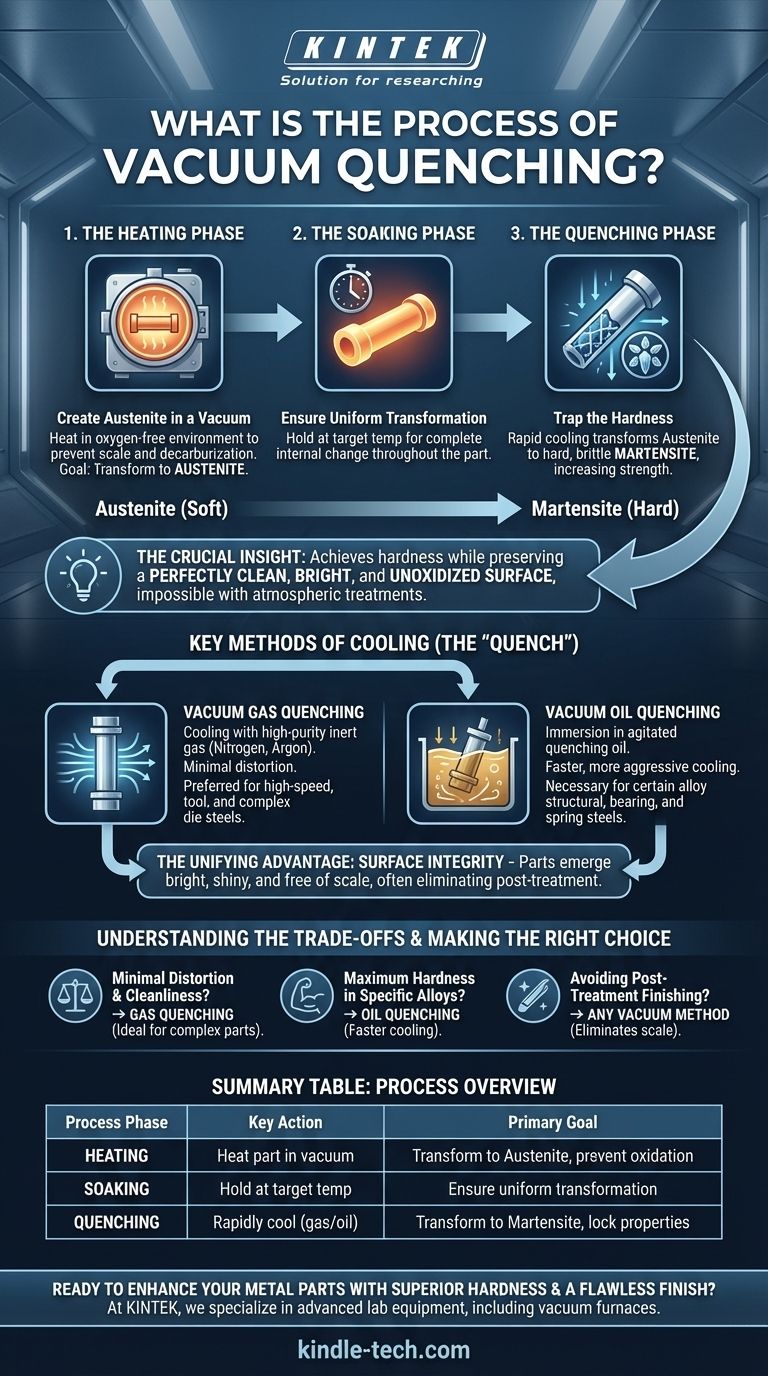
At its core, vacuum quenching is a sophisticated heat treatment process where a metal part is heated to a specific temperature within a vacuum furnace, held there to ensure a complete internal structural change, and then cooled rapidly. This rapid cooling, or "quenching," transforms the metal's microstructure from austenite to a much harder state called martensite, significantly increasing the part's strength and durability.
The crucial insight is that vacuum quenching isn't just about hardening the metal; it's about achieving that hardness while preserving a perfectly clean, bright, and unoxidized surface, which is impossible with traditional atmospheric heat treatments.

The Core Principles of Vacuum Quenching
To understand why this process is so effective, we need to look at each of its three distinct phases. The vacuum is the common thread that provides control and precision throughout.
The Heating Phase: Creating Austenite in a Vacuum
The process begins by placing the workpiece into a vacuum furnace. Heating the part in a controlled, oxygen-free environment is the defining feature of this method.
