At its core, a mesh belt furnace is an automated system for continuous heat treatment. It works by transporting parts on a moving conveyor belt through a series of precisely controlled heating and cooling zones. This design ensures that every part receives the exact same thermal processing, leading to highly consistent and repeatable results.
The fundamental advantage of a mesh belt furnace lies in its ability to transform complex heat treatments into a seamless, continuous, and highly automated production line process. It is designed for consistency and efficiency, especially when processing large quantities of small to medium-sized components.
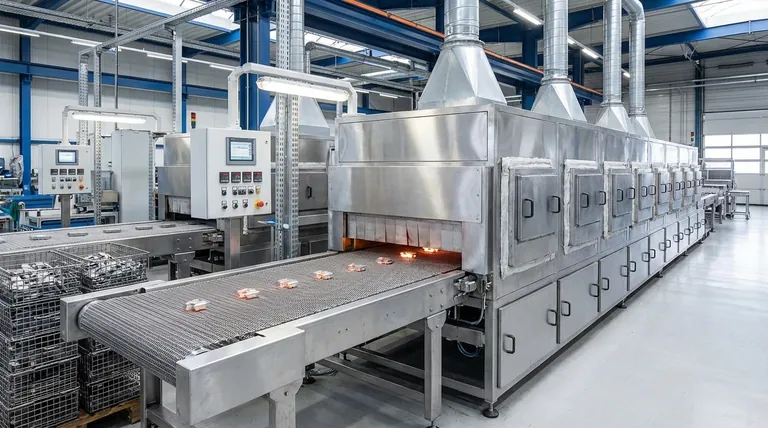

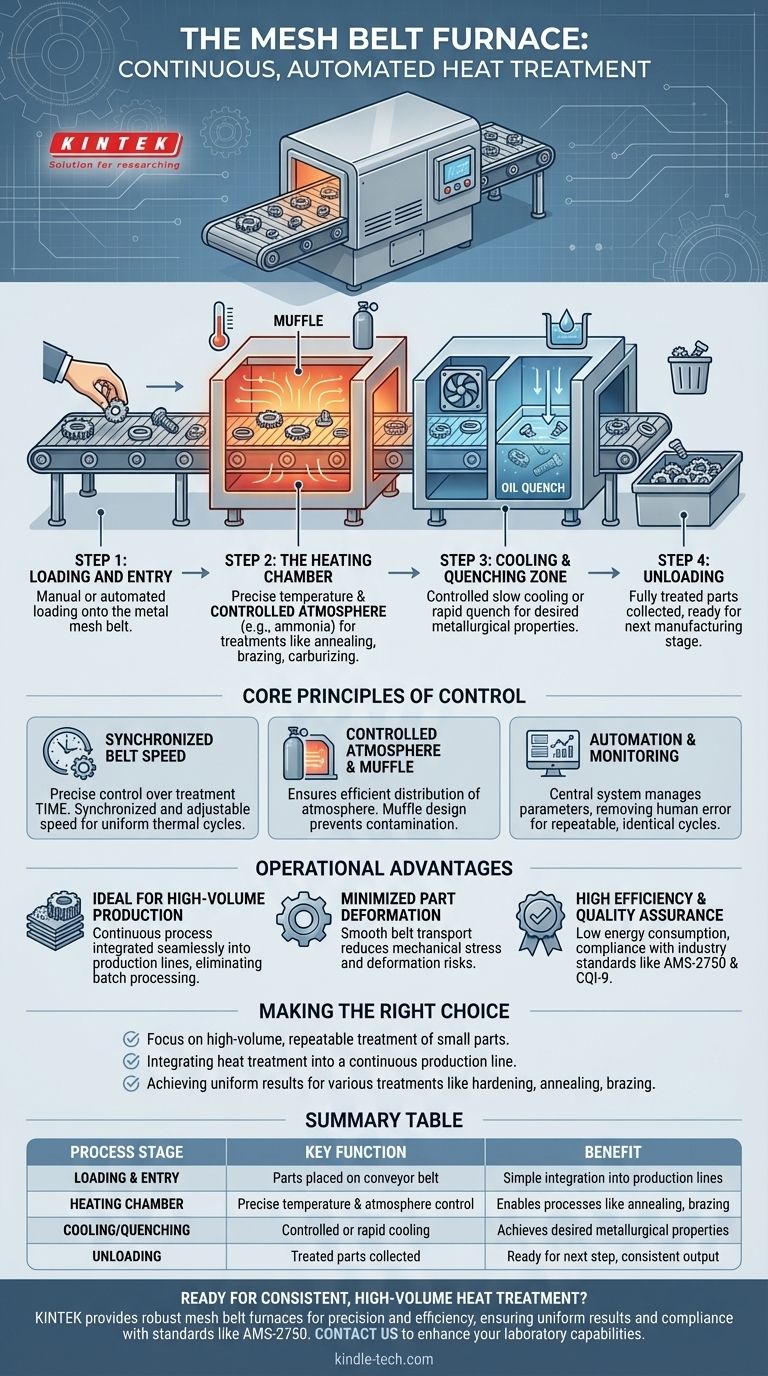
Deconstructing the Continuous Process
The journey of a component through a mesh belt furnace is a meticulously controlled sequence. The entire operation is designed to be a "hands-off" process once the initial loading is complete.
