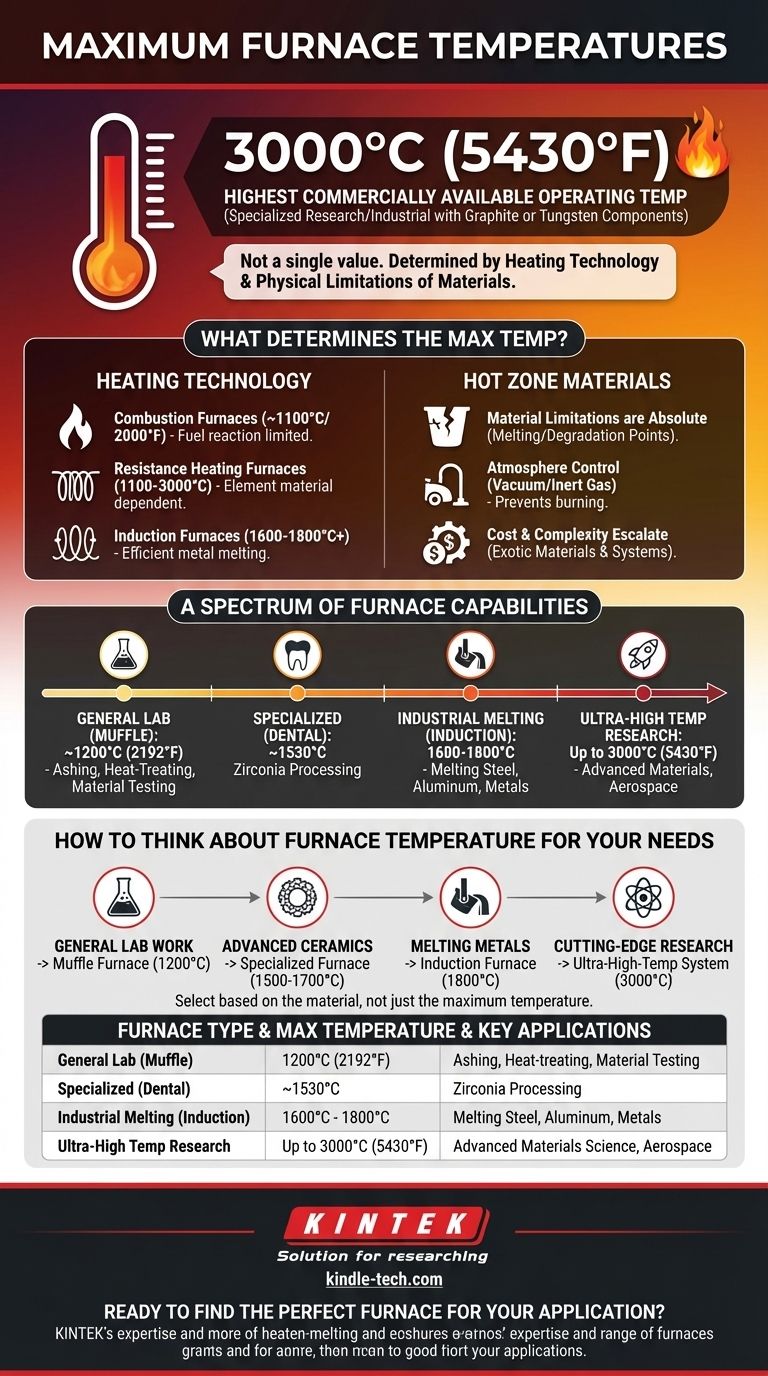
The highest operating temperature for a commercially available furnace is approximately 3000°C (5430°F). This level of extreme heat is achievable only in highly specialized research and industrial furnaces that use graphite or tungsten components for their heating elements and insulation, as very few materials can withstand such conditions.
The maximum temperature of a furnace is not one single value. It is fundamentally determined by the heating technology used and the physical limitations of the materials from which the furnace itself is constructed.
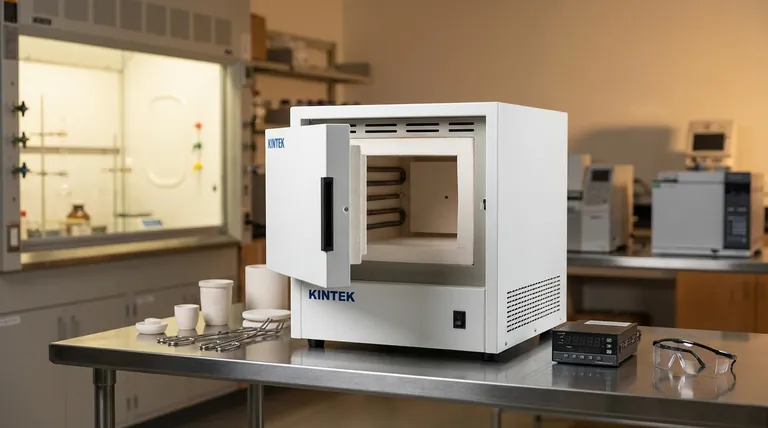

What Determines a Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
The key to understanding furnace capabilities is to look at the method used to generate heat. Different technologies have vastly different thermal ceilings.