This vacuum prevents oxidation (scale or rust) and decarburization—the loss of carbon from the steel's surface, which would otherwise soften the final product. The goal is to heat the material to a specific temperature where its internal crystal structure transforms into austenite.
The Soaking Phase: Ensuring Uniform Transformation
Once at the target temperature, the workpiece is "soaked" or held for a predetermined period. This step is critical for ensuring the austenitic transformation is complete throughout the entire mass of the part, from the surface to the core.
The Quenching Phase: Trapping the Hardness
This is the rapid cooling stage that locks in the desired properties. The speed of cooling is carefully controlled to prevent the austenite from reverting to its softer forms.
Instead, the rapid cooling traps the carbon atoms within the iron crystal lattice, forcing the creation of martensite—a very hard, strong, and brittle microstructure. This transformation is the source of the significant increase in hardness.
Key Methods of Cooling (The "Quench")
The quenching medium is the key variable that defines the specific type of vacuum quenching process. The choice depends entirely on the type of material and the required final properties.
Vacuum Gas Quenching
In this method, the workpiece is cooled by filling the chamber with a high-pressure, high-purity inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon.
This is a very clean process that results in minimal distortion of the part. It is the preferred method for materials like high-speed steel, tool steel, and complex die steels.
Vacuum Oil Quenching
For this method, the heated workpiece is moved into a separate vacuum chamber and immersed in a tank of agitated quenching oil.
Oil provides a faster, more aggressive cooling rate than gas. This is necessary for certain alloy structural steels, bearing steels, and spring steels that require a more severe quench to achieve full hardness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between quenching methods involves balancing the need for cooling speed against the risk of part distortion and the desire for cleanliness.
Why Choose Gas over Oil?
Gas quenching offers superior dimensional stability, meaning the part is much less likely to warp or distort during the process. For high-precision components with intricate geometries, this is a significant advantage. The parts also emerge perfectly clean.
When is Oil Necessary?
Some alloys, particularly those with lower alloy content, have a lower "hardenability." They require the faster heat extraction rate that only an oil quench can provide to fully transform into martensite and achieve their maximum potential hardness.
The Unifying Advantage: Surface Integrity
Regardless of the cooling medium, the primary benefit of any vacuum process is the pristine surface of the final part. By eliminating atmospheric interaction, the workpiece emerges bright, shiny, and free of scale. This often removes the need for costly and time-consuming post-treatment cleaning or machining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct process requires a clear understanding of your material and your final objective.
- If your primary focus is minimal distortion and surface cleanliness: Vacuum gas quenching is the superior choice, especially for complex tool and die steels.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness in specific alloy steels: Vacuum oil quenching is often necessary due to its faster and more aggressive cooling rate.
- If your primary focus is avoiding post-treatment finishing: Any vacuum quenching method is vastly superior to atmospheric processes, as it eliminates scale and decarburization.
Ultimately, vacuum quenching is about achieving superior material properties with unparalleled precision and surface quality.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Key Action | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Heating | Heat part in a vacuum furnace | Transform microstructure to austenite, prevent oxidation |
| Soaking | Hold at target temperature | Ensure uniform transformation throughout the part |
| Quenching | Rapidly cool with gas or oil | Transform austenite to hard martensite, lock in properties |
Ready to enhance your metal parts with superior hardness and a flawless finish?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment, including vacuum furnaces, to meet your precise heat treatment needs. Whether you're working with high-speed tool steels requiring gas quenching or alloy steels needing an oil quench, our solutions deliver unmatched surface integrity and dimensional stability.
Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum quenching expertise can optimize your laboratory's processes and deliver exceptional results for your most demanding applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is physical vapor deposition process? A Guide to High-Performance Vacuum Coating
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- Why is a high-purity argon protection system required in a vacuum arc furnace? Protect Ti-Zr-Hf-V-Ta Alloy Integrity
- What is microwave sintering furnace? Unlock Faster, More Uniform Thermal Processing
- What is the primary function of a vacuum arc furnace in the preparation of Fe-Mn-Cr shape memory alloys?
- What is the role of a vacuum drying oven in Alloy 690TT preparation? Secure Flawless Data Baselines
- What are the key technical advantages of using a vacuum diffusion bonding furnace? Superior Titanium Laminate Bonding
- What is the primary function of a high-performance vacuum furnace? Master Precision Heat Treatment for Tool Steels



















