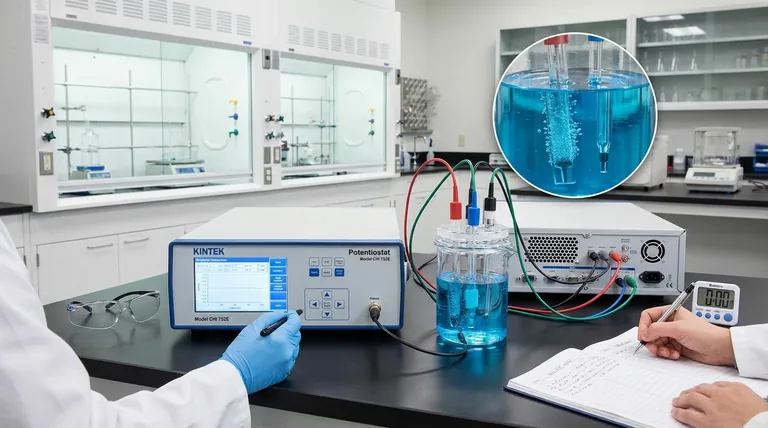
To start the experiment, you must first ensure all equipment is correctly set up, including the proper installation and immersion of the electrodes in the electrolyte. Once the system is prepared, turn on the power supply and gradually increase the voltage to your target, carefully observing the electrode surfaces for any reactions and recording all experimental data.
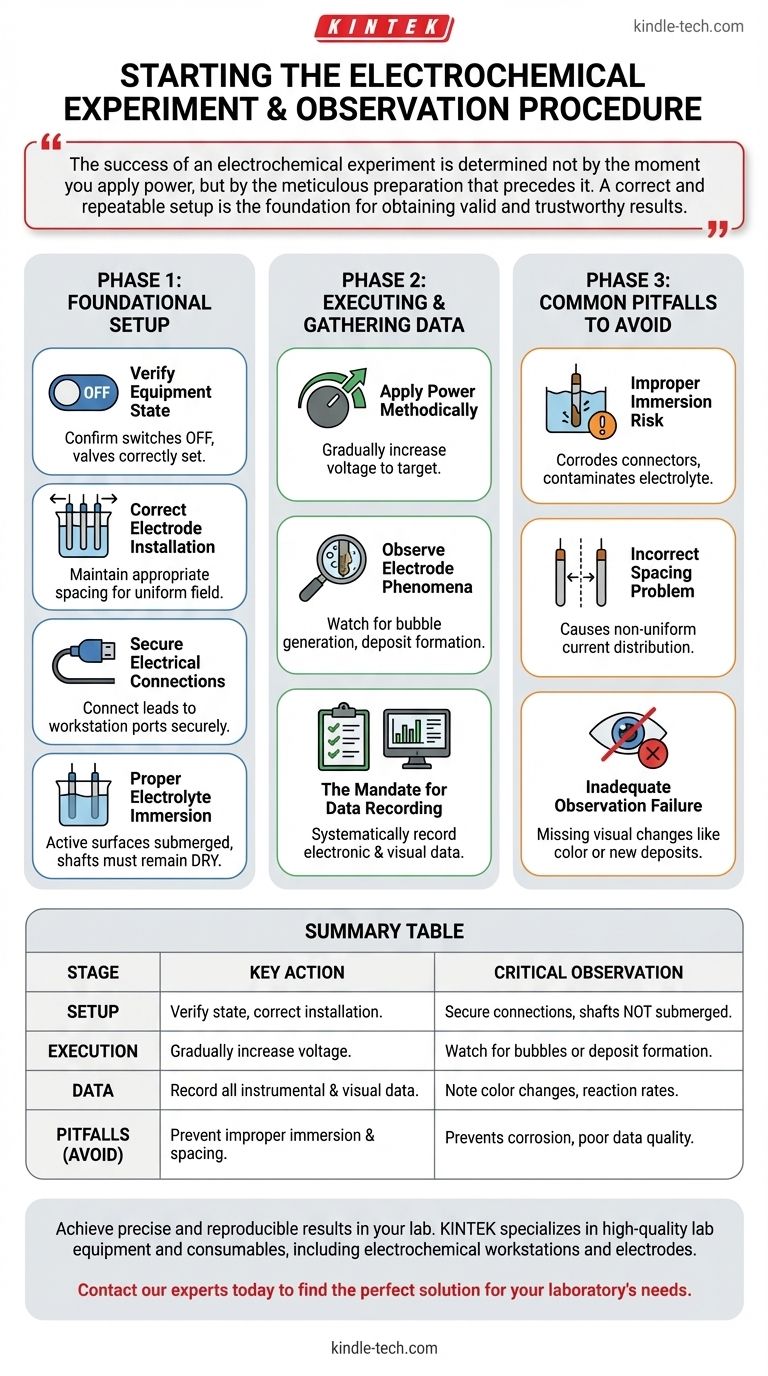
The success of an electrochemical experiment is determined not by the moment you apply power, but by the meticulous preparation that precedes it. A correct and repeatable setup is the foundation for obtaining valid and trustworthy results.

