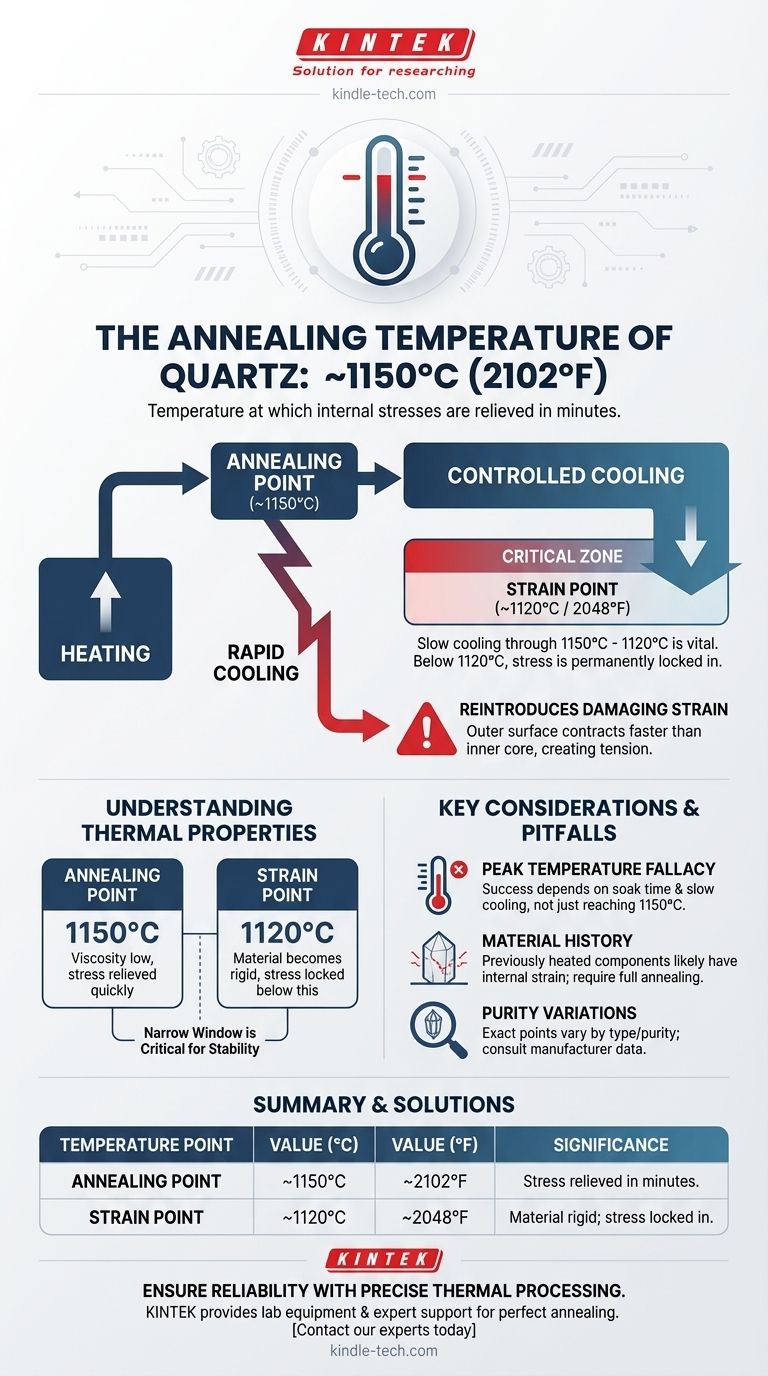
The annealing temperature of quartz is approximately 1150°C (2102°F). This is the temperature at which internal stresses within the material can be relieved in a matter of minutes. This value generally applies to both crystalline quartz and amorphous silica glass, such as fused quartz.
The key to successfully working with quartz is not just reaching the 1150°C annealing temperature, but managing the cooling process. Cooling too quickly from above the strain point of 1120°C will undo the benefits of annealing by re-introducing damaging internal stress.

