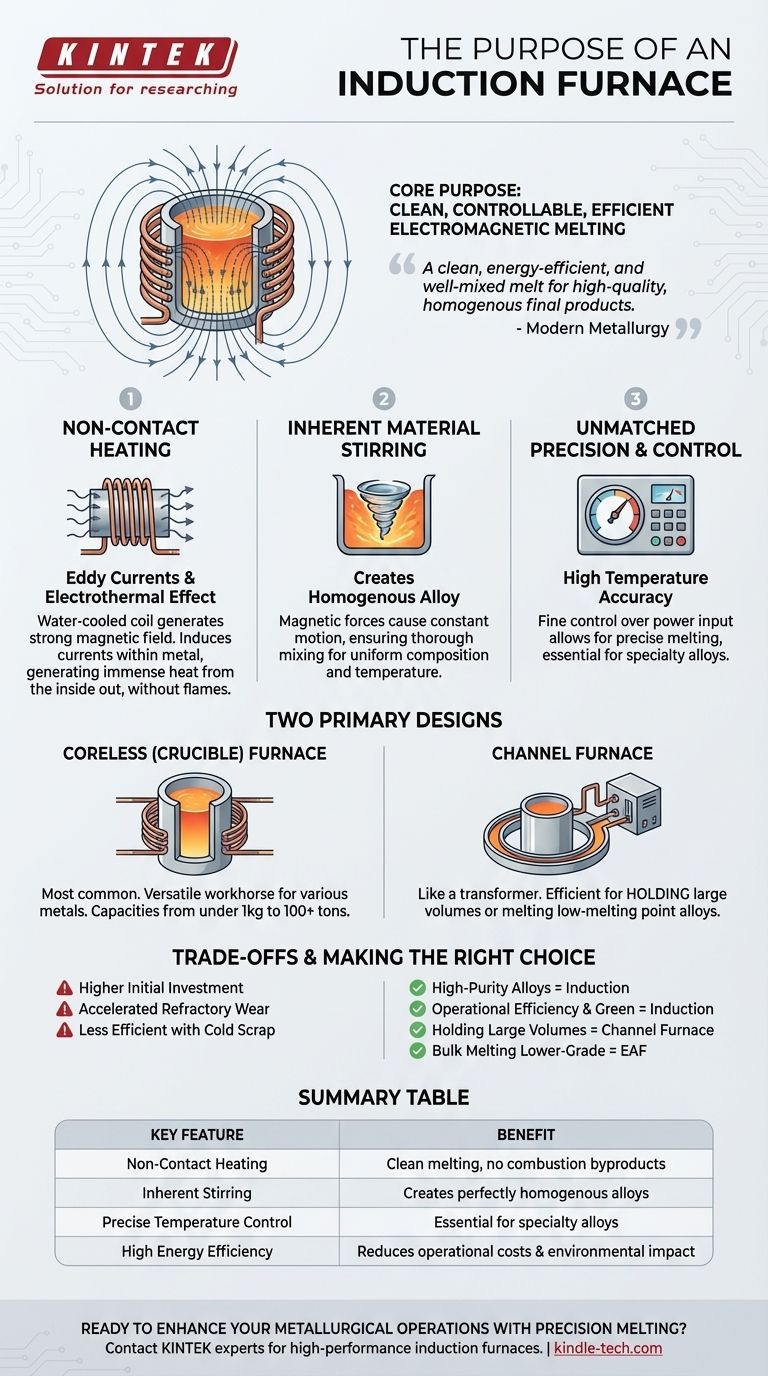
At its core, the purpose of an induction furnace is to melt metal using clean, controllable, and highly efficient electromagnetic induction. Unlike traditional furnaces that burn fuel, an induction furnace uses a powerful, alternating magnetic field to generate heat directly within the metal itself, offering unparalleled control over the melting process.
The true value of an induction furnace is not just its ability to melt metal, but its capacity to do so with exceptional precision. It provides a clean, energy-efficient, and well-mixed melt, ensuring high-quality, homogenous final products which is a fundamental requirement in modern metallurgy.