Step 1: Loading and Entry
Parts are placed onto the metal mesh conveyor belt at the front of the furnace. This is one of the few points where manual intervention is required, as operators load the components that need treatment.
Step 2: The Heating Chamber
The belt moves the parts from the loading area directly into the heating chamber, often a protective internal chamber called a muffle. Here, the parts are brought to a specific temperature required for the desired treatment, such as annealing, hardening, or brazing.
This chamber is filled with a controlled atmosphere, such as ammonia gas, to facilitate specific thermo-chemical processes like carburizing or to prevent oxidation during heating.
Step 3: The Cooling and Quenching Zone
After spending a precise amount of time in the heat, the parts are conveyed into a cooling zone. This cooling can be a slow, controlled process or a rapid quench, often in oil, depending on the metallurgical properties required in the final product.
Step 4: Unloading
The fully treated parts emerge from the back end of the furnace on the conveyor belt. They are then collected, either manually or by an automated system, ready for the next stage of manufacturing.
The Core Principles of Control and Consistency
The effectiveness of a mesh belt furnace comes from its precise control over the three critical variables of heat treatment: time, temperature, and atmosphere.
Synchronized Belt Speed
The belt speed is the primary control for the treatment time. It is fully synchronized and widely adjustable, allowing operators to precisely dictate how long a part spends in each heating and cooling zone. This ensures every component receives the identical thermal cycle.
Controlled Atmosphere and Muffle Design
The furnace muffle is a critical component that contains the controlled atmosphere. It is supported by ceramic elements to ensure a long service life and prevent contamination. This design allows for highly efficient atmosphere distribution, which is essential for uniform results in processes like carbonitriding.
Automation and Monitoring
The entire technological line is typically automated and monitored by a central control system. This system manages belt speed, temperature profiles, and atmosphere composition, removing the risk of human error and ensuring that every cycle is identical and repeatable.
Understanding the Operational Advantages
The design of a mesh belt furnace provides several key benefits that make it a preferred choice for specific manufacturing environments.
Ideal for High-Volume Production
The continuous nature of the process makes it perfectly suited for treating large quantities of small elements. It integrates seamlessly into production lines, eliminating the batch-style processing of other furnace types.
Minimized Part Deformation
Because parts are carried smoothly on a belt, the risk of mechanical stress and deformation is significantly reduced compared to other handling methods. Efficient quenching oil circulation further helps in minimizing thermal shock.
High Efficiency and Quality Assurance
These furnaces are engineered for low energy consumption and are built to comply with stringent industry standards like AMS-2750 (pyrometry) and CQI-9 (heat treat system assessment). This ensures a high level of quality control and process reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this process fits your needs, consider your primary operational objective.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable treatment of small parts: The furnace's continuous, automated process provides unparalleled consistency at scale.
- If your primary focus is integrating heat treatment into a continuous production line: This furnace is designed to eliminate batch processing and streamline your workflow.
- If your primary focus is achieving uniform results for various treatments like hardening, annealing, or brazing: The precise control over time, temperature, and atmosphere makes it a highly versatile and reliable solution.
Ultimately, the mesh belt furnace is a powerful tool for achieving uniform metallurgical results in a high-volume manufacturing environment.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Loading & Entry | Parts placed on conveyor belt | Simple integration into production lines |
| Heating Chamber | Precise temperature control in a controlled atmosphere | Enables processes like annealing, brazing, and carburizing |
| Cooling/Quenching | Controlled or rapid cooling (e.g., oil quench) | Achieves desired metallurgical properties |
| Unloading | Treated parts are collected | Ready for next manufacturing step, ensures consistent output |
Ready to integrate consistent, high-volume heat treatment into your production line? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust mesh belt furnaces designed for precision and efficiency. Our solutions help laboratories achieve uniform results in processes like hardening and annealing, ensuring compliance with standards like AMS-2750. Contact us today to discuss how our equipment can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and throughput!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What hazard is involved when using a furnace? Protect Your Home from the Silent Killer
- What are the materials for vacuum hardening? A Guide to High-Performance Steel Selection
- What is the difference between liquid and gas carburizing? Precision, Safety & Environmental Impact
- Why is a vacuum arc furnace with inert atmosphere protection necessary? Ensure Precision in Duplex Stainless Steel.
- How does a vertical Bridgman furnace control CsI crystal quality? Achieve High-Performance Radionuclide Detection
- What are the 5 types of brazing process? Choose the Right Heating Method for Your Project
- What is the critical role of a vacuum furnace in the calcination of TiO2? Optimize Your Powder Microstructure
- What are the different methods of annealing? Choose the Right Heat Treatment for Your Material's Needs



















