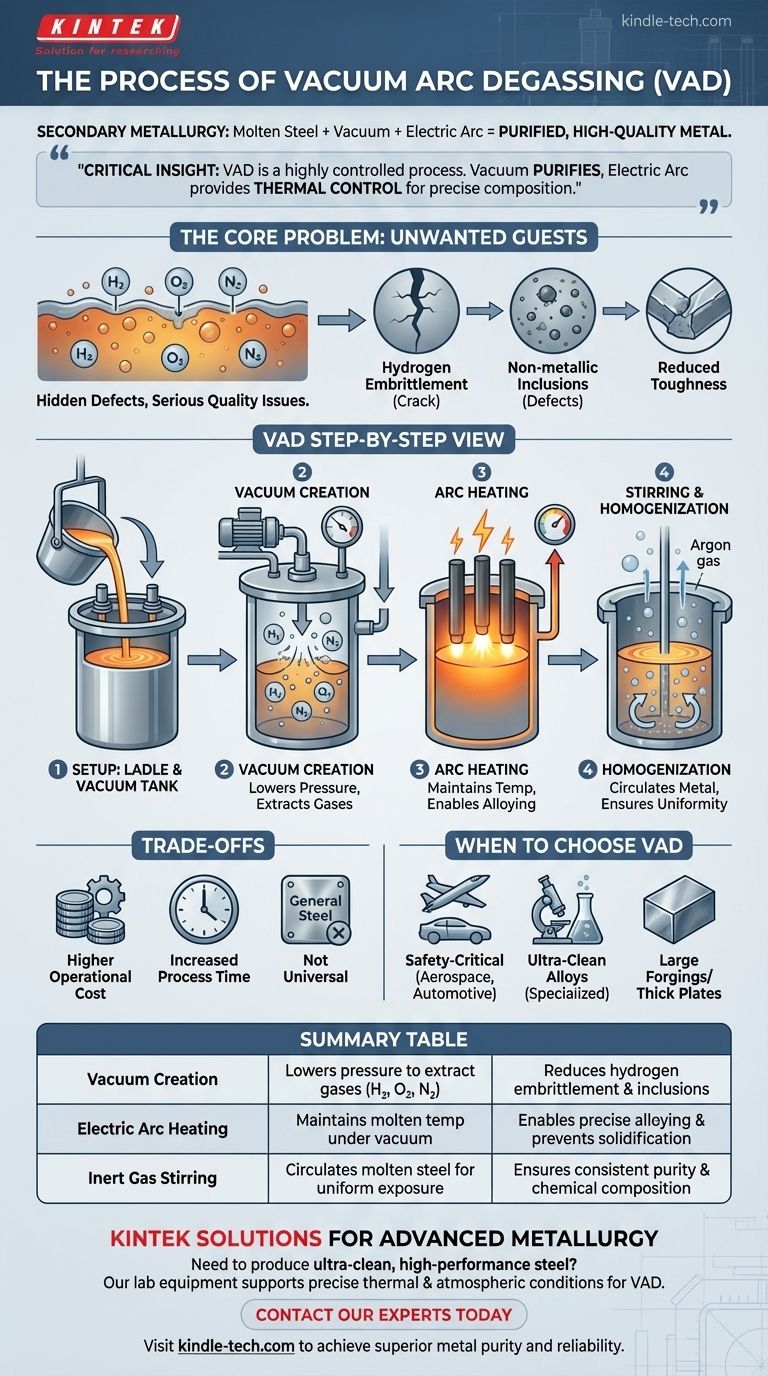
At its core, Vacuum Arc Degassing (VAD) is a secondary metallurgy process used to refine molten steel by exposing it to a vacuum while simultaneously heating it with an electric arc. The vacuum extracts undesirable dissolved gases like hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen, while the arc provides the energy needed to maintain the steel's temperature and facilitate precise alloying additions.
The critical insight is that VAD is not just about removing gases. It's a highly controlled process where the vacuum purifies the steel, and the electric arc provides the thermal control necessary for precise chemical composition adjustments, creating high-quality, specialized metal grades.

