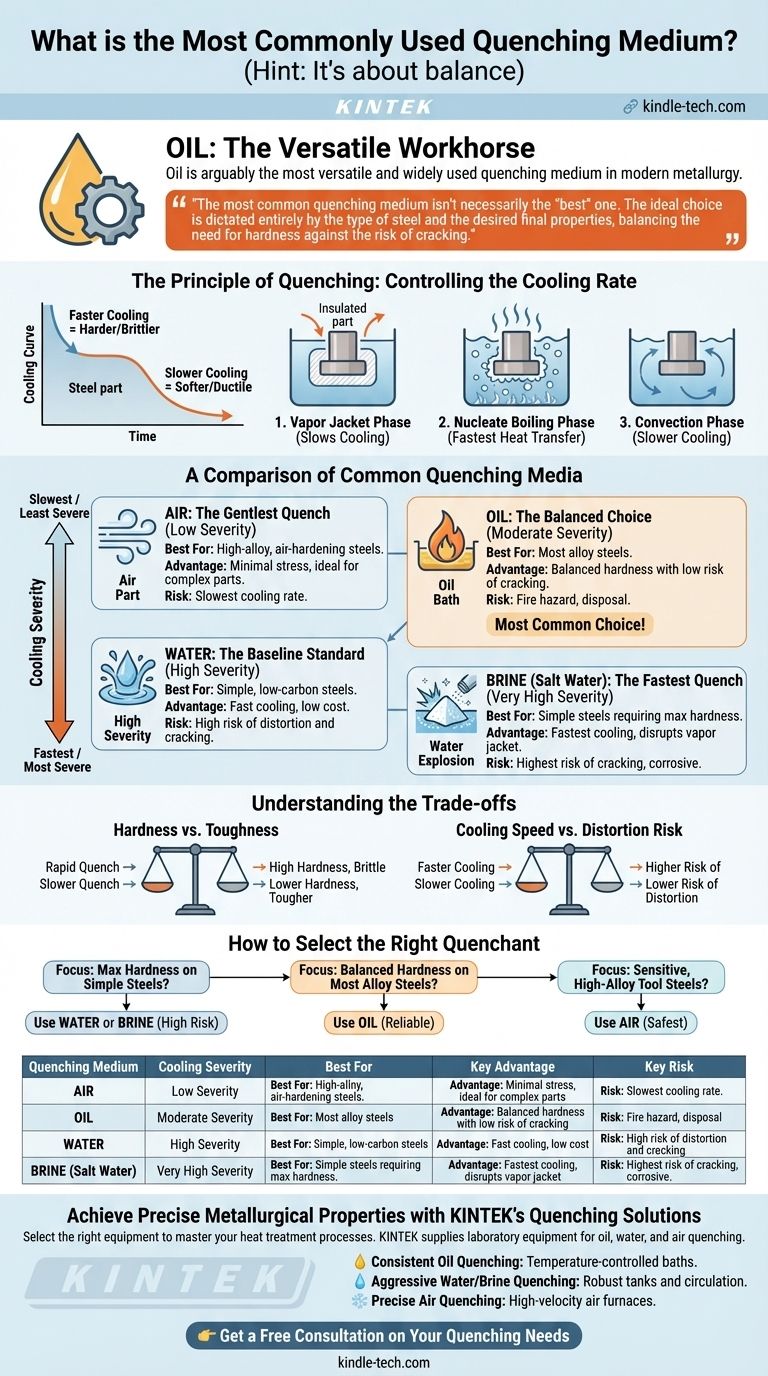
While no single medium is used for all applications, oil is arguably the most versatile and widely used quenching medium in modern metallurgy. It offers a controlled cooling rate that is fast enough to harden most common alloy steels but slow enough to minimize the risk of distortion and cracking, a major concern with more aggressive quenchants like water or brine.
The most common quenching medium isn't necessarily the "best" one. The ideal choice is dictated entirely by the type of steel and the desired final properties, balancing the need for hardness against the risk of cracking.
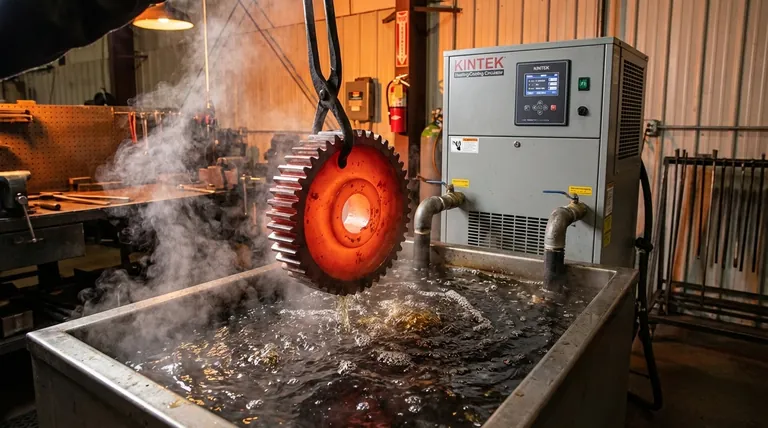

The Principle of Quenching: Controlling the Cooling Rate
The entire purpose of quenching is to cool a heated piece of steel at a specific speed. This rate of cooling locks in a desirable microscopic structure, which in turn dictates the material's final mechanical properties.
Why Cooling Rate Matters
When steel is heated to its critical temperature, its internal crystal structure changes. If cooled very quickly, carbon atoms are trapped within this structure, forming a very hard and brittle phase called martensite.
