Sintering bonding is a solid-state joining process that fuses materials together using heat and pressure, all without reaching their melting point. Instead of liquefying the materials, this technique energizes the atoms at the contact surfaces, causing them to diffuse across the boundary and form a strong, continuous metallurgical bond.
The core principle of sintering bonding is to join materials without melting them. This reliance on atomic diffusion preserves the original material properties, making it an essential technique for joining dissimilar or advanced materials where traditional welding is not an option.

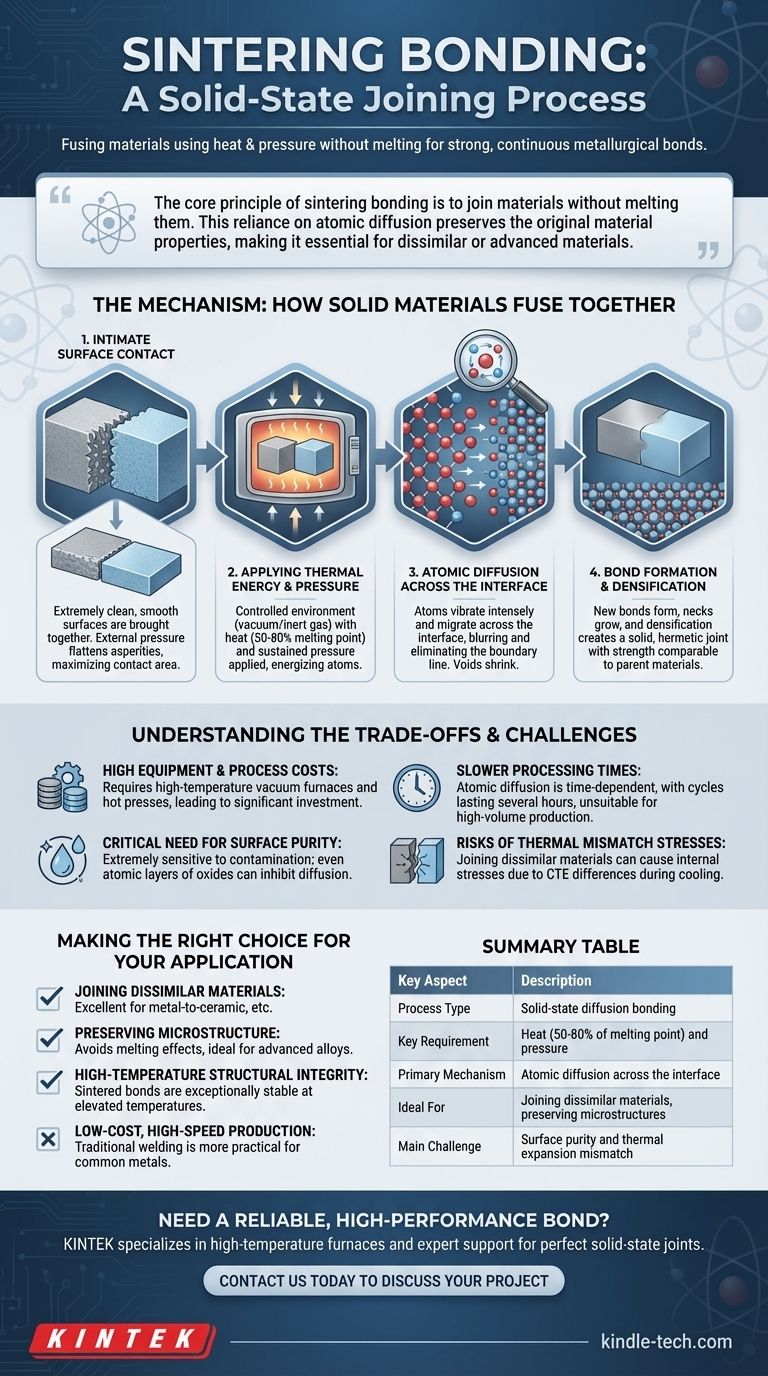
The Mechanism: How Solid Materials Fuse Together
Understanding sintering bonding requires looking at the atomic level. The process transforms two separate pieces into a single, unified component by encouraging atoms to migrate and eliminate the boundary between them.