The Difference Between Annealing and Strain Points
Understanding the thermal properties of quartz requires knowing two critical temperature thresholds: the annealing point and the strain point. They are close in value but represent very different states of the material.
What is the Annealing Point?
The annealing point is the temperature where the viscosity of the glass is low enough to relieve internal stresses relatively quickly.
At 1150°C, quartz becomes just soft enough for its internal atomic structure to rearrange, releasing the mechanical tension that can lead to fractures or optical distortions.
What is the Strain Point?
The strain point is a lower temperature threshold, approximately 1120°C for quartz. Below this point, the material is essentially rigid, and any internal stress is permanently locked in.
Between the strain point and the annealing point, stress can still be relieved, but it takes an exponentially longer time (hours instead of minutes).
Why This Distinction Matters
The narrow window between the annealing point (1150°C) and the strain point (1120°C) is the most critical phase of the thermal process.
While stress is removed at the higher temperature, new stress is introduced if the material cools too quickly through this range. The cooling rate determines the final stability of the product.
The Critical Role of Cooling Rate
Simply heating quartz is not enough. The success of the annealing process is defined by how the material is cooled.
The Goal of Annealing
The primary purpose of annealing is to remove internal stress. This stress is often introduced during manufacturing or from rapid temperature changes during use.
Eliminating this stress is essential for improving the mechanical strength and optical performance of the quartz component, preventing unexpected failure.
How Rapid Cooling Reintroduces Strain
When quartz is cooled quickly from above its strain point, the outer surface cools and contracts faster than the interior.
This difference in contraction creates a powerful tension between the outer "skin" and the inner core. If this happens while the material is still pliable (above 1120°C), that stress becomes a permanent, damaging feature.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes in the thermal processing of quartz are common and can easily lead to component failure.
The "Peak Temperature" Fallacy
A frequent error is focusing only on reaching the 1150°C annealing temperature. The soak time at that temperature and, most importantly, the slow cooling ramp that follows are equally critical to the outcome.
Ignoring the Material's History
If a quartz product has been used at high temperatures and cooled in ambient air, it has likely developed significant internal strain. It cannot be considered stable without a proper annealing cycle.
Assuming All Quartz is Identical
While 1150°C is a reliable figure, the exact annealing and strain points can vary slightly based on the purity and specific type of quartz or fused silica. For high-precision applications, consulting the material manufacturer's datasheet is always advisable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to heating and cooling should be dictated by your final objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum stability and fracture prevention: Heat to ~1150°C, hold to ensure a uniform temperature, and then cool at a very slow, controlled rate, especially through the 1150°C to 1120°C range.
- If you are working with high-precision optics: The cooling rate is paramount. Even minor residual stress can cause an optical defect known as birefringence, so an extremely slow and controlled cooling process is non-negotiable.
- If a component has been used at high temperatures: Assume it has developed strain. To restore its properties and prevent future failure, it must undergo a full annealing cycle before being returned to service.
Properly managing the entire thermal cycle, not just the peak temperature, is the key to ensuring the reliability and performance of quartz components.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Point | Value (°C) | Value (°F) | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annealing Point | ~1150°C | ~2102°F | Stress is relieved in minutes. |
| Strain Point | ~1120°C | ~2048°F | Material becomes rigid; stress is locked in below this point. |
Ensure the reliability of your quartz components with precise thermal processing. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and expert support needed for perfect annealing cycles. From high-temperature furnaces to technical guidance, we help you achieve maximum stability and performance for your laboratory applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific quartz processing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the use of furnace in laboratory? Unlock Material Transformation for Your Research
- What is the use of electric muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, High-Temperature Processing
- What are the disadvantages of dry ashing? Key Limitations for Accurate Elemental Analysis
- What is the thermal debinding process? A Guide to Safe Binder Removal for MIM & Ceramics
- What is the difference between a furnace and an oven in a laboratory? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Heat Needs



















