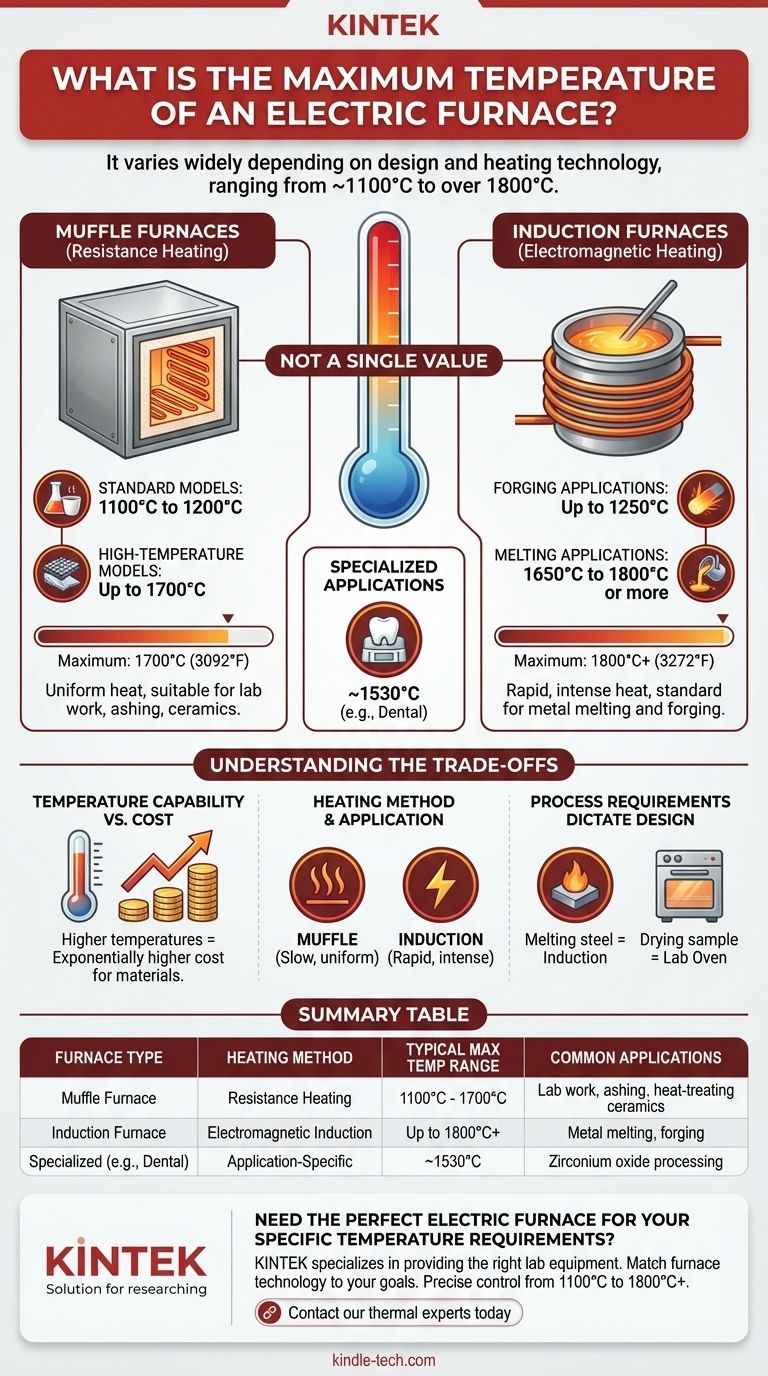
The maximum temperature of an electric furnace is not a single value but varies widely depending on its design and heating technology. Standard electric muffle furnaces often operate in the 1100°C to 1700°C (2012°F to 3092°F) range, while more advanced induction furnaces can easily exceed 1800°C (3272°F) for applications like metal melting.
The critical takeaway is that the term "electric furnace" describes several distinct technologies. The furnace's maximum temperature is fundamentally determined by its heating method—primarily resistance heating (in muffle furnaces) or electromagnetic induction—and its intended industrial or laboratory application.
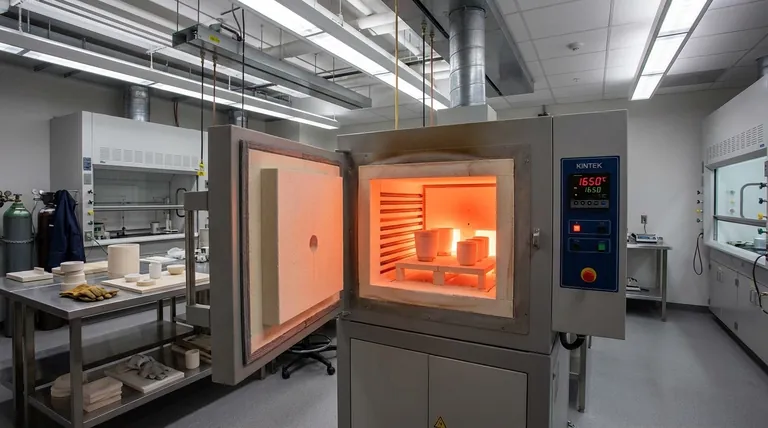

Understanding the Different Types of Electric Furnaces
The phrase "electric furnace" is a broad category. The technology used to generate heat dictates the unit's performance, cost, and ultimate temperature limit. Two primary types dominate the landscape: muffle furnaces and induction furnaces.