The Core Problem: Unwanted Guests in Molten Metal
Before detailing the VAD process, it's essential to understand the problem it solves. Molten metals, particularly steel, readily absorb gases from their environment.
Dissolved Gases: The Hidden Defects
Gases like hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen become trapped within the metal's structure as it cools and solidifies.
These trapped gases are highly detrimental, leading to serious quality issues.
The Impact of Gas Impurities
Hydrogen can cause a phenomenon known as hydrogen embrittlement, leading to catastrophic failures under stress.
Oxygen reacts with other elements to form non-metallic inclusions (like oxides), which act as internal weak points. Nitrogen can negatively affect the metal's toughness and formability.
How Vacuum Arc Degassing Works: A Step-by-Step View
The VAD process is designed to systematically remove these harmful gases and give metallurgists precise control over the final product. The process occurs in a specialized vessel called a ladle.
The Setup: Ladle and Vacuum Tank
A ladle containing molten steel from the primary furnace is placed inside a large, sealed vacuum tank.
A lid with three graphite electrodes is lowered over the ladle, creating an airtight seal.
Creating the Vacuum
Powerful pumps remove the air from the tank, dramatically lowering the pressure above the molten steel.
This pressure drop reduces the partial pressure of the dissolved gases, creating a powerful driving force for them to escape from the liquid metal and be pumped away.
The Crucial Role of the Arc
Exposing the molten steel to a vacuum causes it to cool rapidly. Without a heat source, the steel would solidify before the degassing process is complete.
This is where the electric arc is essential. The electrodes generate a powerful arc that reheats the steel, precisely compensating for heat loss and maintaining the optimal temperature for purification and alloying.
Stirring and Homogenization
To accelerate degassing, an inert gas like argon is often bubbled up from the bottom of the ladle.
This gentle stirring action circulates the molten metal, ensuring that all of it is exposed to the low-pressure environment. It also promotes a uniform temperature and chemical composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While VAD is a powerful refining tool, it represents a significant investment in both equipment and operational cost. Its application is a calculated decision based on the desired outcome.
Higher Operational Cost
VAD units are complex and expensive to build and maintain. The consumption of electricity for the arc and graphite for the electrodes adds significant cost compared to simpler refining methods.
Increased Process Time
The VAD cycle adds time to the overall steel production process, which can impact the throughput of a steel mill.
Not a Universal Requirement
For many general-purpose steel applications, the level of purity achieved through VAD is unnecessary. Simpler and less expensive degassing methods are often sufficient for standard grades.
When to Choose Vacuum Arc Degassing
The decision to use VAD is driven entirely by the performance requirements of the final product. It is a tool for creating high-value, high-performance materials.
- If your primary focus is safety-critical components (aerospace, automotive, power generation): VAD is essential to remove hydrogen and prevent embrittlement, ensuring maximum reliability.
- If your primary focus is creating ultra-clean, specialized alloy steels: The precise temperature and atmospheric control of VAD allows for complex alloy additions and the removal of inclusions.
- If your primary focus is producing large forgings or thick plates: VAD is critical for ensuring deep cleanliness and uniform properties throughout the entire volume of the metal.
Ultimately, Vacuum Arc Degassing is a key technology that empowers the creation of advanced metals for the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| VAD Process Step | Key Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Creation | Lowers pressure to extract dissolved gases (H₂, O₂, N₂) | Reduces hydrogen embrittlement & inclusions |
| Electric Arc Heating | Maintains molten temperature under vacuum | Enables precise alloying and prevents solidification |
| Inert Gas Stirring | Circulates molten steel for uniform exposure | Ensures consistent purity and chemical composition |
Need to produce ultra-clean, high-performance steel for critical applications?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for metallurgical research and quality control. Our solutions support the precise thermal and atmospheric conditions required for processes like Vacuum Arc Degassing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior metal purity and reliability in your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Ultimate Purity for High-Performance Alloys
- What is var in metals? A Guide to Vacuum Arc Remelting for Superior Alloys
- What is VAR in metallurgy? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Performance
- What is the remelting process? Achieve Ultimate Purity and Performance for High-Strength Alloys
- What is the overview of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Performance Alloys



















