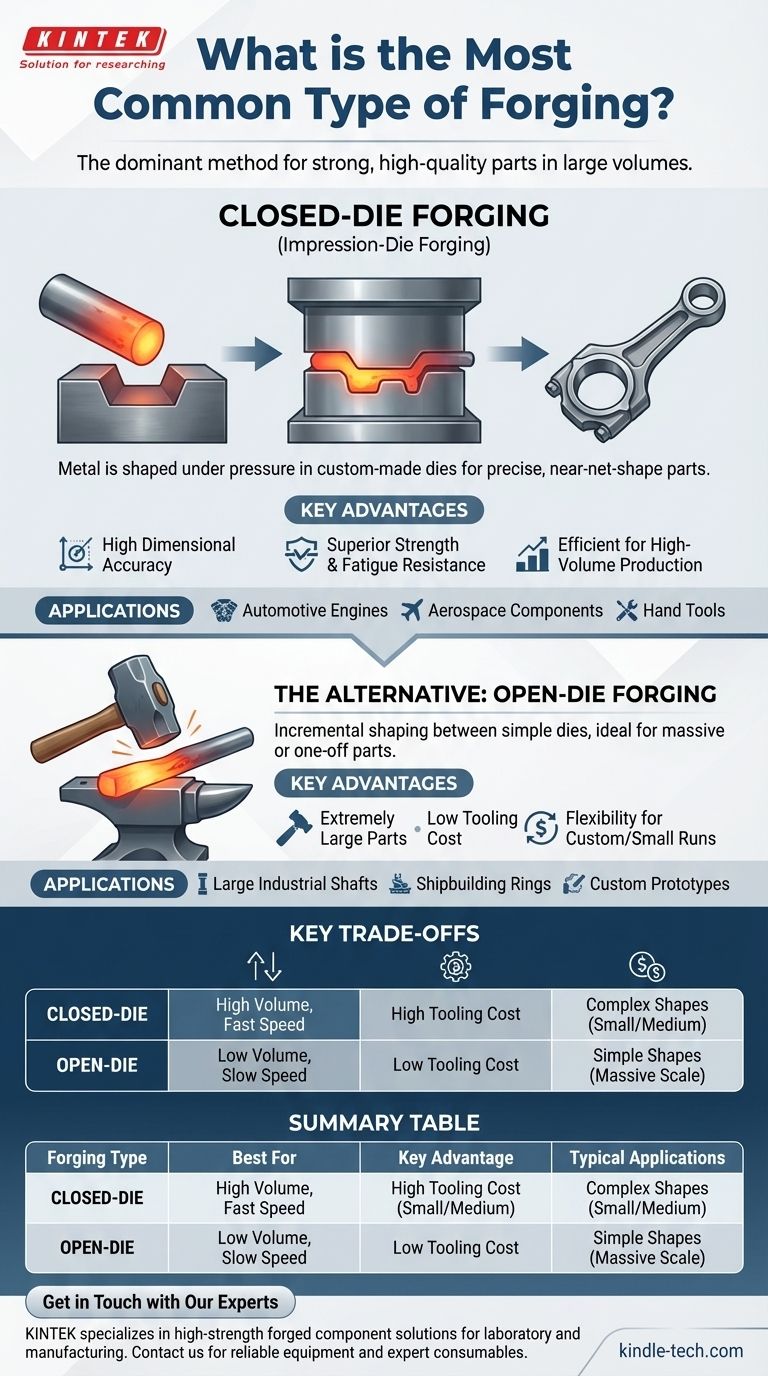
In industrial manufacturing, the most common type of forging is closed-die forging, also known as impression-die forging. This method is the dominant choice for producing strong, high-quality parts in large volumes, from automotive connecting rods to aerospace components and common hand tools. Its prevalence is due to its ability to create complex shapes with excellent dimensional accuracy and minimal material waste.
The choice between forging methods is fundamentally a decision between scale and specificity. Closed-die forging excels at producing vast quantities of precise, identical parts, while open-die forging offers flexibility for creating large, simpler components in low volumes.

Understanding Closed-Die Forging (Impression-Die)
Closed-die forging is a process where a pre-formed metal billet is squeezed between two custom dies that contain a precise impression of the final part shape. The metal is forced to flow and fill the die cavities completely.
The Core Process: Shaping Under Pressure
The process is analogous to using a mold. A heated metal workpiece is placed on the lower die, and the upper die is forced down upon it. The intense pressure ensures the metal conforms to the exact shape of the die impressions, creating a near-net-shape part.