Muffle Furnaces (Resistance Heating)
A muffle furnace is a common type of electric furnace, especially in laboratory and small-scale industrial settings. It uses electric resistance heating elements to heat an insulated chamber, or "muffle."
These furnaces provide excellent temperature uniformity but have a ceiling based on the materials used for the heating elements and insulation. The temperature range found in typical models can vary significantly.
- Standard Models: Often reach a maximum temperature of 1100°C to 1200°C.
- High-Temperature Models: Specialized units designed for advanced materials can achieve up to 1700°C.
Induction Furnaces (Electromagnetic Heating)
Induction furnaces operate on a completely different principle. They use powerful alternating magnetic fields to induce an electric current directly within the metallic material (the charge) inside the furnace.
This direct heating method is extremely fast and efficient, allowing it to reach much higher temperatures. It is the standard for metal melting and forging industries.
- Forging Applications: Typically operate up to 1250°C.
- Melting Applications: Can readily achieve 1650°C to 1800°C or more, depending on the specific metal and furnace design.
Specialized Application Furnaces
Many electric furnaces are designed for a single, highly specific task, which dictates their maximum temperature.
For example, a dental furnace used for processing zirconium oxide materials is calibrated for a maximum temperature around 1530°C. This is not its absolute physical limit, but the temperature required to successfully process the intended material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace isn't just about finding the highest possible temperature. The right choice depends on a balance of performance, cost, and the specific requirements of your process.
Temperature Capability vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between a furnace's maximum temperature and its cost. The materials required for heating elements, insulation, and power control systems become exponentially more expensive as the target temperature increases. A furnace rated for 1800°C is a far more significant investment than one rated for 1200°C.
Heating Method and Application
The way a furnace heats material is as important as how hot it gets.
A muffle furnace provides slow, stable, and uniform heat, which is ideal for processes like annealing, ashing, or heat-treating ceramics where precise control over time and temperature is critical.
An induction furnace delivers rapid, intense heat directly to the material. This is perfect for melting metals quickly but is unsuitable for processes that require gradual heating.
Process Requirements Dictate Design
The ultimate decision is driven by the material you are working with. Melting steel requires the high temperatures of an induction furnace, while drying a scientific sample may only require a few hundred degrees in a simple lab oven.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate equipment, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is general lab work, ashing, or heat-treating up to 1200°C: A standard electric muffle furnace is the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is processing high-performance ceramics or materials requiring up to 1700°C: You will need a specialized high-temperature chamber or muffle furnace.
- If your primary focus is melting metals or achieving temperatures above 1700°C: An induction furnace is the necessary technology for the task.
Ultimately, the key is to match the furnace's capabilities precisely to the thermal requirements of your specific material and process.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Heating Method | Typical Max Temperature Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | Resistance Heating | 1100°C - 1700°C | Lab work, ashing, heat-treating ceramics |
| Induction Furnace | Electromagnetic Induction | Up to 1800°C+ | Metal melting, forging |
| Specialized (e.g., Dental) | Application-Specific | ~1530°C | Zirconium oxide processing |
Need the Perfect Electric Furnace for Your Specific Temperature Requirements?
KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment for your unique thermal processing needs. Whether you require the uniform heating of a muffle furnace for precise laboratory work or the intense heat of an induction system for metal melting, our experts will help you select the ideal solution.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Match furnace technology (resistance or induction) to your material and process goals.
- Precise Temperature Control: Equipment rated from 1100°C to 1800°C+ for any application.
- Reliable Performance: Durable furnaces and consumables designed for laboratory and industrial use.
Don't guess on temperature limits—get a solution tailored for your success.
Contact our thermal experts today to discuss your project and find the perfect electric furnace!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do high-temperature furnaces and ceramic crucibles impact Li-ion battery stability? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is the use of electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What is the use of furnace in laboratory? Unlock Material Transformation for Your Research
- What is the annealing temperature of quartz? Achieve Optimal Thermal Stability for Your Components
- What is an electric muffle furnace? Achieve Unmatched Thermal Purity and Uniformity



















