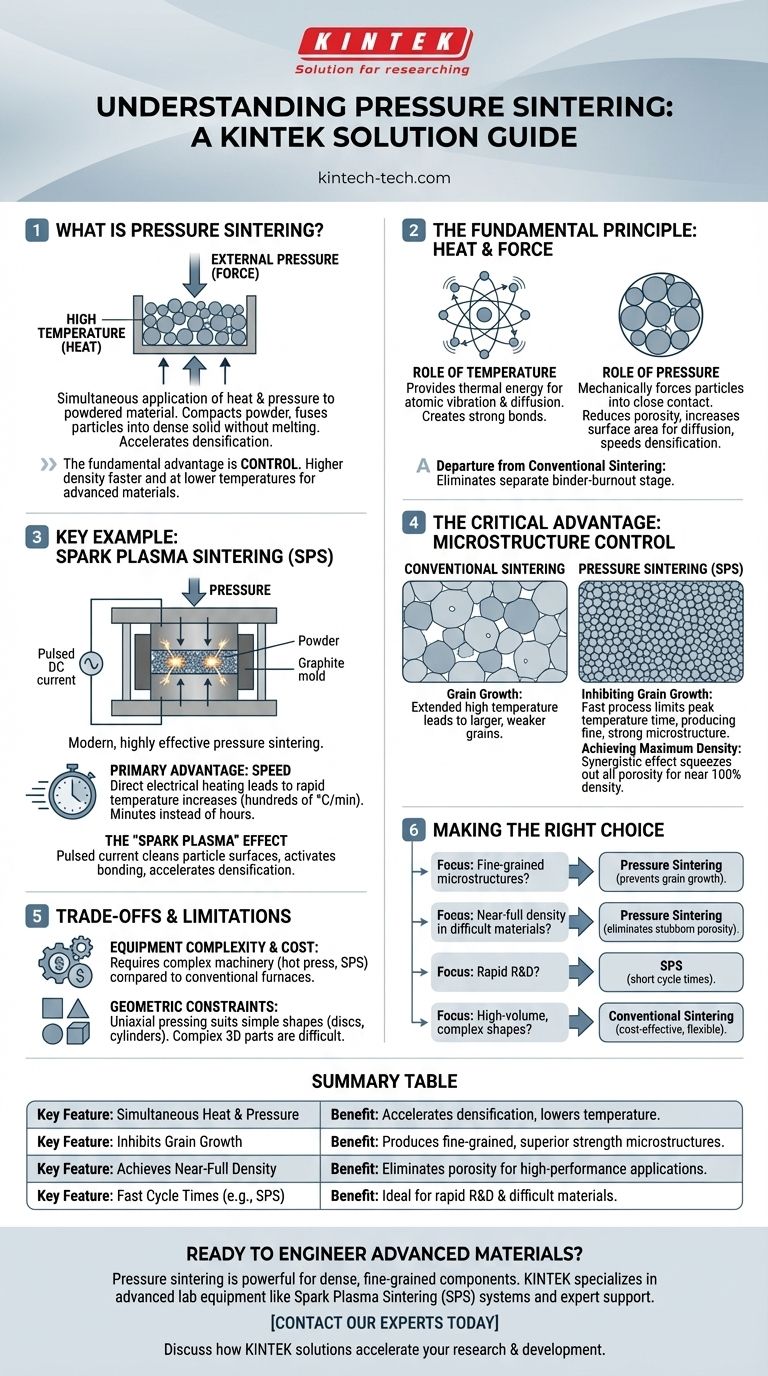
At its core, pressure sintering is a manufacturing process that simultaneously applies high temperature and external pressure to a powdered material. This combination compacts the powder and fuses the individual particles together into a dense, solid object, all without melting the material to a liquid state. The key is using pressure to accelerate the densification that would otherwise require much higher temperatures or longer processing times.
The fundamental advantage of pressure sintering is control. By actively forcing particles together while heating them, the process achieves higher density faster and at lower temperatures than conventional methods, which is critical for creating advanced materials with superior properties.
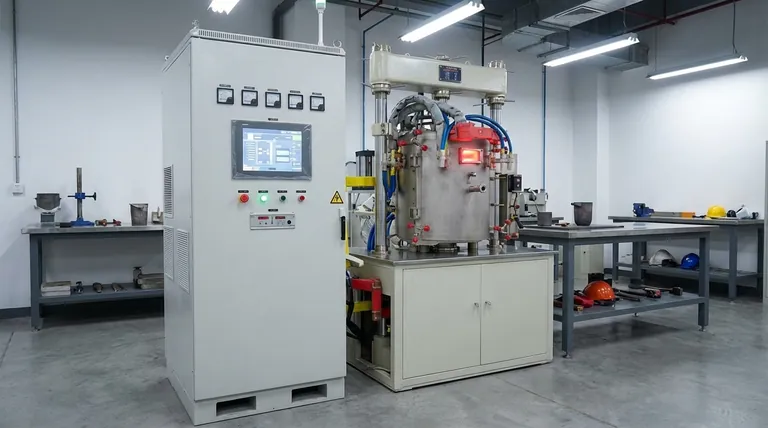

The Fundamental Principle: Combining Heat and Force
Pressure sintering enhances the natural process of atomic diffusion. Instead of relying solely on heat to encourage atoms to bond across particle boundaries, it adds a powerful mechanical assist.