Key Advantages: Precision and Repeatability
The primary benefit of closed-die forging is its ability to produce parts with high dimensional accuracy and a superior surface finish. This method also refines the metal's internal grain structure, aligning it with the part's shape and significantly enhancing its strength and fatigue resistance.
Where It's Used: High-Volume Production
This method is the backbone of industries requiring strong, reliable components at scale. You will find closed-die forged parts in automotive engines, aircraft structural components, industrial equipment, and agricultural machinery.
The Alternative: Open-Die Forging
Open-die forging is the most traditional form of the process, reminiscent of a blacksmith using a hammer and anvil. The metal workpiece is shaped between two dies that do not fully enclose it, allowing the metal to flow outward as it is struck or pressed.
The Core Process: Incremental Shaping
Instead of a single impression, open-die forging relies on a series of compressions and manipulations to gradually shape the part. The operator, or a computer-controlled system, rotates and moves the workpiece between strikes to achieve the desired form.
Key Advantages: Size and Flexibility
The main advantage of open-die forging is its ability to produce extremely large parts—some weighing tens of thousands of pounds—that would be impossible to create in a closed die. It requires much simpler, less expensive tooling and is ideal for one-off parts or small production runs.
Where It's Used: Custom and Heavy-Duty Parts
Open-die forging is used to create large shafts, rings, and discs for industrial machinery, shipbuilding, and power generation. It is the go-to process for custom-made components or prototypes where creating expensive closed dies is not feasible.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
The choice between these two primary forging methods involves a direct trade-off between upfront investment, production speed, and part complexity.
Tooling Cost and Lead Time
Closed-die forging requires significant upfront investment in custom-machined dies, which can be complex and time-consuming to produce. In contrast, open-die forging uses simple, often flat or basic dies that are inexpensive and readily available.
Production Volume and Speed
Once the tooling is created, closed-die forging is extremely fast and efficient, making it ideal for high-volume runs where the per-part cost drops significantly. Open-die forging is a much slower, more labor-intensive process, better suited for individual pieces or very small batches.
Part Complexity vs. Size
Closed-die forging excels at producing intricate, complex shapes with tight tolerances. However, it is generally limited to smaller or medium-sized components. Open-die forging is best for simpler, often symmetrical shapes but can handle parts of a massive scale and weight.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate process, you must first define your project's most critical constraint.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of complex, strong parts: Closed-die forging is the clear and most common industrial choice.
- If your primary focus is producing a very large, simple component or a single prototype: Open-die forging provides the necessary flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Ultimately, understanding the strengths of each process allows you to align the manufacturing method with your specific design and business requirements.
Summary Table:
| Forging Type | Best For | Key Advantage | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Closed-Die Forging | High-volume production of complex parts | High dimensional accuracy & superior strength | Automotive engines, aerospace components, hand tools |
| Open-Die Forging | Large, simple parts & low-volume/custom work | Flexibility for massive sizes & low tooling cost | Large shafts, industrial rings, custom prototypes |
Need High-Strength Forged Components for Your Laboratory or Manufacturing Process?
KINTEK specializes in providing the equipment and consumables that support advanced manufacturing processes like forging. Whether your R&D or production requires durable, precision parts, understanding the right manufacturing method is key.
Let us help you achieve your goals:
- Source Reliable Lab Equipment for materials testing and analysis.
- Access Expert Consumables that meet the demands of high-performance manufacturing.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory and production needs with precision equipment and supplies.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Ring Press Mold for Lab Applications
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory hydraulic press for powder compaction? Achieve Precise Pellet Densification
- Why KBr is used for pellet? Master FTIR Sample Prep for Clear, Reliable Spectra
- Why is a uniaxial hydraulic press utilized for cold-pressing metal powders? Enhance Your Sintering Quality
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in battery assembly? Ensure Superior Structural Integrity & Data.
- How do you prepare a KBr pellet for IR spectroscopy? Master the Key Steps for a Clear Spectrum
- How is a laboratory hydraulic press utilized in the preparation of TiC/Ti composite green compacts? Expert Guide
- What are the safety precautions for KBr? Achieve Flawless FTIR Pellet Preparation and Data Accuracy
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press serve in copper-nickel alloy forming? Achieve High-Density Green Bodies