Foundational Setup: Preparing for a Valid Experiment
Before any power is applied, a precise and correct setup is mandatory. Each step is designed to eliminate variables that could compromise your data.
Verifying Initial Equipment State
Before beginning, perform a pre-flight check. Confirm that all equipment switches are in their off position and any relevant valves are correctly open or closed. This prevents unexpected behavior upon startup.
Correct Electrode Installation
The three electrodes must be installed correctly within the reaction vessel. Pay close attention to maintaining appropriate spacing between them, as this directly influences the electric field and current distribution.
Secure Electrical Connections
Connect the electrode leads to the corresponding ports on the electrochemical workstation. A common source of error is a mismatched or loose connection, which can lead to faulty readings or a failed experiment.
Proper Electrolyte Immersion
Add the electrolyte to the vessel, ensuring the active surfaces of the electrodes are fully immersed. Crucially, the electrode shafts themselves must remain above the electrolyte level to prevent corrosion, contamination, or electrical shorting.
Executing the Experiment and Gathering Data
With the setup verified, you can proceed with the active phase of the experiment. This phase is defined by controlled execution and diligent observation.
Applying Power Methodically
Turn on the power supply. Do not apply the full voltage at once; instead, gradually increase the voltage to the predetermined target value. This controlled ramp-up prevents shock to the system and allows for more stable initial conditions.
Observing Electrode Phenomena
Throughout the experiment, your primary focus should be on the electrode surfaces. Watch for key reaction indicators such as bubble generation (gas evolution) or deposit formation (electroplating or precipitation).
The Mandate for Data Recording
All observations and instrumental data must be recorded systematically. This includes the electronic data from the workstation as well as any visual phenomena noted during the process. This complete record is essential for analysis and reproducibility.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes in procedure are a common cause of failed or misleading experiments. Understanding these pitfalls is as important as knowing the correct steps.
The Risk of Improper Immersion
If the electrolyte level is too low, you will have incomplete reactions. If the level is too high and submerges the electrode shafts, you risk corroding the connectors and contaminating your electrolyte, invalidating the results.
The Problem with Incorrect Spacing
Inconsistent or improper spacing between electrodes leads to a non-uniform current distribution. This can cause skewed reaction rates across the electrode surface, making your quantitative data unreliable.
The Failure of Inadequate Observation
Simply recording the electronic data is not enough. Failing to observe and note visual changes, like a subtle color change in the electrolyte or a new deposit on an electrode, means you are missing a critical part of the experimental story.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your experimental goal dictates which procedural details require the most attention.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: Meticulously control and document electrode spacing and immersion depth, as these directly impact the current and potential measurements.
- If your primary focus is qualitative synthesis: Ensure you have a clear line of sight to the electrode surfaces and be prepared to document visual changes (e.g., with photos or detailed notes) as they occur.
- If your primary focus is reproducibility: Create a detailed checklist of your setup, from the initial state of all switches to the final measured volume of the electrolyte.
Adhering to this disciplined procedure transforms a simple series of steps into a reliable and repeatable scientific inquiry.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Critical Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | Verify equipment state, install electrodes with correct spacing, ensure full electrolyte immersion. | Check for secure connections and that electrode shafts are NOT submerged. |
| Execution | Gradually increase voltage to the target value. | Watch electrode surfaces for bubble generation or deposit formation. |
| Data Collection | Systematically record all instrumental data and visual phenomena. | Note any color changes, unexpected deposits, or reaction rates. |
| Common Pitfalls | Avoid improper immersion, incorrect spacing, and inadequate visual observation. | Prevents corrosion, non-uniform current, and loss of critical qualitative data. |
Achieve precise and reproducible results in your lab. The right equipment is fundamental to following these procedures correctly. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including electrochemical workstations and electrodes, designed to deliver the reliability and precision your research demands. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Battery Lab Equipment Battery Capacity and Comprehensive Tester
People Also Ask
- How does an electrochemical workstation assist in assessing corrosion resistance? Quantify Laser-Remelted Steel Performance
- What is the operational mechanism of a three-electrode Electrochemical Workstation? Master Coating Corrosion Analysis
- What is the significance of using a high-precision potentiostat for PDP scanning? Unlock Accurate Corrosion Insights
- What role does an electrochemical workstation play in TiNO coating evaluation? Quantify Biological Corrosion Protection
- How does a three-electrode electrochemical workstation assess TA10 titanium corrosion? Expert Testing Insights



















