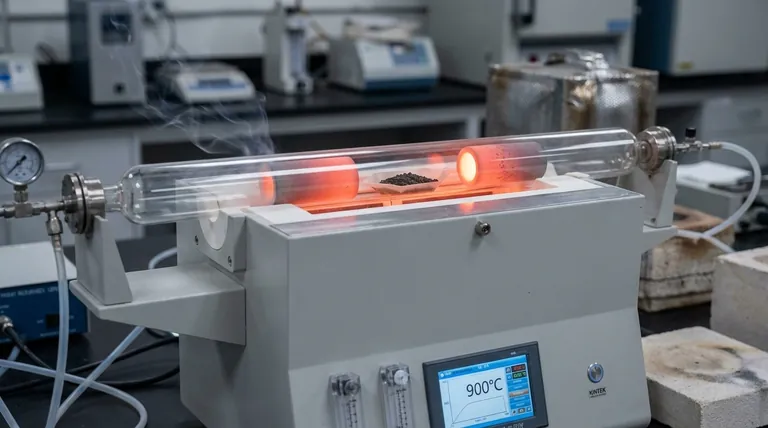
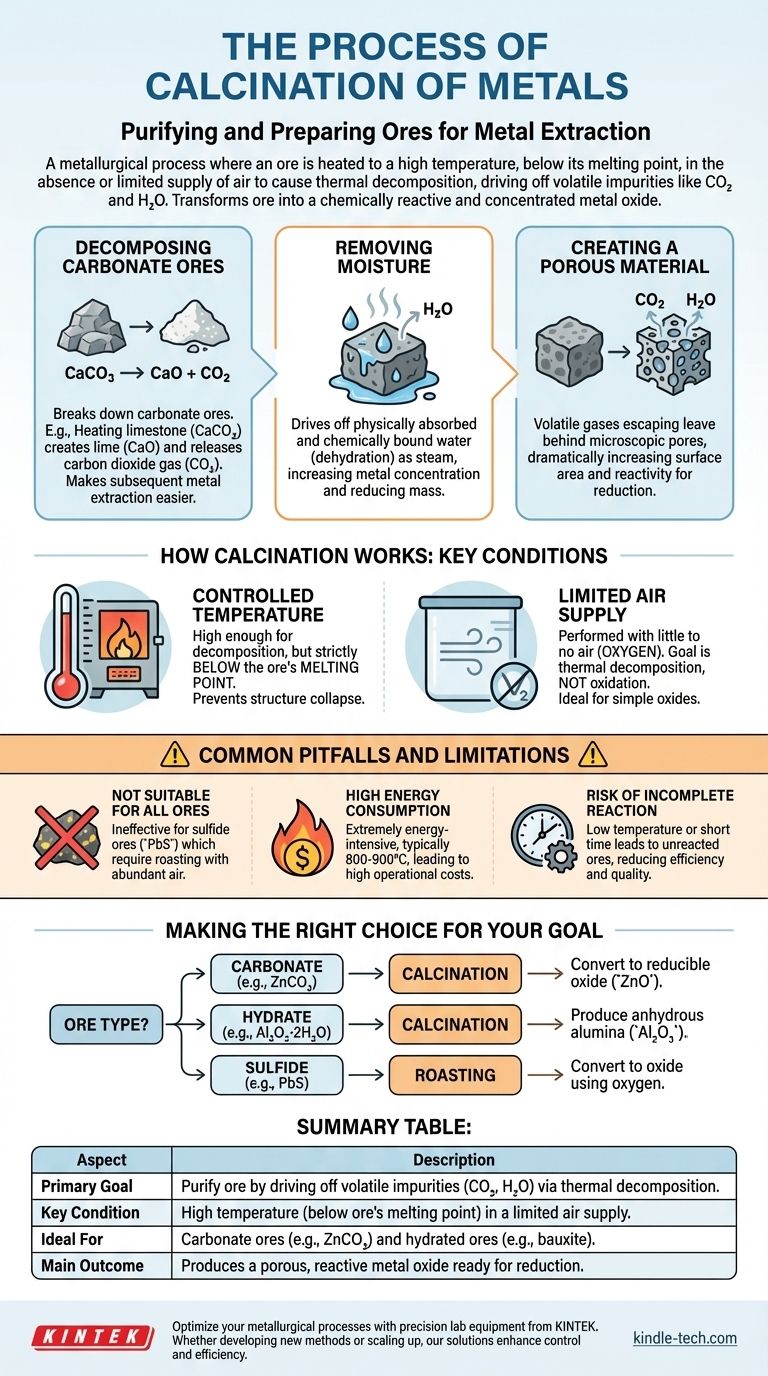
In simple terms, calcination is a metallurgical process where an ore is heated to a high temperature, below its melting point, in the absence or with a very limited supply of air. The primary purpose is not to melt the ore but to cause thermal decomposition, driving off volatile impurities like carbon dioxide and water. This purifies and prepares the ore for the next stage of metal extraction.
