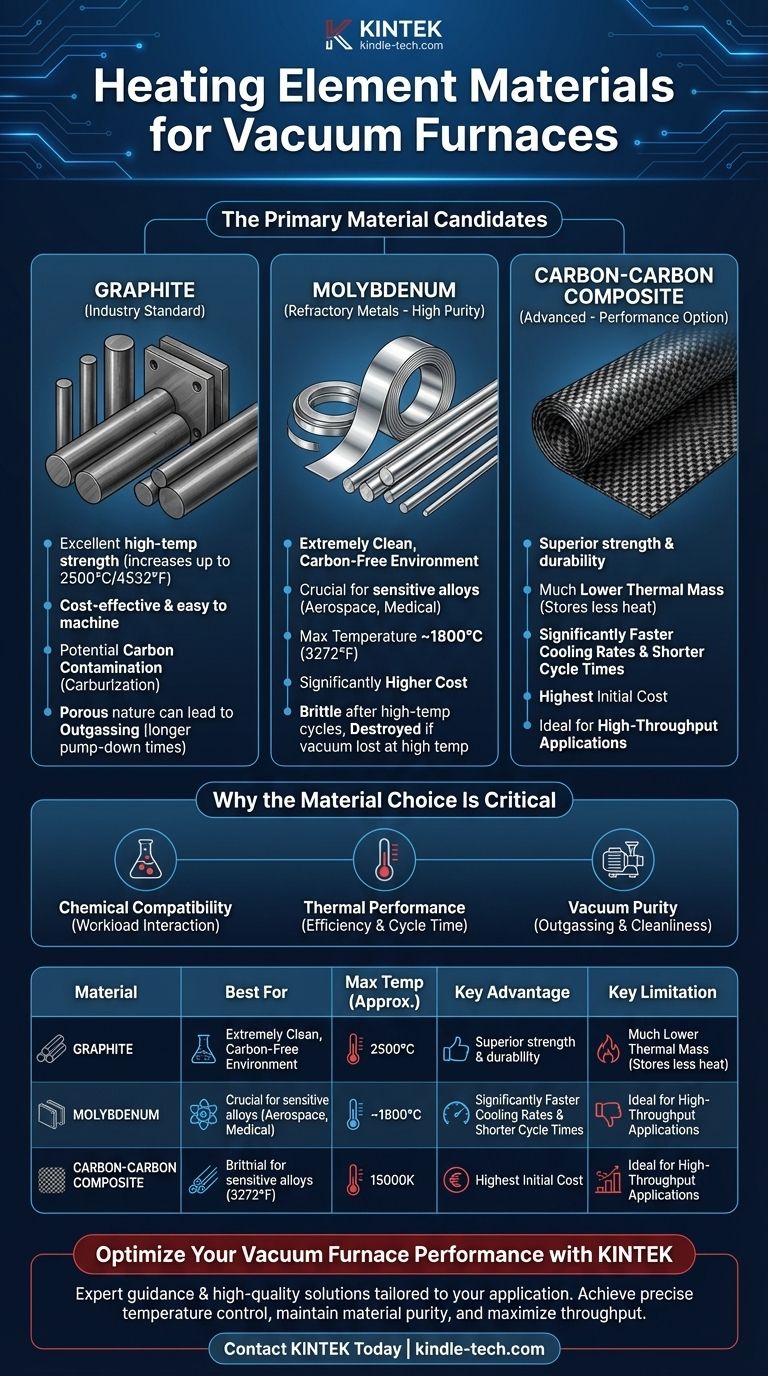
The choice of heating element material for a vacuum furnace is a critical design decision, not a one-size-fits-all specification. The most common materials are high-purity graphite and certain refractory metals, primarily molybdenum. More advanced applications may use carbon-carbon composites for their superior thermal properties. The selection depends entirely on the required operating temperature, the chemical sensitivity of the parts being processed, and performance goals like heating and cooling rates.
The material used for a heating element is not just a component; it is the core of the furnace's thermal and chemical environment. Your choice between graphite and metal directly dictates the types of processes you can run, the purity you can achieve, and the overall operational efficiency of the system.
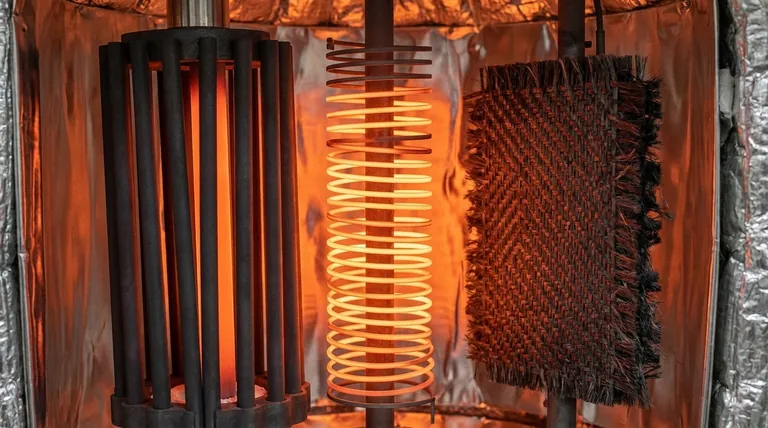
The Primary Material Candidates
Vacuum furnaces operate in an oxygen-free environment, allowing for the use of materials that would quickly oxidize and fail in a traditional air-fired furnace. This opens the door to two main classes of materials: graphite-based and refractory metal-based.
Graphite: The Industry Standard
Graphite is the most widely used material for vacuum furnace heating elements, typically formed into robust rods or curved plates.
