At its core, an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is a powerful metallurgical furnace that melts metal, primarily steel scrap, by using the immense heat of an electric arc. This process does not rely on chemical combustion or electromagnetic induction but on the direct thermal energy generated when a high-current electric arc forms between graphite electrodes and the metallic charge.
An electric arc furnace fundamentally converts massive amounts of electrical energy into intense heat. The process is a brute-force thermal event, where a controlled, high-energy arc—essentially a man-made lightning bolt—is used to melt tons of metal scrap in a refractory-lined vessel.

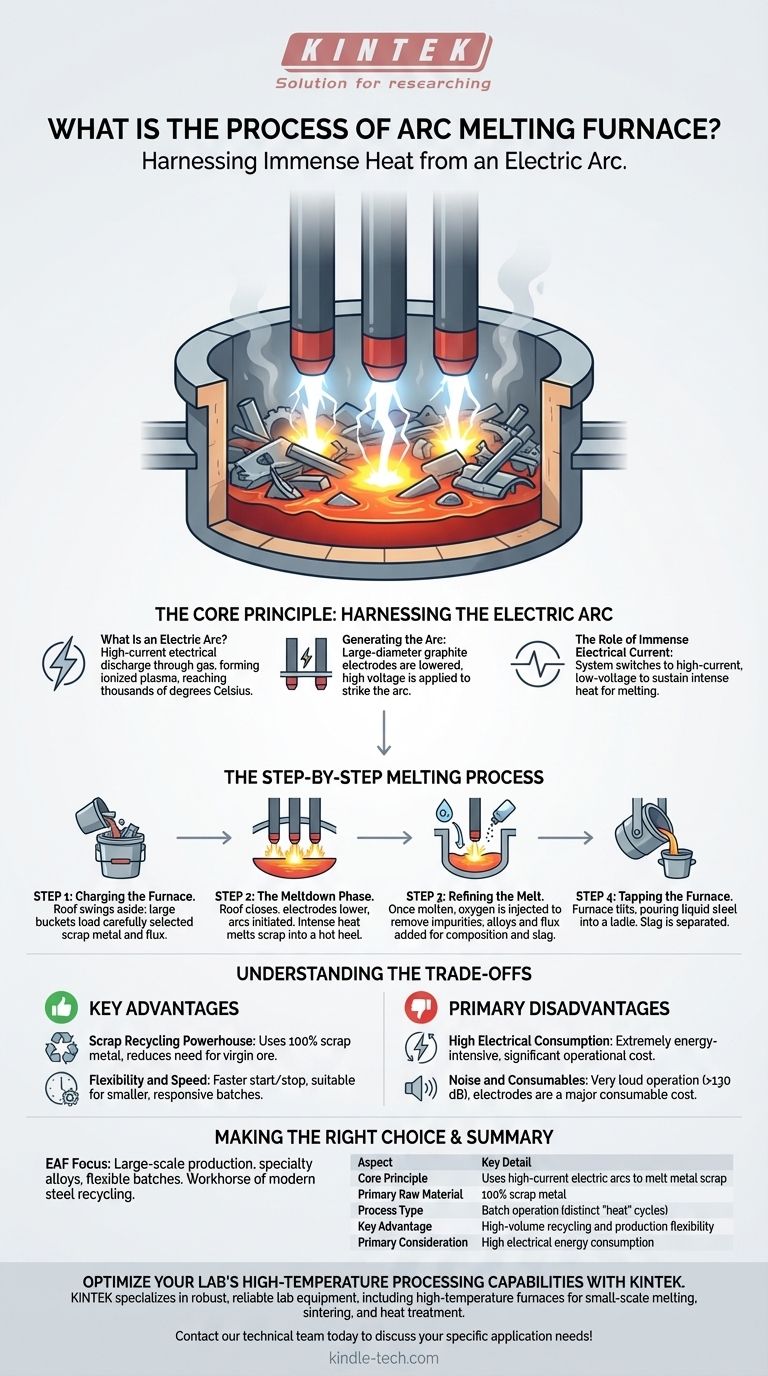
The Core Principle: Harnessing the Electric Arc
The entire operation of an EAF hinges on a single, powerful physical phenomenon: the electric arc. Understanding this is key to understanding the furnace.