If cooled more slowly, the atoms have time to rearrange into softer, more ductile structures like pearlite or bainite. The quenchant's job is to manage this cooling speed precisely.
The Three Stages of Liquid Quenching
When hot metal enters a liquid, it doesn't cool at a constant rate. It goes through three distinct phases:
- Vapor Jacket Phase: A layer of vapor instantly forms around the hot part, insulating it and slowing down cooling. This is known as the Leidenfrost effect.
- Nucleate Boiling Phase: The vapor jacket collapses, and violent boiling begins on the metal's surface. This is the fastest stage of heat transfer.
- Convection Phase: The metal cools below the liquid's boiling point. Heat is now transferred more slowly via simple convection.
The effectiveness of a quenchant depends on how it behaves in these three stages.
A Comparison of Common Quenching Media
Quenching media are ranked by their ability to extract heat, which is directly related to their cooling severity.
Brine (Salt Water): The Fastest Quench
Brine is a mixture of water and salt (typically sodium chloride). The salt crystals violently disrupt the initial vapor jacket, moving the part into the fast nucleate boiling phase almost immediately.
This provides the most severe quench possible but carries the highest risk of distortion and cracking. It is typically reserved for simple, low-carbon steels where maximum hardness is required.
Water: The Baseline Standard
Water offers a very fast cooling rate and is cheap and readily available. However, it tends to form a stable vapor jacket, which can lead to uneven cooling and soft spots.
Like brine, its high cooling severity creates significant internal stresses, making it suitable for simple carbon steels but too aggressive for most alloy steels.
Oil: The Versatile Workhorse
Oil provides a much slower cooling rate than water. Its higher boiling point means the initial, slow-cooling vapor jacket phase lasts longer, and the transition to the convection phase is less dramatic.
This "slower" quench is still fast enough to fully harden a wide range of alloy steels while significantly reducing the risk of thermal shock and cracking. This balance of effectiveness and safety is why oil is so common.
Air: The Gentlest Quench
For certain high-alloy steels (often called "air-hardening steels"), even oil is too severe. These materials are designed to transform to martensite with a very slow cooling rate.
Quenching is done with still or forced air. This is the gentlest method, creating minimal internal stress, and is essential for complex and dimensionally sensitive parts like tool dies.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a quenchant is a balancing act. The faster you cool the steel, the harder it gets, but the more you risk destroying the part in the process.
Hardness vs. Toughness
A rapid quench maximizes the formation of hard martensite, but this structure is also very brittle. The resulting part must almost always be tempered (reheated to a lower temperature) to restore some toughness and reduce brittleness.
The Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The primary danger in quenching is thermal shock. If one part of the component cools much faster than another, the resulting internal stresses can cause it to warp, distort, or crack catastrophically. Aggressive quenchants like water and brine greatly increase this risk.
Safety and Environmental Factors
Oil quenching carries an obvious fire risk if the oil's flash point is exceeded. Furthermore, all liquid quenchants can present disposal challenges, and brine is highly corrosive to both the parts and the quenching equipment.
How to Select the Right Quenchant
Your choice must be guided by the material's hardenability—its innate ability to form martensite.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness on simple, low-alloy steels: Use water or brine, but be prepared for a high risk of cracking and distortion.
- If your primary focus is achieving good hardness in most alloy steels with minimal risk: Oil is the most balanced and reliable choice for a wide range of applications.
- If your primary focus is treating sensitive, high-alloy tool steels: Air quenching is often the only safe method to avoid thermal shock.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment lies in selecting the quenchant that gives you precise control over the final properties of your material.
Summary Table:
| Quenching Medium | Cooling Severity | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil | Moderate | Most alloy steels | Balanced hardness with low risk of cracking | Fire hazard, disposal |
| Water | High | Simple, low-carbon steels | Fast cooling, low cost | High risk of distortion and cracking |
| Brine (Salt Water) | Very High | Simple steels requiring max hardness | Fastest cooling, disrupts vapor jacket | Highest risk of cracking, corrosive |
| Air | Low | High-alloy, air-hardening steels | Minimal stress, ideal for complex parts | Slowest cooling rate |
Achieve Precise Metallurgical Properties with KINTEK's Quenching Solutions
Selecting the right quenching medium is critical to achieving the desired hardness, toughness, and dimensional stability in your heat-treated components. The wrong choice can lead to costly scrap due to cracking or distortion.
KINTEK specializes in supplying the laboratory equipment and consumables you need to master your heat treatment processes. Whether you are quenching with oil, water, or air, having reliable and consistent equipment is paramount.
Let us help you optimize your results:
- For consistent oil quenching: Our temperature-controlled baths ensure uniform cooling.
- For aggressive water or brine quenching: We provide robust tanks and circulation systems.
- For precise air quenching: Our high-velocity air furnaces offer the gentle, controlled cooling required for tool steels.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application. Our experts will help you select the right equipment to achieve perfect hardness while minimizing the risk of part failure.
👉 Get a Free Consultation on Your Quenching Needs
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 30L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- 10L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 50L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 20L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- How does a high-precision constant temperature circulator contribute to mineral dissolution kinetic studies?
- What are water baths used for? Achieve Precise & Gentle Temperature Control for Your Lab Samples
- How does a water bath work? Master Precise and Gentle Heating for Your Lab
- What is the function of a constant temperature water bath in CO2 absorption kinetics? Achieve High-Precision Research
- What role does a high-precision constant temperature circulating water bath play in AEM research? Stability & Control



