Its popularity stems from its excellent high-temperature strength, which actually increases with temperature up to around 2500°C (4532°F). It is also relatively cost-effective and easy to machine into complex shapes.
Refractory Metals: The High-Purity Choice
For applications where any risk of carbon contamination is unacceptable, an all-metal hot zone is used. The most common heating element material in this design is molybdenum.
Molybdenum elements, often in the form of thin strips or rods, provide an extremely clean heating environment. This is crucial when processing certain medical alloys, aerospace components, or materials that react negatively with carbon.
Advanced Composites: The Performance Option
A more recent development is the use of carbon-carbon composite (CFC) materials. These are created by reinforcing a graphite matrix with carbon fibers.
CFC elements offer superior strength and durability compared to standard graphite. Their key advantage is a much lower thermal mass, meaning they store less heat. This allows for significantly faster cooling rates, which can shorten overall cycle times and increase throughput.
Why the Material Choice Is Critical
Selecting a heating element goes far beyond just its ability to get hot. The material's properties have a direct and significant impact on the entire heat-treating process.
Impact on Chemical Compatibility
The most important factor is the chemical interaction between the heating element and the parts being processed (the "workload").
Graphite elements can introduce trace amounts of carbon into the furnace atmosphere, a phenomenon known as "carburization." While insignificant for most steels, this can be detrimental to materials like titanium or certain refractory alloys. In these cases, a molybdenum element is essential.
Influence on Thermal Performance
The physical properties of the element material affect the furnace's efficiency. Graphite elements are typically thicker and have a higher thermal mass.
By contrast, the thin strips of a molybdenum element or the lightweight nature of carbon-carbon composites store far less heat. This enables the furnace to cool down much faster once power is shut off, shortening the processing cycle.
Considerations for Vacuum Purity
The furnace's ability to achieve and hold a deep vacuum is also influenced by the hot zone materials. Graphite is porous and can absorb moisture and other contaminants from the air when the furnace is open.
During the heating cycle, these absorbed molecules are released in a process called "outgassing," which the vacuum pumps must work to remove. Metal hot zones are far less porous and generally allow for cleaner operation and deeper vacuum levels more quickly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every material choice involves a balance of performance, cost, and operational limitations. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for a specific task.
Graphite: Cost vs. Contamination
- Advantage: Relatively low cost, excellent high-temperature strength, and robust mechanical properties make it a reliable workhorse.
- Disadvantage: It is a potential source of carbon contamination and its porous nature can lead to outgassing, increasing pump-down times.
Molybdenum: Purity vs. Brittleness
- Advantage: Provides an exceptionally clean, carbon-free heating environment, ideal for sensitive materials.
- Disadvantage: It is significantly more expensive than graphite and becomes brittle after repeated high-temperature cycles, requiring more careful handling. It will also be destroyed if the vacuum is lost at high temperatures.
Carbon-Carbon Composites: Performance vs. Price
- Advantage: Offers superior strength, damage resistance, and low thermal mass for the fastest possible heating and cooling cycles.
- Disadvantage: Carries the highest initial cost of the three options, making it a choice for high-performance, high-throughput applications where cycle time is critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct material, you must first define your primary operational goal. The answer flows directly from that priority.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating and cost-effectiveness: Graphite is the most common and reliable choice for a wide range of applications.
- If your primary focus is processing materials sensitive to carbon contamination: A refractory metal element, such as molybdenum, is the necessary selection to ensure product purity.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput with rapid cooling cycles: Advanced carbon-carbon composites offer the best thermal performance, despite their higher initial cost.
Ultimately, selecting the correct heating element material is a foundational step in ensuring your vacuum furnace operates with the required precision, purity, and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Material | Best For | Max Temperature (Approx.) | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | General-purpose heat treating, cost-effectiveness | ~2500°C (4532°F) | High strength at temperature, cost-effective | Potential carbon contamination, outgassing |
| Molybdenum | High-purity processes (aerospace, medical alloys) | ~1800°C (3272°F) | Carbon-free, clean environment | High cost, brittle at high temperatures |
| Carbon-Carbon Composite | High-throughput, rapid heating/cooling cycles | >2000°C (3632°F) | Low thermal mass, fast cycling, durable | Highest initial cost |
Optimize Your Vacuum Furnace Performance with KINTEK
Selecting the right heating element is critical to your process success. The wrong choice can lead to contamination, inefficient cycles, and damaged products. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and high-quality vacuum furnace solutions tailored to your specific application—whether you require the cost-effectiveness of graphite, the ultra-clean environment of molybdenum, or the rapid cycling of carbon-carbon composites.
Let our experts help you achieve precise temperature control, maintain material purity, and maximize your furnace's throughput.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation to ensure your furnace is equipped with the ideal heating element for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum annealing furnace serve in enhancing Co40Fe40B10Dy10 films? Unlock Peak Magnetic Performance
- Does sintering increase density? Master the Thermal Process for Superior Material Performance
- What keeps the mould together in vacuum casting? Harness Atmospheric Pressure for Perfect Casts
- What are the benefits of a heat treatment furnace? Achieve Precise Control Over Material Properties
- What is the process of vacuum heat treating? Achieve Superior Hardening with a Clean, Bright Finish
- Will heat transfer occur in vacuum? Yes, Through Radiation, the Sun's Method
- Can heat transfer occur in a vacuum? Yes, through radiation, the only way heat travels in space.
- What role does a high-precision tempering furnace play in 42CrMo4 steel treatment? Optimize Strength and Toughness



