What Is an Electric Arc?
An electric arc is a high-current electrical discharge through a gas, which becomes an ionized plasma. This plasma channel can reach temperatures of several thousand degrees Celsius, far exceeding the melting point of steel. The EAF creates and sustains this arc in a controlled environment.
Generating the Arc
The furnace uses large-diameter graphite electrodes. These electrodes are mounted on movable arms that can be raised or lowered. To start the process, the electrodes are lowered until they are close to the scrap metal charge, and a very high voltage is applied, causing an arc to strike.
The Role of Immense Electrical Current
Once the arc is established, the system switches to a high-current, lower-voltage state. This massive flow of electrical current through the arc and the metal itself is what generates the intense, sustained heat required for melting.
The Step-by-Step Melting Process
The EAF process is a batch operation, meaning it follows a distinct cycle for each load, or "heat," of steel produced.
Step 1: Charging the Furnace
The cycle begins by loading the furnace. The roof is swung aside, and large buckets filled with carefully selected scrap metal are used to "charge" the furnace from above. This charge can also include other iron sources and fluxing agents.
Step 2: The Meltdown Phase
With the roof closed, the electrodes are lowered, and the arc is initiated. The intense radiant heat from the arcs begins to melt the scrap directly beneath them, boring down into the pile. As a molten pool, or "hot heel," forms at the bottom, heat transfer becomes more efficient.
Step 3: Refining the Melt
Once the scrap is fully molten, the process shifts from melting to refining. The goal is to adjust the chemical composition of the molten steel to meet specifications. This is often achieved by injecting oxygen, which removes impurities like carbon, and by adding alloys and fluxing agents to form a protective slag layer.
Step 4: Tapping the Furnace
When the molten steel reaches the desired temperature and chemical composition, the furnace is tilted. The liquid steel is poured out through a tap-hole into a large refractory-lined container called a ladle. The slag is either poured off separately or held back in the furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any industrial process, the EAF has distinct advantages and disadvantages that make it suitable for specific applications.
Key Advantage: The Scrap Recycling Powerhouse
The EAF's greatest strength is its ability to use 100% scrap metal as its primary raw material. This makes it a cornerstone of modern steel recycling, reducing the need for virgin iron ore and the associated environmental impact of mining.
Key Advantage: Flexibility and Speed
EAFs are far more flexible than traditional blast furnaces. They can be started and stopped relatively quickly and can produce a wide variety of steel grades in smaller batches, allowing for more responsive production.
Primary Disadvantage: High Electrical Consumption
The process is incredibly energy-intensive. An EAF is one of the largest single electrical loads on a regional power grid, and electricity costs are a major factor in its operational budget.
Primary Disadvantage: Noise and Consumables
The operation is extremely loud, often exceeding 130 decibels. Furthermore, the graphite electrodes are a significant consumable cost, as they are gradually consumed during the melting process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an EAF is driven by raw material availability, production scale, and desired product.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel production from scrap: The EAF is the undisputed industry standard for this application.
- If your primary focus is producing specialty steel alloys in flexible batches: The EAF offers superior control over melt chemistry and faster turnaround times compared to ore-based methods.
- If you are comparing it to an induction furnace: Use an arc furnace for high-volume, carbon steel scrap melting and an induction furnace for smaller, cleaner melts, high-value alloys, or non-ferrous metals where contamination must be minimized.
Ultimately, the Electric Arc Furnace is the workhorse of modern steel recycling, valued for its raw material flexibility and production speed.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Uses high-current electric arcs to melt metal scrap |
| Primary Raw Material | 100% scrap metal |
| Process Type | Batch operation (distinct 'heat' cycles) |
| Key Advantage | High-volume recycling and production flexibility |
| Primary Consideration | High electrical energy consumption |
Optimize your lab's high-temperature processing capabilities with KINTEK.
Whether you're working with metal alloys, ceramics, or advanced materials, having the right furnace technology is critical for your research and development. KINTEK specializes in supplying robust and reliable lab equipment, including high-temperature furnaces ideal for small-scale melting, sintering, and heat treatment applications.
Let our experts help you select the perfect equipment to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve precise, repeatable results.
Contact our technical team today to discuss your specific application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation



