The Role of Temperature
Heat provides the thermal energy necessary for the process. It makes the atoms within the material particles vibrate and move, allowing them to diffuse across the surfaces where particles touch. This atomic movement is what creates strong bonds, turning loose powder into a solid mass.
The Role of Pressure
External pressure is the defining feature of this method. It mechanically forces the powder particles into close contact, which significantly reduces the empty space (porosity) between them. This intimate contact creates more surface area for atomic diffusion to occur, dramatically speeding up the densification process.
A Departure from Conventional Sintering
Traditional sintering often involves forming a "green part" by mixing powder with a binder, compacting it, and then heating it in a furnace. During heating, the binder burns off, and the particles slowly fuse. Pressure sintering streamlines this by applying the compressive force directly during the heating cycle, eliminating the need for a separate binder-burnout stage and achieving better results.
A Key Process Example: Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)
Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is a modern and highly effective form of pressure sintering that highlights the benefits of the technique.
The Mechanism of SPS
In an SPS system, the powdered sample is placed in a conductive graphite mold. This entire assembly is then positioned between electrodes while under pressure. A high-amperage, pulsed direct current (DC) is passed directly through the graphite mold and, in some cases, the powder itself.
The Primary Advantage: Speed
This direct electrical heating results in incredibly rapid temperature increases—hundreds of degrees Celsius per minute. This allows the entire sintering process to be completed in a matter of minutes, compared to the hours often required for conventional furnace sintering.
The "Spark Plasma" Effect
The pulsed current is thought to generate momentary "sparks" or plasma discharges in the voids between powder particles. This effect helps to clean the particle surfaces and activates them for bonding, further accelerating the densification and fusion of the material.
The Critical Advantage: Controlling Microstructure
The true value of pressure sintering lies in its ability to engineer the final material's internal structure, or microstructure, with high precision.
Inhibiting Grain Growth
In any sintering process, the individual powder particles (grains) tend to grow larger as they are held at high temperatures. This can be detrimental to the final mechanical properties. Because pressure sintering processes like SPS are so fast, they limit the time the material spends at peak temperature, effectively inhibiting grain growth and producing materials with a fine, strong microstructure.
Achieving Maximum Density
For high-performance applications, eliminating all porosity is crucial. The synergistic effect of heat and pressure is exceptionally effective at squeezing out the last remnants of empty space, allowing for the creation of materials that are nearly 100% dense.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, pressure sintering is not a universal solution. It comes with specific constraints that are important to understand.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
The machinery required to safely apply high pressure and high temperatures simultaneously—such as a hot press or an SPS system—is significantly more complex and expensive than a conventional furnace.
Geometric Constraints
Pressure is typically applied along a single axis (uniaxial pressing). This means the process is best suited for producing relatively simple shapes, such as discs, cylinders, or rectangular blocks. Complex, three-dimensional parts are difficult to produce with this method.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right sintering method depends entirely on the desired properties of the final component.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced materials with fine-grained microstructures: Pressure sintering is the superior choice because its speed prevents the undesirable grain growth that weakens materials.
- If your primary focus is achieving near-full density in difficult-to-sinter materials: The combination of heat and pressure provides the necessary driving force to eliminate stubborn porosity that heat alone cannot.
- If your primary focus is rapid research and development: The short cycle times of processes like SPS make it highly efficient for iterating on and testing new material compositions.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of complex shapes: Conventional press-and-sinter methods are often more cost-effective and geometrically flexible.
Ultimately, pressure sintering provides a powerful tool for engineering materials with properties and performance levels unattainable through conventional heat-treatment alone.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Simultaneous Heat & Pressure | Accelerates densification, lowers required temperature. |
| Inhibits Grain Growth | Produces fine-grained microstructures for superior strength. |
| Achieves Near-Full Density | Eliminates porosity for high-performance applications. |
| Fast Cycle Times (e.g., SPS) | Ideal for rapid R&D and processing difficult-to-sinter materials. |
Ready to engineer advanced materials with superior properties?
Pressure sintering is a powerful technique for creating dense, fine-grained components. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment, like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) systems, and expert support to help you achieve your material science goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can accelerate your research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Is diffusion bonding the same as sintering? Key Differences in Solid-State Processes
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is a SPS machine? A Guide to Rapid, High-Performance Material Fabrication
- Which features of vacuum hot pressing equipment are utilized by the dual-step vacuum hot press process? Optimize AlMgTi
- What is the significance of the vacuum environment in a VHP furnace? Create Pure Al3Ti/Al Composites with Ease
- Why is a vacuum hot press furnace required for TiAl-based composite preforms? Ensure Purity and Density
- What is the primary function of a Vacuum Hot Press (VHP) furnace? Master Titanium Composite Consolidation
- How is a K-type thermocouple utilized during the hot pressing process of metal composites for precise thermal control?



















