splashes or shattering glassware. For tasks involving open flames or the potential for spills, a lab coat and closed-toe shoes are mandatory. Heat-resistant gloves should be used when handling hot objects, but be aware they can reduce dexterity.
Know Your Substance
Before you begin, you must understand the properties of the chemical you are heating. Look up its boiling point, flash point, and any specific hazards. A highly volatile substance (one that evaporates easily) requires much more caution and ventilation than a stable, non-flammable one.
Choose the Right Glassware
Not all glassware is created equal. Use only borosilicate glass (branded as Pyrex or Kimax) that is designed to withstand thermal shock—rapid changes in temperature. Inspect every piece of glassware for cracks or chips before use, as these imperfections can become failure points when heated.
Never Heat a Closed System
Heating a sealed container will cause pressure to build up as the gas or liquid inside expands. This will inevitably lead to an explosion, propelling glass and hot chemicals across the lab. Ensure any container being heated is open to the atmosphere or connected to a pressure-releasing apparatus.
Mastering the Heating Process
Once you begin applying heat, constant vigilance and proper technique are essential to maintaining control.
Directing the Heat Safely
This may seem obvious, but it is the most frequently violated rule. Always ensure the opening of the test tube or flask is pointed away from your face, your lab partner, and anyone else in the vicinity. This prevents accidental splashes or vapor release from causing injury.
Controlling the Temperature
Apply heat gradually and evenly. When using a Bunsen burner, move the container through the flame gently to avoid creating superheated "hot spots" that can cause violent boiling or damage the glassware. For hot plates, start at a low setting and increase the temperature slowly.
Handling Hot Glassware
Hot glass looks identical to cold glass. Never touch glassware with your bare hands unless you are certain it has cooled down. Place hot items on a heat-resistant ceramic pad, not directly on a cold lab bench, which could cause the glass to shatter from thermal shock.
Never Leave a Reaction Unattended
A heating process can change from stable to dangerous in a matter of seconds. Never walk away from an active heating setup, even for a moment. If you must leave the area, shut off the heat source completely.
Common Heating Methods and Their Risks
Choosing the right tool for the job is a key safety decision. Each method has distinct advantages and hazards.
Bunsen Burners: High Heat, High Risk
Burners provide direct, intense heat but also introduce an open flame. This makes them unsuitable for flammable liquids. Always ensure long hair is tied back, loose clothing is secured, and no flammable materials are nearby before lighting a burner.
Hot Plates: Controlled but Deceptive
Hot plates offer excellent temperature control without an open flame, making them safer for volatile substances. However, their surfaces remain dangerously hot long after being turned off, creating a significant burn risk. Electrical cords should also be kept away from the hot surface to prevent melting.
Water or Oil Baths: Gentle and Even
Using a water or oil bath on top of a hot plate provides the most gentle and uniform heating. This is ideal for sensitive reactions. The primary risk here is spilling the hot liquid or, in the case of an oil bath, the potential for the oil to catch fire if heated past its flash point.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of heating method and safety precautions should be dictated by the specific substance and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is rapidly heating a stable, non-flammable solid or liquid: A Bunsen burner can be used, but always with constant attention and by moving the container to ensure even heating.
- If your primary focus is controlled heating of a volatile or flammable liquid: A hot plate, ideally combined with a water bath and performed in a fume hood, is the safest method.
- If your primary focus is gently warming a temperature-sensitive reaction: A water bath on a hot plate provides the best control and uniformity, minimizing the risk of decomposition or runaway reactions.
Ultimately, safety in the lab is not a passive checklist but an active, thinking process of anticipating and mitigating risk.
Summary Table:
| Key Safety Rule | Why It's Critical |
|---|---|
| Wear Appropriate PPE | Protects from splashes, fumes, and burns. |
| Never Heat a Closed Container | Prevents pressure buildup and explosions. |
| Point Opening Away from People | Avoids injury from splashes or vapor release. |
| Use Correct, Inspected Glassware | Prevents thermal shock and glass failure. |
| Never Leave Heating Unattended | Allows for immediate response to hazards. |
| Know Substance Properties | Informs proper method selection and risk assessment. |
Ensure your lab operates with the highest safety standards. Proper heating is fundamental to countless procedures, and using the right, reliable equipment is the first step in risk mitigation. KINTEK specializes in providing durable, heat-resistant lab equipment and consumables—from borosilicate glassware to controlled hot plates—designed for safety and precision. Contact us today (#ContactForm) to discuss how our products can help you build a safer, more efficient laboratory environment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is a muffle oven used for? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment and Analysis
- What is a muffle furnace for laboratory use? A Guide to Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the heat capacity of a muffle furnace? Understanding Thermal Mass for Optimal Performance
- What does a muffle furnace do? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- How does heat affect strength materials? The Science of Thermal Degradation Explained



