Step 1: Intimate Surface Contact
The process begins by bringing two extremely clean, smooth surfaces into contact. Any oxides, contaminants, or microscopic debris can act as a barrier and prevent the atomic diffusion necessary for a successful bond.
This initial contact is typically enhanced by applying external pressure, which flattens surface asperities (microscopic peaks and valleys) and maximizes the contact area between the two parts.
Step 2: Applying Thermal Energy and Pressure
The assembly is placed in a controlled environment, often a vacuum or inert gas furnace, to prevent oxidation at high temperatures. Heat is applied, typically to between 50% and 80% of the absolute melting point of the lower-melting-point material.
This thermal energy doesn't melt the material but causes its atoms to vibrate intensely, giving them the mobility needed to move. Pressure is maintained to keep the surfaces in intimate contact.
Step 3: Atomic Diffusion Across the Interface
With sufficient thermal energy, atoms at the contact points begin to jump across the interface from one material to the other. This two-way migration is the heart of the sintering process.
Diffusion effectively blurs and eventually erases the original boundary line. The voids and gaps that once existed between the two surfaces gradually shrink as they are filled by these migrating atoms.
Step 4: Bond Formation and Densification
As atoms diffuse, they form new metallic or ceramic bonds, creating small "necks" that bridge the two surfaces. Over time, these necks grow wider and more numerous.
The continued diffusion leads to densification of the interface, eliminating pores and creating a solid, hermetic joint. The final result is a single, continuous component with a bond that can be as strong as the parent materials themselves.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, sintering bonding is not a universal solution. Its unique requirements introduce specific challenges that must be managed for success.
High Equipment and Process Costs
The need for high-temperature vacuum furnaces, hot presses, and precision-controlled atmospheres makes the initial investment and operational costs significant compared to conventional joining methods like welding or brazing.
Critical Need for Surface Purity
The process is extremely sensitive to surface contamination. The presence of even a few atomic layers of oxides or organic films can completely inhibit diffusion and prevent a bond from forming, demanding rigorous cleaning and handling protocols.
Slower Processing Times
Atomic diffusion is a time-dependent phenomenon. Sintering cycles can last for several hours, making it less suitable for high-volume, rapid production compared to processes that rely on melting.
Risks of Thermal Mismatch Stresses
When joining dissimilar materials (e.g., a metal to a ceramic), a difference in their coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is a major concern. As the bonded part cools, one material will shrink more than the other, inducing internal stresses that can weaken the joint or even cause it to crack.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct joining process depends entirely on your material constraints and performance goals.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials (like metal-to-ceramic): Sintering bonding is one of the most effective and sometimes only available options.
- If your primary focus is preserving the precise microstructure of advanced alloys: The solid-state nature of sintering avoids the damaging effects of melting, making it the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature structural integrity: Sintered bonds are exceptionally stable at elevated temperatures, outperforming lower-temperature joints like those made by brazing or soldering.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, high-speed production of common metals: Traditional fusion welding or mechanical fastening is almost always a more practical and economical solution.
Ultimately, choosing sintering bonding is a strategic decision to achieve performance characteristics that are impossible with conventional, melt-based joining techniques.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Solid-state diffusion bonding |
| Key Requirement | Heat (50-80% of melting point) and pressure |
| Primary Mechanism | Atomic diffusion across the interface |
| Ideal For | Joining dissimilar materials, preserving microstructures |
| Main Challenge | Surface purity and thermal expansion mismatch |
Need a reliable, high-performance bond for advanced or dissimilar materials?
The sintering bonding process is ideal for applications where traditional welding fails. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-temperature furnaces and expert support needed to achieve perfect solid-state joints. Our lab equipment ensures the precise control and clean environments critical for successful sintering.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your material joining capabilities and bring your most challenging projects to life.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- What is the significance of precise temperature control in melt infiltration? Achieve High-Performance Li-Alloy Electrodes
- Why is a high vacuum preferred over argon for sintering VC/Cu composites? Achieve Superior Wetting and Bond Strength
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- How does a vacuum hot pressing furnace facilitate the consolidation of (Cu–10Zn)-Al2O3 nanocomposites?



