How Induction Furnaces Revolutionize Metal Processing
An induction furnace operates on a principle that is fundamentally different from combustion-based heating. This difference is the source of its primary advantages in industrial settings.
The Principle of Non-Contact Heating
The furnace uses a water-cooled copper coil to generate a strong, alternating magnetic field. When conductive material like metal is placed inside this field, it induces powerful electrical currents within the metal, known as eddy currents.
The metal's natural electrical resistance causes these eddy currents to generate immense heat, a phenomenon called the electrothermal effect. This process heats the material from the inside out, without any external flame or heating element making contact.
Inherent Material Stirring for Uniformity
The same magnetic forces that generate heat also create a natural stirring or agitating effect within the molten metal.
This constant motion is critical because it ensures that all elements in the melt are thoroughly mixed. The result is a perfectly homogenous alloy with uniform composition and temperature throughout the entire batch.
Unmatched Precision and Control
Because the heat is generated directly by the power supplied to the coil, operators have extremely fine control over the melting process.
This allows for high temperature control accuracy and a very small temperature difference between the surface and the core of the melt. This level of control is essential for producing specialty alloys and meeting strict quality standards.
The Two Primary Designs
While the principle is the same, induction furnaces are generally built in two distinct configurations, each suited for different applications.
The Coreless (Crucible) Furnace
This is the most common design, featuring a refractory-lined crucible that holds the metal, surrounded by the induction coil.
Coreless furnaces are versatile workhorses, with capacities ranging from under a kilogram to over one hundred tons. They are the go-to choice for melting a wide range of metals, including iron, steel, copper, aluminum, and precious metals.
The Channel Furnace
A channel furnace functions more like a transformer. It consists of a main vessel holding molten metal, connected to a smaller "channel" surrounded by an induction unit and an iron core.
The molten metal in the channel forms a secondary loop of the transformer, where it is heated and circulated back into the main bath. This design is exceptionally efficient for holding large volumes of metal at a specific temperature or for melting low melting point alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly advanced, the induction furnace is a specific tool with its own set of operational considerations.
Initial Capital Investment
The sophisticated power supplies, control systems, capacitors, and water-cooling infrastructure required for an induction furnace typically result in a higher upfront cost compared to simpler furnace types.
Refractory Management
The intense heat and constant stirring of the molten metal, while beneficial for quality, can accelerate the wear on the refractory lining of the crucible. This necessitates a rigorous maintenance and relining schedule.
Starting From "Cold"
Induction heating relies on the material being electrically conductive. While highly effective with a molten heel or dense scrap, starting a melt from a pile of loose, light, or poorly conductive scrap can be less efficient until a molten pool is formed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right melting technology depends entirely on your end goal, balancing cost, quality, and operational demands.
- If your primary focus is high-purity alloys and precise composition: The induction furnace's clean melting and inherent stirring action make it the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and environmental control: The high energy efficiency and lack of combustion byproducts significantly reduce running costs and environmental impact.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of metal at temperature: A channel-type induction furnace offers an exceptionally efficient solution for holding and superheating.
- If your primary focus is bulk melting of lower-grade scrap with less stringent chemistry: A traditional electric arc furnace might offer a more robust and cost-effective solution for the initial melt-down.
Ultimately, the adoption of induction furnace technology represents a commitment to precision, cleanliness, and efficiency in metallurgical operations.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Non-Contact Heating | Clean melting with no combustion byproducts |
| Inherent Stirring | Creates perfectly homogenous alloys |
| Precise Temperature Control | Essential for specialty alloys and strict quality standards |
| High Energy Efficiency | Reduces operational costs and environmental impact |
Ready to Enhance Your Metallurgical Operations with Precision Melting?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment, including high-performance induction furnaces, to meet the demanding needs of modern laboratories and metallurgical facilities. Our solutions are designed to deliver the clean, efficient, and controllable melting processes required for producing high-quality, homogenous alloys.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our induction furnaces can revolutionize your metal processing, improve your product quality, and boost your operational efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing



