The Heating Technology
A furnace's temperature limit is set by its heating source. A natural gas flame simply cannot burn as hot as a specialized resistive element.
- Combustion Furnaces: These, like a natural gas furnace, generate heat by burning fuel. Their maximum temperatures are limited by the chemical reaction of the fuel and are typically around 1100°C (2000°F).
- Resistance Heating Furnaces: These work by passing a large electrical current through a heating element. Their limits depend entirely on the element's material.
- Common Muffle Furnaces: Use robust metallic or ceramic elements and typically operate in the 1100°C to 1200°C range, with some specialized models reaching 1700°C.
- Ultra-High Temperature Furnaces: Use advanced materials like graphite or tungsten for their elements, allowing them to reach 3000°C.
- Induction Furnaces: These use electromagnetic induction to heat a conductive material directly. They are very efficient for melting metals and can readily reach temperatures of 1600°C to 1800°C or higher.
The "Hot Zone" Materials
A furnace cannot get hotter than its own internal components can withstand. The insulation, chamber walls, and element supports must all survive the target temperature. This is why reaching 3000°C requires exotic and expensive materials like tungsten and high-purity graphite.
A Spectrum of Furnace Capabilities
Furnaces are tools designed for specific jobs. Their temperature ranges reflect their intended purpose, from general lab work to cutting-edge research.
General-Purpose Lab Furnaces (Muffle)
Muffle furnaces are common in laboratories for applications like ashing, heat-treating, and material testing. Their typical maximum temperature is around 1200°C (2192°F).
Specialized Process Furnaces (Dental)
Many industries require furnaces designed for a single material. For example, dental furnaces for processing zirconium oxide are built to operate at a specific maximum temperature, often around 1530°C.
Industrial Melting Furnaces (Induction)
Used heavily in metallurgy for melting steel, aluminum, and other metals, induction furnaces are designed for efficiency and speed, operating in the 1600°C to 1800°C range.
Ultra-High Temperature Research Furnaces
These systems, capable of reaching 3000°C, are not common. They are used in advanced materials science to create or test materials for aerospace, nuclear, and other extreme-environment applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or understanding a furnace isn't just about finding the highest number. Higher temperatures introduce significant complexity and cost.
Material Limitations are Absolute
The single most important factor is the melting or degradation point of the furnace components. You cannot build a 2000°C furnace out of materials that melt at 1800°C. This is the fundamental law of furnace design.
Atmosphere Control is Critical
At very high temperatures, oxygen becomes incredibly reactive. A graphite element operating in the presence of air would instantly burn up. Therefore, ultra-high-temperature furnaces must operate with a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon) to protect their internal components.
Cost and Complexity Escalate
The move from a standard 1200°C furnace to a 3000°C system is not a small step. It involves a massive jump in cost due to exotic materials, precision engineering, and the complex vacuum and cooling systems required.
How to Think About Furnace Temperature for Your Needs
The right furnace is defined by the task, not by a catalogue's maximum temperature rating.
- If your primary focus is general lab work (ashing, basic heat treating): A standard muffle furnace operating up to 1200°C is the industry workhorse.
- If your primary focus is processing advanced ceramics (like zirconia): You require a specialized furnace engineered specifically for the 1500°C to 1700°C range.
- If your primary focus is melting most common metals: An induction furnace capable of reaching 1800°C provides the necessary heat and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge materials research: An ultra-high-temperature system, potentially reaching 3000°C, is necessary and involves significant investment.
Ultimately, selecting a furnace begins not with its maximum temperature, but with a clear understanding of the material you need to heat.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| General Lab (Muffle) | 1200°C (2192°F) | Ashing, heat-treating, material testing |
| Specialized (Dental) | ~1530°C | Zirconia processing |
| Industrial Melting (Induction) | 1600°C - 1800°C | Melting steel, aluminum, metals |
| Ultra-High Temp Research | Up to 3000°C (5430°F) | Advanced materials science, aerospace |
Ready to Find the Perfect Furnace for Your Application?
Whether you need a reliable workhorse for daily lab tasks or a specialized system for advanced materials research, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your exact temperature requirements. Our range of high-quality lab furnaces, from standard muffle furnaces to ultra-high-temperature systems, is designed to deliver precision, durability, and performance.
Let us help you select the right furnace for your specific material and process needs. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does pressure affect pyrolysis? Control Product Yields from Bio-oil to Syngas
- What is bio-oil in biomass? A Guide to the Liquid Fuel from Pyrolysis
- Do cannabinoids evaporate? How to Preserve Potency and Prevent Degradation
- What does the sample size depend on? Master the 3 Key Factors for Accurate Research
- What is the minimum melting-temperature for brazing material? The 450°C Threshold Explained
- What are the basics of an electric arc furnace? A Guide to Efficient Metal Recycling
- What is sintered steel used for? Creating High-Performance, Complex Metal Components
- What is the advantage of magnetron sputtering? High-Quality, Dense Thin Films at High Deposition Rates



