The core function of calcination is to transform an ore into a more chemically reactive and concentrated form—typically a metal oxide. By removing unwanted volatile components, it makes the subsequent process of reducing the ore to pure metal significantly more efficient.

The Core Purpose of Calcination
Calcination is fundamentally a preparatory step. It doesn't extract the metal itself but makes the ore more suitable for extraction by altering its chemical and physical structure.
Decomposing Carbonate Ores
Many important metals, such as zinc and calcium, are found in nature as carbonate ores. Calcination breaks these down.
For example, heating limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO3) creates lime (calcium oxide, CaO) and releases carbon dioxide gas (CO2). It is far easier to extract metal from an oxide than from a carbonate.
Removing Moisture
Ores mined from the earth often contain significant amounts of water, both physically absorbed and chemically bound (hydrates).
Heating the ore during calcination drives this water off as steam. This process, known as dehydration, increases the concentration of the metal within the ore, reducing the total mass that needs to be processed later.
Creating a Porous Material
A critical, often overlooked, benefit of calcination is the change in the ore's physical structure.
As volatile substances like CO2 and H2O escape as gases, they leave behind microscopic pores and channels. This makes the resulting solid material much more porous, dramatically increasing its surface area and making it more reactive for the subsequent reduction step.
How Calcination Works: Key Conditions
The success of calcination depends entirely on maintaining precise control over two key variables: temperature and atmosphere.
Controlled Temperature
The temperature must be high enough to initiate the desired decomposition reactions but must remain strictly below the melting point of the ore.
If the ore were to melt, its structure would collapse, trapping impurities and reducing the surface area, defeating the primary purpose of the process.
Limited Air Supply
Calcination is intentionally performed with little to no air (oxygen). This is a critical distinction from a similar process called roasting.
The goal is to break down the compound through heat alone, not to oxidize it. Preventing oxidation ensures the ore is converted into a simple oxide, which is the ideal starting material for reduction.
Common Pitfalls and Limitations
While effective, calcination is not a universal solution and has specific requirements and downsides that must be managed.
Not Suitable for All Ores
Calcination is specifically designed for carbonate and hydrated ores.
It is ineffective for sulfide ores (like lead sulfide, PbS). These require roasting, a process that involves heating in an abundance of air to convert the sulfide into an oxide.
High Energy Consumption
Heating vast quantities of ore to temperatures often exceeding 800-900°C is an extremely energy-intensive process.
This carries significant operational costs and a considerable environmental footprint, which are major factors in the economic viability of a mining operation.
Risk of Incomplete Reaction
If the temperature is too low or the heating time is too short, the decomposition reaction may not complete.
This leaves unreacted carbonates or hydrates in the final product, reducing the efficiency of the subsequent extraction stage and potentially contaminating the final metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heat treatment is the first critical decision in designing an efficient metallurgical workflow.
- If your primary ore is a carbonate (e.g., smithsonite,
ZnCO3): Calcination is the essential step to convert it into a more easily reducible metal oxide (ZnO). - If your primary ore is a hydrate (e.g., bauxite,
Al2O3·2H2O): Calcination is used to drive off the chemically bound water to produce anhydrous alumina (Al2O3). - If your primary ore is a sulfide (e.g., galena,
PbS): You must use roasting, not calcination, to convert the ore into an oxide by reacting it with oxygen.
Ultimately, understanding calcination is key to appreciating how raw, impure ores are methodically prepared for efficient metal extraction.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Purify ore by driving off volatile impurities (CO₂, H₂O) via thermal decomposition. |
| Key Condition | High temperature (below ore's melting point) in a limited air supply. |
| Ideal For | Carbonate ores (e.g., ZnCO₃) and hydrated ores (e.g., bauxite). |
| Main Outcome | Produces a porous, reactive metal oxide ready for reduction. |
Optimize your metallurgical processes with precision lab equipment from KINTEK.
Whether you are developing a new extraction method or scaling up production, the right tools are critical for controlling temperature and atmosphere during steps like calcination. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnaces and lab equipment designed for reliability and precision, helping laboratories and mining operations achieve efficient and consistent results.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how our solutions can enhance your metal extraction workflow and improve your outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control



















