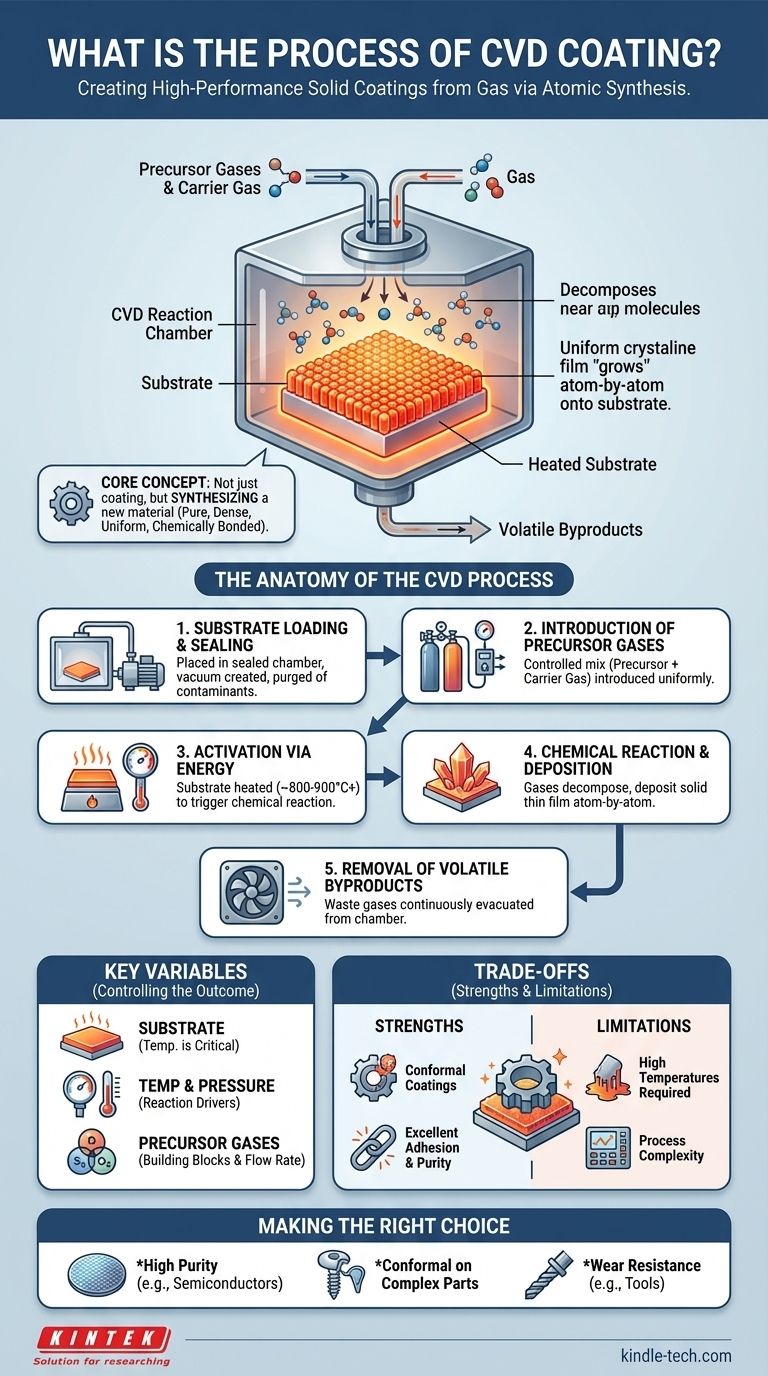
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process for creating a high-performance solid coating on a surface from a gas. It works by introducing specific "precursor" gases into a high-temperature chamber containing the object to be coated, known as the substrate. The heat triggers a chemical reaction, causing the gases to decompose and deposit a new, solid thin film, atom by atom, onto the substrate's surface.
The central concept of CVD is not just coating a surface, but synthesizing a new material directly onto it. By carefully controlling temperature, pressure, and gas chemistry, you can build extremely pure, dense, and uniform films that are chemically bonded to the underlying substrate.
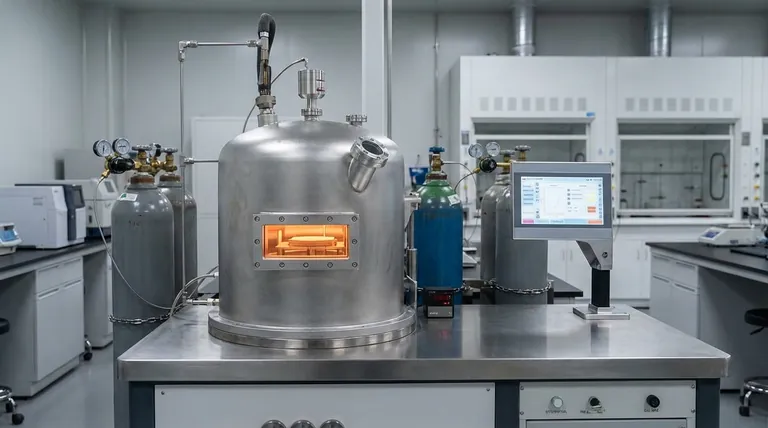

The Anatomy of the CVD Process
The CVD process can be broken down into four fundamental stages. Each step is critical for controlling the final properties of the deposited film.
Step 1: Substrate Loading and Chamber Sealing
The process begins by placing the object to be coated—the substrate—inside a sealed reaction chamber. The chamber is then purged and a vacuum is created to remove any contaminants and control the pressure precisely.
