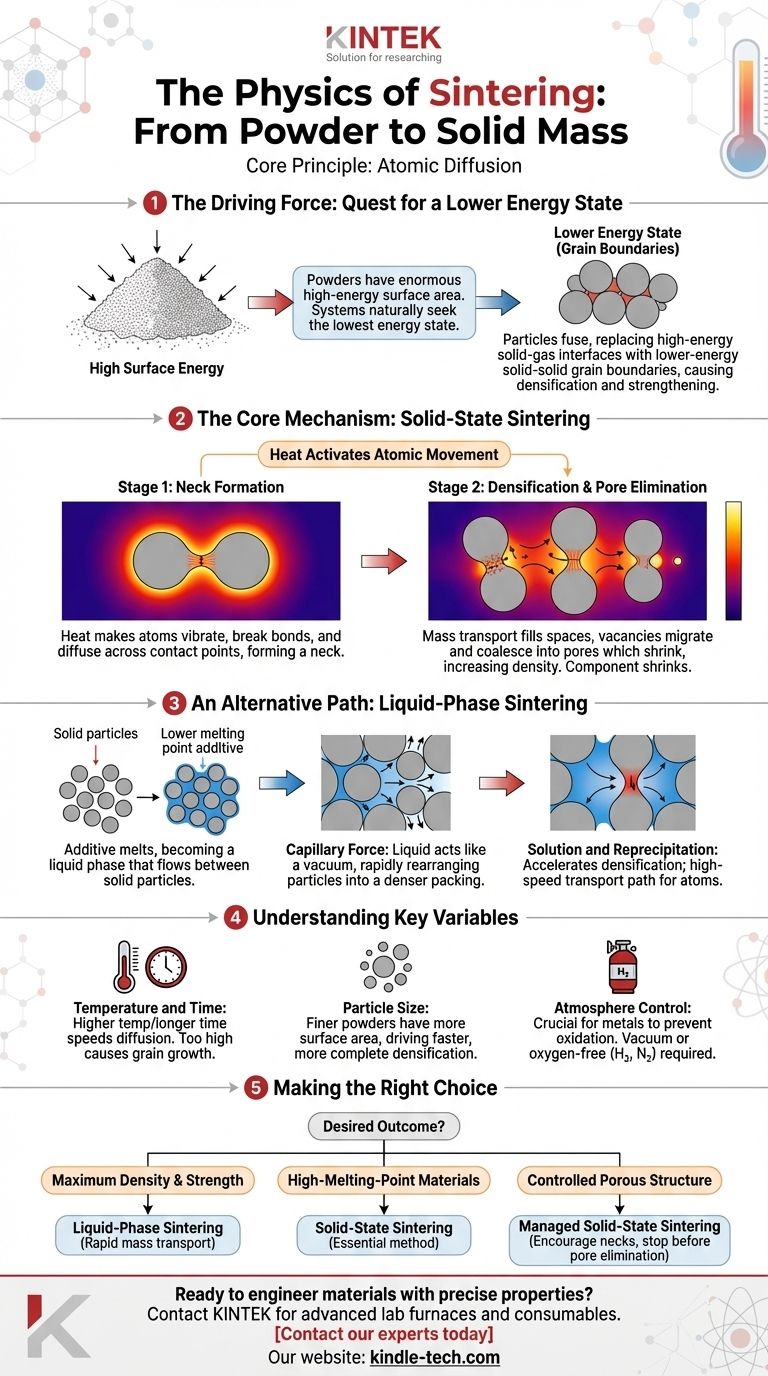
At its core, the physics of sintering is about atomic diffusion. It is a thermally-activated process where individual particles of a material, heated to a temperature below their melting point, fuse together. The added heat gives atoms enough energy to migrate across the boundaries where particles touch, gradually eliminating the empty spaces between them and forming a single, densified solid mass.
Sintering is fundamentally driven by a reduction in surface energy. A collection of fine powders has an enormous amount of high-energy surface area. By heating the powder, you enable atoms to move and replace these high-energy solid-gas interfaces with lower-energy solid-solid interfaces (known as grain boundaries), which causes the material to densify and strengthen.

The Driving Force: Why Sintering Happens
The Quest for a Lower Energy State
A pile of fine powder has an exceptionally high surface area relative to its volume. From a thermodynamic perspective, this surface represents a high-energy state. Like a ball rolling downhill, physical systems naturally seek the lowest energy state possible.
Sintering is the mechanism that allows the powder compact to move towards this lower energy state.