Step 2: Introduction of Precursor Gases
A carefully controlled mixture of gases is introduced into the chamber. This mix includes one or more volatile precursor gases, which contain the atoms needed for the final film (e.g., a carbon-bearing gas like methane to create diamond).
Often, an inert carrier gas like argon or nitrogen is also used to dilute the precursors and help transport them evenly over the substrate.
Step 3: Activation via Energy
Energy is applied to trigger the chemical reaction. In traditional thermal CVD, this is done by heating the substrate to extremely high temperatures, often between 800°C and 900°C or higher.
The substrate's hot surface provides the energy needed to break the chemical bonds in the precursor gas molecules that come into contact with it.
Step 4: Chemical Reaction and Deposition
As the precursor gases decompose on the hot substrate, a chemical reaction occurs. This reaction forms a stable, solid material that deposits onto the surface, creating a thin film.
For example, in graphene production, carbon-containing gas decomposes on a hot copper substrate, and the carbon atoms arrange themselves into a graphene lattice. The substrate can act as a simple hot surface or as a catalyst that actively participates in and facilitates the reaction.
Step 5: Removal of Volatile Byproducts
The chemical reaction not only produces the desired solid film but also creates volatile byproducts. These waste gases are continuously removed from the chamber by the vacuum system to prevent them from contaminating the film and to drive the reaction forward.
The Key Variables That Control the Outcome
The quality, thickness, and structure of a CVD coating are not accidental. They are the direct result of manipulating a few key parameters.
The Substrate: More Than Just a Surface
The substrate is the foundation for the coating. Its temperature is the single most critical factor, as it dictates the rate and type of chemical reaction that occurs. In some cases, like the growth of graphene on copper, the substrate's material also acts as a catalyst.
Temperature and Pressure: The Reaction Drivers
Temperature provides the activation energy for the deposition. Higher temperatures generally lead to faster deposition rates and can influence the crystalline structure of the film.
Pressure within the chamber determines the concentration of gas molecules and how they travel. Lower pressures help ensure that reactions happen primarily on the substrate surface rather than in the gas phase, leading to higher-quality films.
Precursor Gases: The Building Blocks
The choice of precursor gases is fundamental, as it defines the elemental composition of the final coating. The flow rate at which these gases are introduced into the chamber is precisely metered to ensure a stable and repeatable deposition process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any technology, CVD has distinct characteristics that make it ideal for some applications and unsuitable for others.
Strength: High-Quality, Conformal Coatings
Because the deposition occurs from a gas phase, CVD can uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with high aspect ratios. This ability to create conformal coatings is a significant advantage over line-of-sight methods like PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition).
Strength: Excellent Adhesion and Purity
The film is created through a chemical reaction with the surface, resulting in a strong, adherent bond. The controlled, high-vacuum environment allows for the creation of extremely pure and dense films with specific crystalline structures.
Limitation: The Need for High Temperatures
The high temperatures required for many CVD processes can damage or warp heat-sensitive substrates, such as plastics or certain metals. This limits the range of materials that can be coated with traditional thermal CVD.
Challenge: Process Complexity
CVD requires precise control over multiple variables (temperature, pressure, gas flow) and involves managing potentially hazardous precursor and byproduct gases. This makes the equipment and process more complex than some other coating methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the core principles of CVD allows you to determine if it aligns with your specific technical requirements.
- If your primary focus is creating highly pure, crystalline films (like semiconductors or diamond): CVD is the industry standard because it synthesizes the material with atomic-level precision.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, three-dimensional parts evenly: The gaseous nature of CVD allows it to produce excellent conformal coatings where other methods fail.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive materials: You must consider low-temperature variants like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), which uses an RF plasma to activate the reaction instead of just heat, or seek alternative methods.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance on cutting tools: CVD is often used to create thick, hard, and durable coatings like titanium nitride (TiN) and diamond-like carbon (DLC).
By mastering the chemistry of gases, CVD empowers us to engineer materials and surfaces with properties unattainable by other means.
Summary Table:
| CVD Process Stage | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Substrate Loading | Place object in sealed, vacuum chamber | Clean, contaminant-free surface |
| 2. Gas Introduction | Introduce precursor & carrier gases | Controlled chemical environment |
| 3. Energy Activation | Heat substrate (800-900°C+) | Breaks gas bonds for reaction |
| 4. Reaction & Deposition | Chemical reaction on hot surface | Atom-by-atom thin film growth |
| 5. Byproduct Removal | Vacuum system removes waste gases | Pure, uncontaminated coating |
Ready to engineer superior surfaces with precision CVD coatings?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for cutting-edge material synthesis. Whether you're developing semiconductors, wear-resistant tool coatings, or exploring graphene applications, our CVD solutions deliver the exceptional purity, conformal coverage, and strong adhesion your research demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our tailored CVD systems can accelerate your laboratory's innovation and achieve your specific coating goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision CVD or tube furnace required for CNT/copper composites? Optimize In-Situ Growth Results
- What is the sputtering process? A Guide to High-Precision Thin Film Deposition
- How is carbon coating done? Enhance Material Performance with Precision Coating
- What is chemical vapour deposition for thin films? A Guide to High-Performance Surface Engineering
- How does a high vacuum reaction chamber contribute to the preparation of diamond coatings via CVD? Unlock Ultra-Hardness
- What is chemical deposition techniques? A Guide to Thin Film Fabrication Methods
- What temperature is CVD coating? Find the Right CVD Process for Your Material
- What is the CVD process reaction? A Guide to Chemical Vapor Deposition Mechanisms



