Replacing Surfaces with Grain Boundaries
The process works by eliminating the surface area of the individual powder particles. As particles fuse together, the surfaces that were once exposed to the furnace atmosphere are transformed into internal boundaries between the crystals, known as grain boundaries.
A solid-solid grain boundary has significantly lower energy than a solid-gas surface. This net reduction in system energy is the fundamental thermodynamic driving force behind the entire sintering process.
The Core Mechanism: Solid-State Sintering
Activating Atomic Movement with Heat
Heat provides the kinetic energy for sintering to occur. While the temperature is kept below the material's melting point, it's high enough to make the atoms vibrate vigorously within their crystal lattice.
This vibration allows atoms to break their bonds, move into adjacent empty lattice sites (vacancies), and diffuse through the material over time.
Stage 1: Neck Formation
At the very beginning of the process, particles are only touching at infinitesimally small points. When heat is applied, atoms begin to diffuse across these contact points.
This movement of material forms a small bridge, or "neck," between the adjacent particles. The formation of these necks is the first step in fusing the powder into a coherent structure.
Stage 2: Densification and Pore Elimination
As the process continues, mass transport occurs on a larger scale. Atoms move from the bulk of the particles toward the growing necks, effectively filling the space between them.
Simultaneously, vacancies (the empty spaces atoms leave behind) migrate away from the growing necks and coalesce into pores, which then shrink and are gradually eliminated. This causes the entire component to shrink and increase in density, a critical feature that must be accounted for in the initial mold design.
An Alternative Path: Liquid-Phase Sintering
When a Liquid Assists
In some processes, an additive with a lower melting point is mixed with the primary powder. When heated, this additive melts and becomes a liquid phase that flows into the spaces between the solid particles.
This method is known as liquid-phase sintering and dramatically accelerates the densification process.
The Power of Capillary Force
The liquid wets the surfaces of the solid particles, creating powerful capillary forces. These forces act like a powerful vacuum, pulling the particles together and rapidly rearranging them into a much denser packing arrangement.
Solution and Reprecipitation
The liquid phase also acts as a high-speed transport path for atoms. Solid material from the primary particles can dissolve into the liquid at high-pressure contact points and then re-precipitate (re-solidify) in the lower-pressure neck regions between particles.
This solution-reprecipitation mechanism moves material far more quickly than solid-state diffusion, allowing for faster processing and often achieving near-full density.
Understanding the Key Variables
Temperature and Time
Sintering is a function of both temperature and time. A higher temperature provides more energy for diffusion, speeding up the process. However, if the temperature is too high, it can cause undesirable grain growth, which can weaken the final part. A lower temperature can achieve the same result but requires a significantly longer time in the furnace.
Particle Size
The initial powder characteristics are critical. Finer powders have more surface area, which increases the thermodynamic driving force for sintering. This results in a faster and more complete densification process at a given temperature.
Atmosphere Control
The furnace atmosphere plays a crucial role. Most metals will rapidly oxidize at sintering temperatures. An oxide layer on the particle surfaces acts as a barrier that prevents atomic diffusion, stopping the sintering process entirely. Therefore, sintering is typically performed in a vacuum or a controlled, oxygen-free atmosphere (e.g., hydrogen or nitrogen).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The physics you leverage depends entirely on the desired outcome for the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: Liquid-phase sintering is often the superior choice, as its rapid mass transport mechanisms are highly effective at eliminating porosity.
- If your primary focus is processing very high-melting-point materials: Solid-state sintering is the essential method, as creating a useful liquid phase is often impractical for materials like tungsten or molybdenum.
- If your primary focus is creating a controlled porous structure (e.g., for filters or self-lubricating bearings): You must carefully manage solid-state sintering, encouraging neck formation between particles while stopping the process before the pores are eliminated.
By understanding these physical drivers, you can manipulate the process variables to engineer a material with the precise microstructure and properties you require.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Type | Key Mechanism | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Solid-State | Atomic diffusion across particle necks | High-melting-point materials (e.g., Tungsten) |
| Liquid-Phase | Capillary forces & solution-reprecipitation | Achieving maximum density and strength |
Ready to engineer materials with precise properties?
Understanding the physics of sintering is the first step. Applying it to achieve the perfect density, strength, and microstructure for your specific application requires the right equipment and expertise.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab furnaces and consumables for all your sintering needs. Whether you are working with high-temperature ceramics or metals requiring precise atmosphere control, our solutions are designed to deliver consistent, reliable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you optimize your sintering process and achieve your material science goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials
- Why is sintering easier in the presence of a liquid phase? Unlock Faster, Lower-Temperature Densification



















